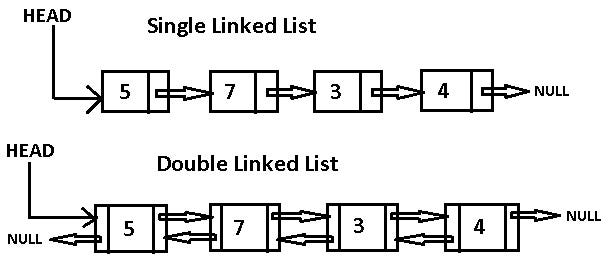
- linked list a a way to structure data together.
- linked list is a sequence of nodes.
- each node contain values, and reference.
- the first node is called also head.
- and current node is the node that we are currntly at.
- the reference refer to the next node in the list.
- There are 3 types of linked lists the singular, doubly and circular linked list.
- singular list: is a list where each node contain only 1 reference that refer to the next node.
- doubly list: is a list where each node contian 2 refrences, one refer to next node and other refer to prevous node.
- circular: is a linked list where each node contain 2 references, exactly like the doubly, the only difference is that the last node in the list refer to the first node in the list.
- since in linked list each node refer to next node by using reference(not a counter) i can't use nor forEach neither for loop.
- that's why while loop is useful here, because I will be using the reference to move to next node.
- While and null : the while run on the reference not value itself, so when I loop over list and value is being null, it will not throw error (because i check for reference) and move to next node.
- Current node and traversing: the current node will allow me to know where exactly i stand in the list, and what is next or prevoius node (depends on type of linked list i am using).
- the big o notation evaluate the preformance of the algorithim, how much time it took, lets say i want to search for item in an array using for loop, so the time complexity of the algo will be O(n) where n is number of times the line of code in for loop will run in worse case(I mean if it's last item in the array and i have size of array is 1000 then it's worse case). and N is that.
- and happy case for algo is item to be at the first index hich is O(1).
- the big o is only meassure the space and time complexity of algo.
- when it comes ti working with linked list, order of operations matter because i don't want to lose the reference, lets say i want to delete a node then i most inform prevous node and give it the reference to next node.
- same goes for adding, when i want to add a new node it should find it's place but before node take it's place it should take the reference from prevoius node so it point to the next node instead of prevoius one do.
example of adding a node : Order here is intended to add new node without losing reference.
ALGORITHM Add(newValue)
// INPUT <-- Value to add
// OUTPUT <-- No output
newNode <-- NEW Node
newNode.Value <-- newValue
newNode.Next <-- Head
Head <-- newNode
reference Code fellows
Example:
ALGORITHM Print()
// INPUT <-- None
// OUTPUT <-- string to console
Current <-- Head
WHILE Current is not equal to NULL
OUTPUT <-- "{Current.Value} --> "
Current <-- Current.Next
OUTPUT <-- "NULL"
reference Code fellows