- a tutrial aims to walk me throught security in spring mvc.
- solve two problems.
- authentication is who are you.
- authorization is what are you allowed to do.
- spring seperate who from what.
- Spring Security a framework that seperate authentication from authorization .
- extension points to both.
AuthenticationManagerhas one method.
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}-
An
AuthenticationManagerhas methodauthenticate(Authentication authentication)- it return
AuthenticationorAuthenticationException.
- it return
-
The Class<?> argument in the supports() method is really Class<? extends Authentication> (it is only ever asked if it supports something that is passed into the authenticate() method). A ProviderManager can support multiple different authentication mechanisms in the same application by delegating to a chain of AuthenticationProviders. If a ProviderManager does not recognize a particular Authentication instance type, it is skipped. resource
-
A ProviderManager has an optional parent, which it can consult if all providers return null. If the parent is not available, a null Authentication results in an AuthenticationException. resource
Sometimes, an application has logical groups of protected resources (for example, all web resources that match a path pattern, such as /api/**), and each group can have its own dedicated AuthenticationManager. Often, each of those is a ProviderManager, and they share a parent. The parent is then a kind of “global” resource, acting as a fallback for all providers. resource .
- Spring Security provides configs helpers to easily get authentication manager features set up in my application.
- when authentication is successful, I can move on to authorization.
- and the core strategy here is
AccessDecisionManager..- There are three implementations provided:
- the three delegate to a chain of
AccessDecisionVoterinstances.
- Spring Security in the web tier based on Servlet Filters.
- Filters layer :
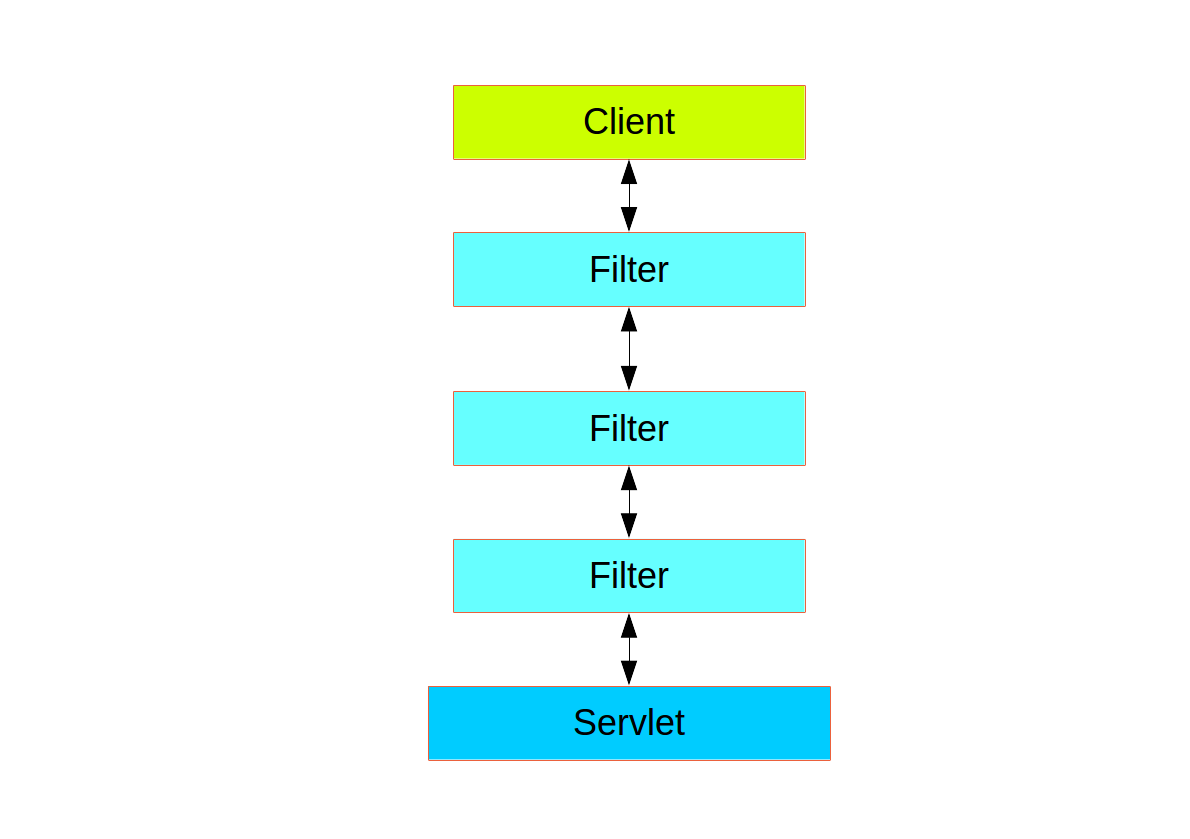
- when client send a request to the app, which filter and which servlet apply will be based on url request path.
- In a Spring Boot application, the security filter is a
@Beanin theApplicationContext, and it is installed by default so that it is applied to every request. - Spring Security is a single filter, but, inside of it, there are additional filters. resource
- A security filter chain has a request matcher used to apply it to an HTTP request.
- when a filter chain is applied, no others are applied.
- the Actuator is for manage endpoints and it's configured by default.
- when we add actuator, there are additional filters gets applied to that actuator.
- Spring Security offers support for applying access rules to Java method.
- Spring Security needs to make the current authenticated available to a variety of consumers.
- it's useful to write a custom authentication filter.