| theme | background | class | highlighter | lineNumbers | info | drawings | css | title | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
seriph |
text-center |
shiki |
true |
## Backend communication design patterns
TechTack session.
|
|
unocss |
TechTalks |
Monday, Decemper 5 · 10:30AM – 12:00PM
layout: two-cols image: >- https://images.unsplash.com/photo-1616362258782-7511b61686ea?crop=entropy&cs=tinysrgb&fit=crop&fm=jpg&h=1080&ixid=MnwxfDB8MXxyYW5kb218MHw5NDczNDU2Nnx8fHx8fHwxNjY5Mzc5ODkx&ixlib=rb-4.0.3&q=80&utm_campaign=api-credit&utm_medium=referral&utm_source=unsplash_source&w=1920
Tier defines the physical separation of components in an application or a service. This separation is at a component level, not the code level(layers).
These layers are at the code level. The difference between layers and tiers is that layers represent the conceptual/logical organization of the code, whereas tiers represent the physical separation of components.
What about Django MVT?
Model, View, and Template are the three layers
Two tier apps implements the client server arch, the business logic is either on the Client side or database side.
In a three-tier application, the user interface, business logic, and the database all reside on different machines and, thus, have different tiers. They are physically separated.
The architecture works on a request-response model. The client sends the request to the server for information and the server responds with it.
The user interface runs on the client. In very simple terms, a client is a gateway to our application.
| Thin | Thick |
| just the user interface of the application. It contains no business logic of any sort. | holds all or some part of the business logic. |
A will send a request to B
| A | B |
| must be able to parse/understand the response | must be able to parse the request |
So client and server must define a structure for the request and response ( protocol, message format) for serialization and derserialziation proess
( request, response waiting example) HTTP request
GET / HTTP1.1
Headers
BODY
Questions:
what if client disconnect?
what if server can not handle the request right now?
what if the request requires long process?
and a lot of limitations of this model
can i do work while waiting?
Ex:
- whenever a user publish new video, we need to notify all folowers
imagine the client needs to ask the server multiple times if there are a new notification or not? how many useless requests and empty responses we will get?
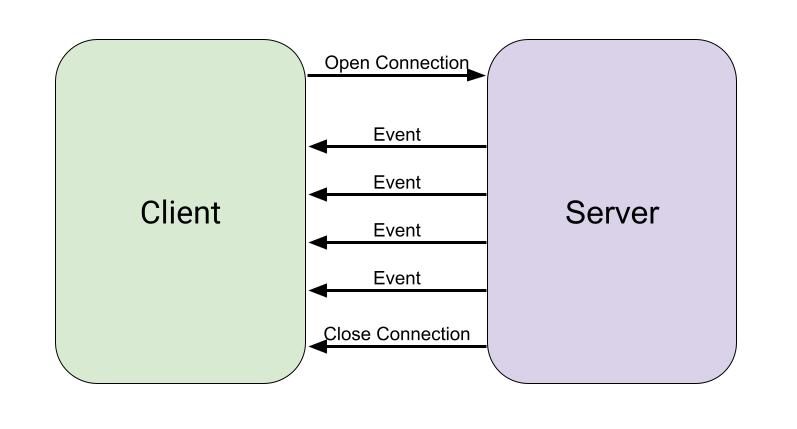
So we can say that if the server holds the information then make sense that server should push the info as soon as it is availalbe without waiting the client to ask.
- the client initiates a request
- Using this established connection, the server can send any new updated down to the client as soon as they are available.
- The client does not need to repeatedly request for updates from the server
- This helps to reduce the load on the network with the advantage that the updates are received in a timely manner.
- A drawback to this style is that the server has to maintain connection to the client which creates certain overhead on the server.
Usecase: request process time is long (export, upload) ( client can disconnect)
| Short Pooling | Long Pooling |
| client requets andserver respond with a key ( handler ) Server starts the process or put in a queue | |
| client keeps asking (pooling) client keeps asking (pooling) | |
| server keeps responding with no till get the result | server keeps the connection open(with timeout)and waits |
| It is a breakdown of long req-res to multiple short req-res | It is based on getting the response. So, It is used for those applications that don’t want empty responses. |
Server
app.get("/stream", (req,res) => {
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/event-stream");
send(res);
})
Client
function rintMessage(message) {
console.log(message)
}
let sse = new EventSource("http://localhost:8080/stream");
sse.onmessage = printMessage
Do you have boundaries?
A boundary is what this part of the codebase (business) is responsible for ( SOLID! ) ( the business capabilities and data access (RW)
--- title: Message Broker and Queues ---Can i do work while waiting?
Do i need to wait for other work to complete if i already done with my job
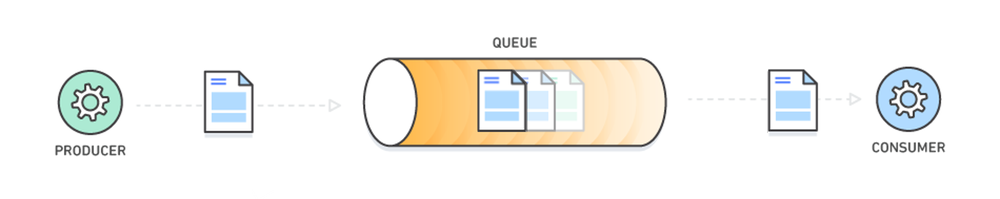
A message queue is a form of asynchronous service-to-service communication used in serverless and microservices architectures. Messages are stored on the queue until they are processed and deleted. Each message is processed only once, by a single consumer. Message queues can be used to decouple heavyweight processing, to buffer or batch work, and to smooth spiky workloads.
Message queuing fulfills this purpose by providing a means for services to push messages to a queue asynchronously and ensure that they get delivered to the correct destination. To implement a message queue between services, you need a message broker, think of it as a mailman, who takes mail from a sender and delivers it to the correct destination.
RabbitMQ consists of:
- producer — the client that creates a message
- consumer — receives a message
- queue — stores messages
- exchange — enables to route messages and send them to queues
The system functions in the following way:
- producer creates a message and sends it to an exchange
- exchange receives a message and routes it to queues subscribed to it
- consumer receives messages from those queues he/she is subscribed to One should note that messages are filtered and routed depending on the type of exchange.
-
Architecture https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLThyvG1mlMzkQklYlHp_CdO5IEJ3i_ary
-
Loosely Coupled Monolith https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLThyvG1mlMznIDBtd5HadrmC5hayjpCtI
-
Monolith to MicroServices: https://cloud.google.com/architecture/microservices-architecture-introduction
-
Long pooling Queue in aws https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSSimpleQueueService/latest/SQSDeveloperGuide/sqs-short-and-long-polling.html#sqs-short-polling.
thank you