The Getting Started tutorial for Node.js uses this sample application to provide you with a sample workflow for working with any Node.js app on IBM Cloud or in IBM Cloud Private; you set up a development environment, deploy an app locally and on the cloud, and then integrate a IBM Cloud database service in your app.
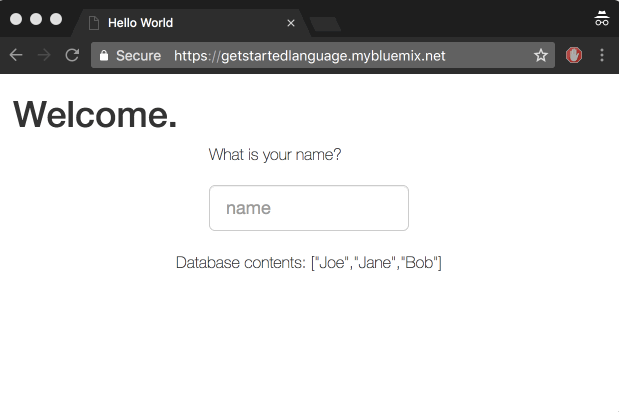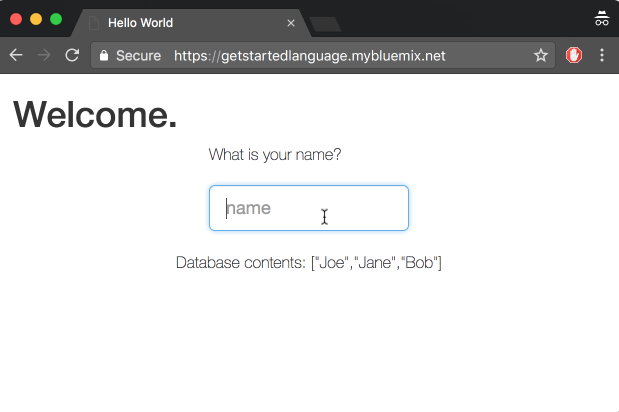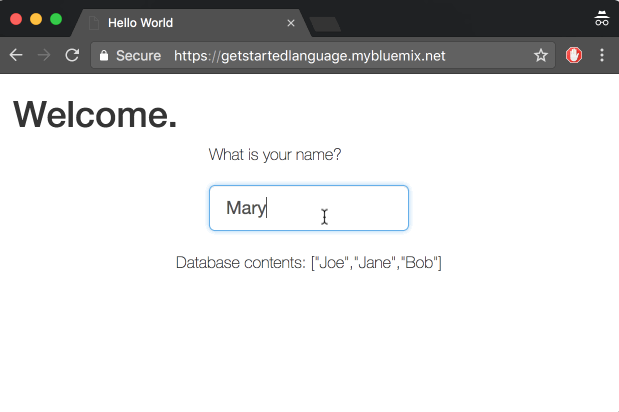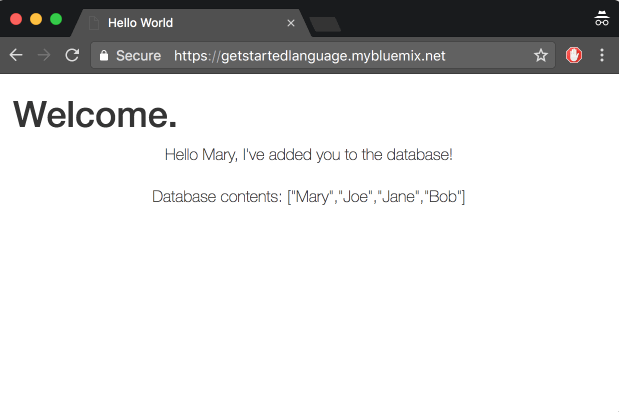
The Node.js app uses Express Framework and Cloudant noSQL DB service or the MongoDB Service to add information to a database and then return information from a database to the UI. To learn more about how the app connects to Cloudant, see the Cloudant library for Node.js.
You'll need a IBM Cloud account, Git, Cloud Foundry CLI, and Node installed. If you use IBM Cloud Private, you need access to the IBM Cloud Private Cloud Foundry environment.
IBM Cloud Cloud Foundry: Getting started tutorial for Node.js.
IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service: Deploy to IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service
Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud: Deploy to Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud Private: The starter application for IBM Cloud Private guides you through a similar process. However, instead of hosting both your service and application in the same cloud environment, you use a user-provided service. This guide shows you how to deploy your application to IBM Cloud Private and bind it to a Cloudant Database in IBM Cloud. For the complete procedure, see Working with user-provided services and the Node.js starter app.