This chapter introduces the basic conception of rotated object detection and the framework of MMRotate, and provides links to detailed tutorials about MMRotate.
Benefiting from the vigorous development of general object detection, most current rotated object detection models are based on classic general object detector. With the development of detection tasks, horizontal boxes have been unable to meet the needs of researchers in some subdivisions. We call it rotating object detection by redefining the object representation and increasing the number of regression degrees of freedom to achieve rotated rectangle, quadrilateral, and even arbitrary shape detection. Performing high-precision rotated object detection more efficiently has become a current research hotspot. The following areas are where rotated object detection has been applied or has great potential: face recognition, scene text, remote sensing, self-driving, medical, robotic grasping, etc.
The most notable difference between rotated object detection and generic detection is the replacement of horizontal box annotations with rotated box annotations. They are defined as follows:
- Horizontal box: A rectangle with the
widthalong thex-axisandheightalong they-axis. Usually, it can be represented by the coordinates of 2 diagonal vertices(x_i, y_i)(i = 1, 2), or it can be represented by the coordinates of the center point and thewidthandheight,(x_center, y_center, width, height). - Rotated box: It is obtained by rotating the horizontal box around the center
point by an
angle, and the definition method of its rotated box is obtained by adding a radian parameter(x_center, y_center, width, height, theta), wheretheta = angle * pi / 180. The unit ofthetaisrad. When the rotation angle is a multiple of 90°, the rotated box degenerates into a horizontal box. The rotated box annotations exported by the annotation software are usually polygons, which need to be converted to the rotated box definition method before training.
In MMRotate, angle parameters are in radians.
A rotated box can be obtained by rotating a horizontal box clockwise or
counterclockwise around its center point. The rotation direction is closely
related to the choice of the coordinate system. The image space adopts the
right-handed coordinate system (y, x), where y is up->down and x is left->right.
There are two opposite directions of rotation:
- Clockwise(CW)
Schematic of CW
0-------------------> x (0 rad)
| A-------------B
| | |
| | box h
| | angle=0 |
| D------w------C
v
y (pi/2 rad)
Rotation matrix of CW
\begin{pmatrix}
\cos\alpha & -\sin\alpha \\
\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha
\end{pmatrix}
Rotation transformation of CW
P_A=
\begin{pmatrix} x_A \\ y_A\end{pmatrix}
=
\begin{pmatrix} x_{center} \\ y_{center}\end{pmatrix} +
\begin{pmatrix}\cos\alpha & -\sin\alpha \\
\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha\end{pmatrix}
\begin{pmatrix} -0.5w \\ -0.5h\end{pmatrix} \\
=
\begin{pmatrix} x_{center}-0.5w\cos\alpha+0.5h\sin\alpha
\\
y_{center}-0.5w\sin\alpha-0.5h\cos\alpha\end{pmatrix}
- Counterclockwise(CCW)
Schematic of CCW
0-------------------> x (0 rad)
| A-------------B
| | |
| | box h
| | angle=0 |
| D------w------C
v
y (-pi/2 rad)
Rotation matrix of CCW
\begin{pmatrix}
\cos\alpha & \sin\alpha \\
-\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha
\end{pmatrix}
Rotation transformation of CCW
P_A=
\begin{pmatrix} x_A \\ y_A\end{pmatrix}
=
\begin{pmatrix} x_{center} \\ y_{center}\end{pmatrix} +
\begin{pmatrix}\cos\alpha & \sin\alpha \\
-\sin\alpha & \cos\alpha\end{pmatrix}
\begin{pmatrix} -0.5w \\ -0.5h\end{pmatrix} \\
=
\begin{pmatrix} x_{center}-0.5w\cos\alpha-0.5h\sin\alpha
\\
y_{center}+0.5w\sin\alpha-0.5h\cos\alpha\end{pmatrix}
The operators that can set the rotation direction in MMCV are:
- box_iou_rotated (Defaults to
CW) - nms_rotated (Defaults to
CW) - RoIAlignRotated (Defaults to
CCW) - RiRoIAlignRotated (Defaults to
CCW).
In MMRotate, the rotation direction of the rotated boxes is `CW`.
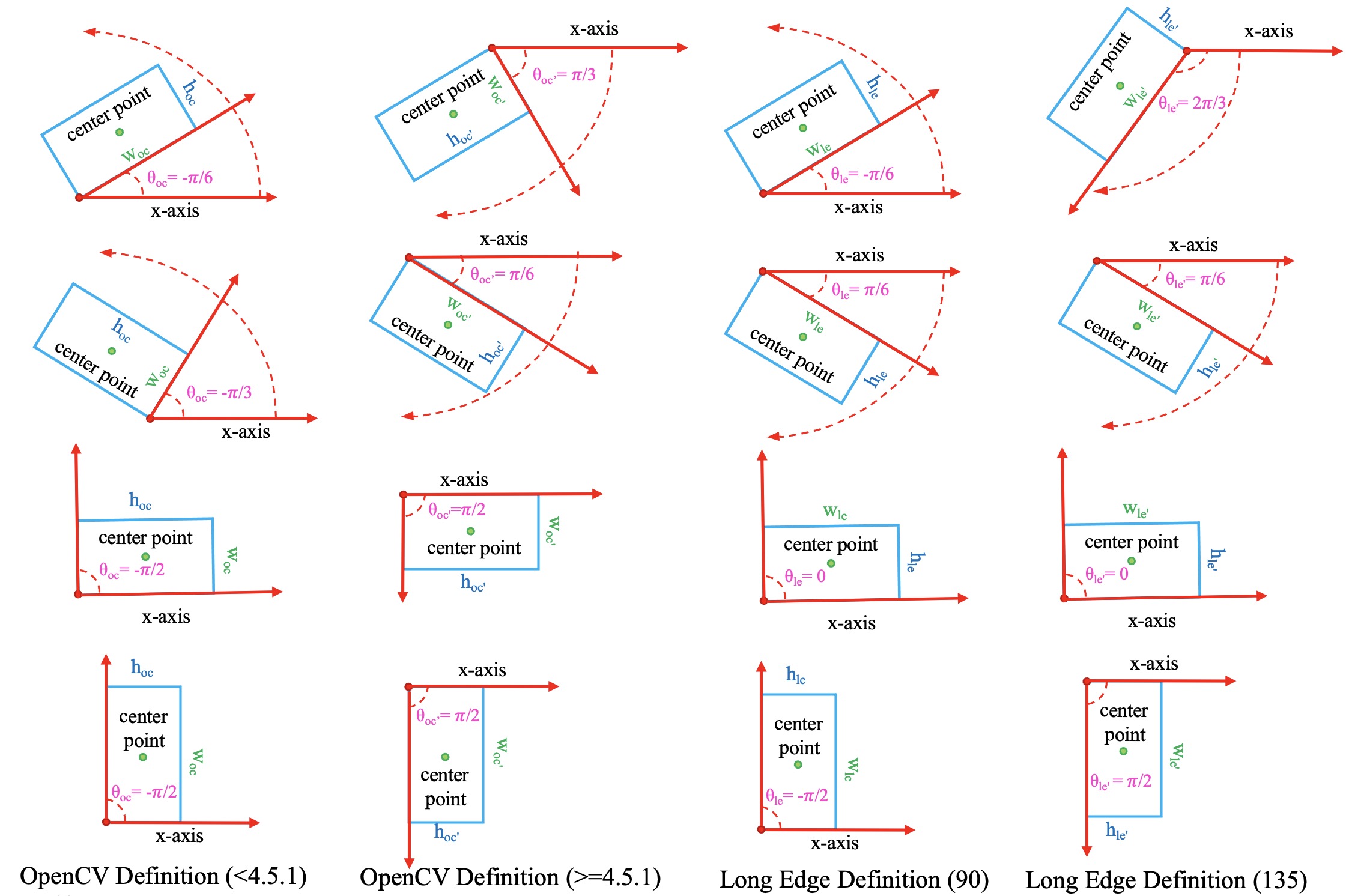
Due to the difference in the definition range of theta, the following three
definitions of the rotated box gradually emerge in rotated object detection:
- {math}
D_{oc^{\prime}}: OpenCV Definition,angle∈(0, 90°],theta∈(0, pi / 2], The angle between thewidthof the rectangle and the positive semi-axis of x is a positive acute angle. This definition comes from thecv2.minAreaRectfunction in OpenCV, which returns an angle in the range(0, 90°]. - {math}
D_{le135}: Long Edge Definition (135°),angle∈[-45°, 135°),theta∈[-pi / 4, 3 * pi / 4)andwidth > height. - {math}
D_{le90}: Long Edge Definition (90°),angle∈[-90°, 90°),theta∈[-pi / 2, pi / 2)andwidth > height.
The conversion relationship between the three definitions is not involved in MMRotate, so we will not introduce it much more. Refer to the below blog to dive deeper.
MMRotate supports the above three definitions of rotated box simultaneously,
which can be flexibly switched through the configuration file.
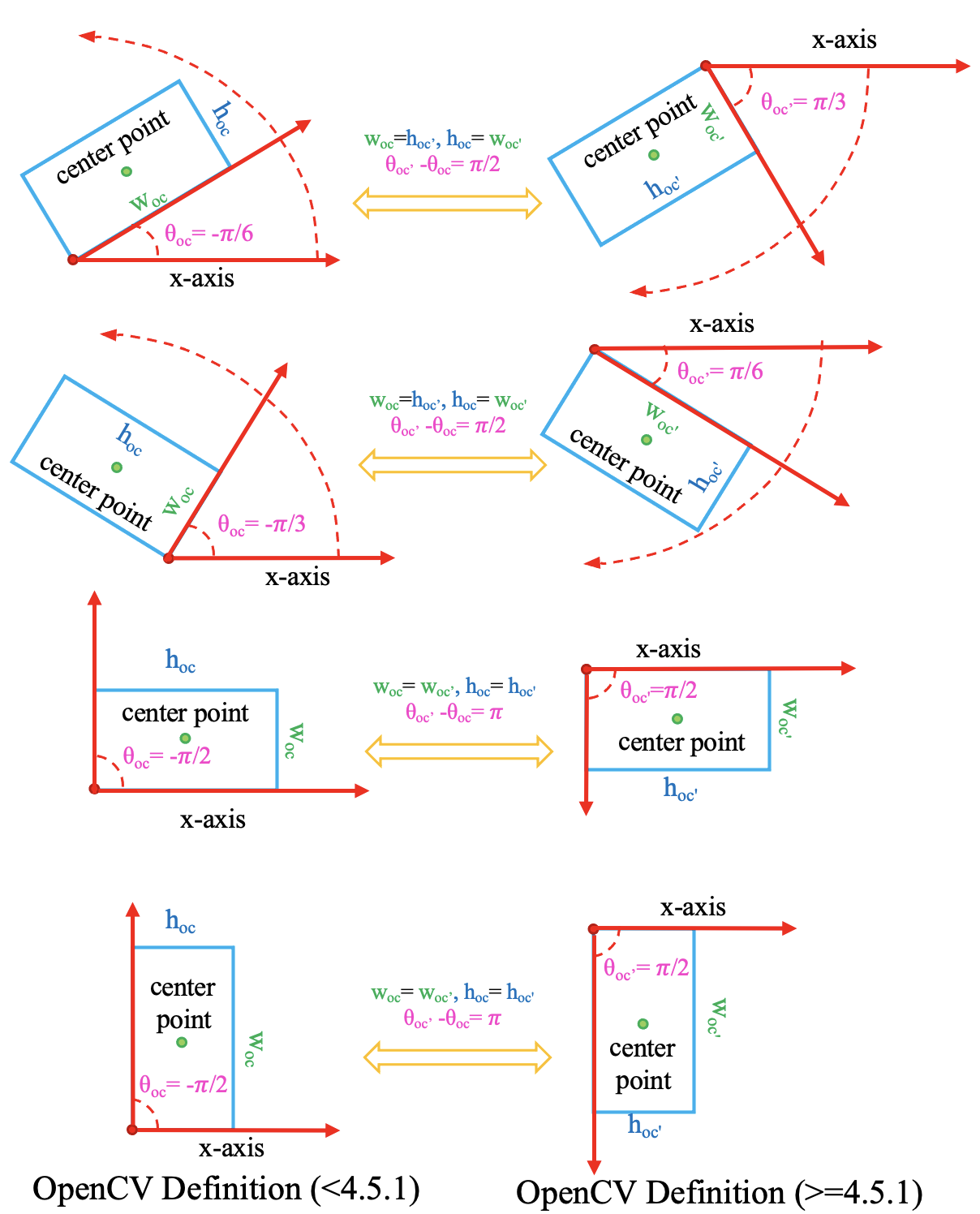
It should be noted that if the OpenCV version is less than 4.5.1, the angle range
of cv2.minAreaRect is between [-90°, 0°). Reference
In order to facilitate the distinction, the old version of the OpenCV definition
is denoted as {math}D_{oc}.
- {math}
D_{oc^{\prime}}: OpenCV definition,opencv>=4.5.1,angle∈(0, 90°],theta∈(0, pi / 2]. - {math}
D_{oc}: Old OpenCV definition,opencv<4.5.1,angle∈[-90°, 0°),theta∈[-pi / 2, 0).
The conversion relationship between the two OpenCV definitions is as follows:
D_{oc^{\prime}}\left( w_{oc^{\prime}},h_{oc^{\prime}},\theta _{oc^{\prime}} \right) =\begin{cases}
D_{oc}\left( h_{oc},w_{oc},\theta _{oc}+\pi /2 \right) , otherwise\\
D_{oc}\left( w_{oc},h_{oc},\theta _{oc}+\pi \right) ,\theta _{oc}=-\pi /2\\
\end{cases}
\\
D_{oc}\left( w_{oc},h_{oc},\theta _{oc} \right) =\begin{cases}
D_{oc^{\prime}}\left( h_{oc^{\prime}},w_{oc^{\prime}},\theta _{oc^{\prime}}-\pi /2 \right) , otherwise\\
D_{oc^{\prime}}\left( w_{oc^{\prime}},h_{oc^{\prime}},\theta _{oc^{\prime}}-\pi \right) , \theta _{oc^{\prime}}=\pi /2\\
\end{cases}
Regardless of the OpenCV version you are using, MMRotate will convert the theta
of the OpenCV definition to (0, pi / 2].
The code for evaluating mAP involves the calculation of IoU. We can directly calculate the IoU of the rotated boxes or convert the rotated boxes to a polygons and then calculate the polygons IoU (DOTA online evaluation uses the calculation of polygons IoU).
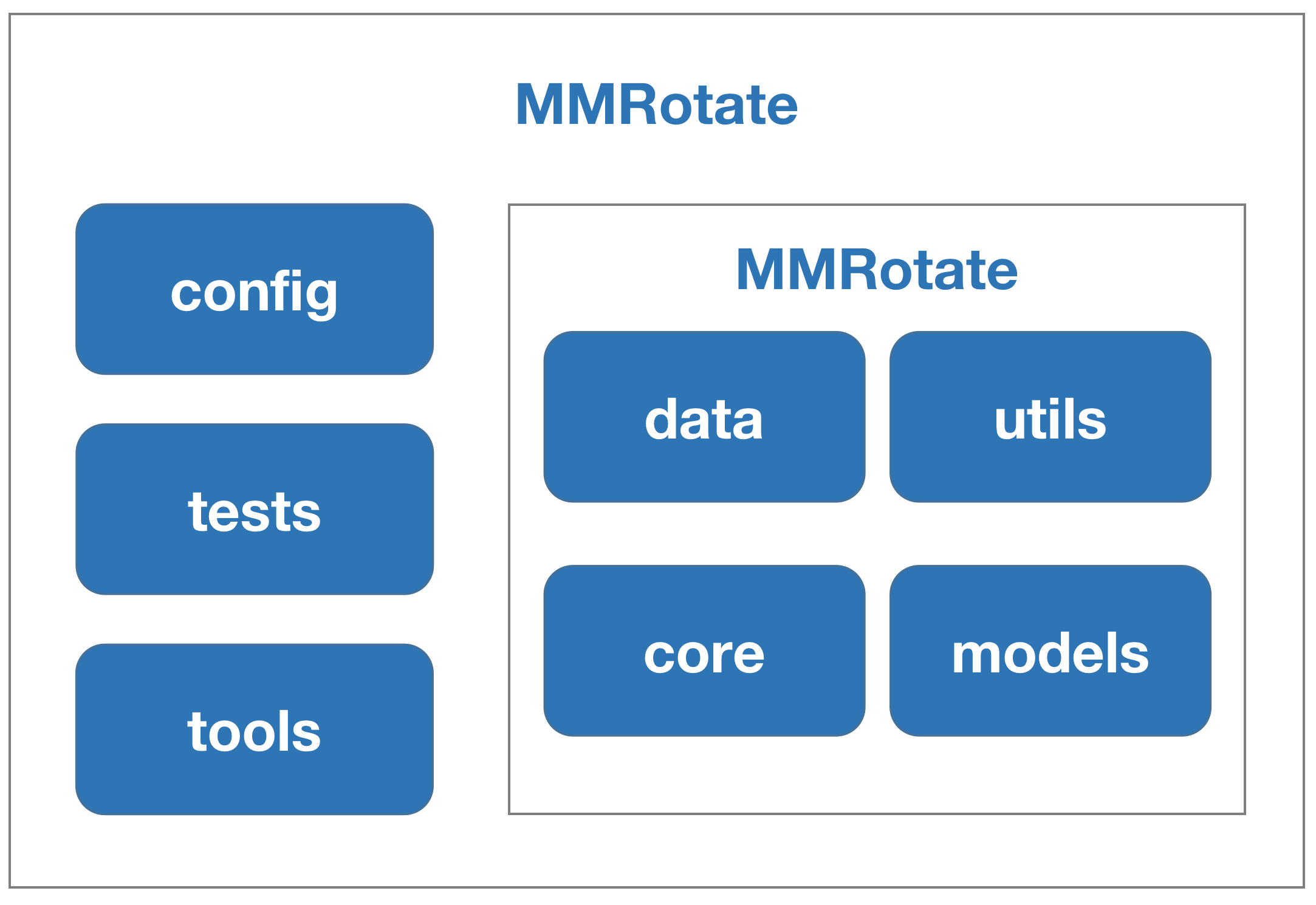
MMRotate is a toolbox that provides a framework for unified implementation and evaluation of rotated object detection, and below is its whole framework:
MMRotate consists of 4 main parts, datasets, models, core and apis.
-
datasetsis for data loading and data augmentation. In this part, we support various datasets for rotated object detection algorithms, useful data augmentation transforms inpipelinesfor pre-processing image. -
modelscontains models and loss functions. -
coreprovides evaluation tools for model training and evaluation. -
apisprovides high-level APIs for models training, testing, and inference.
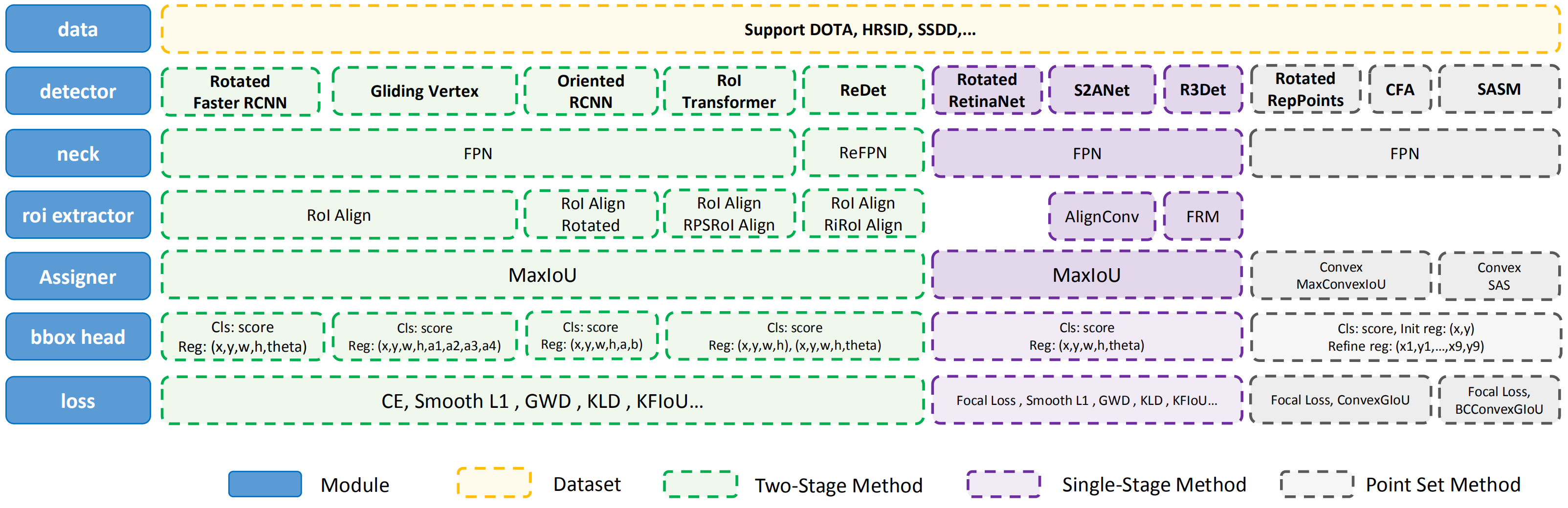
The module design of MMRotate is as follows:
The following points need to be noted due to different definitions of rotated box:
- Loading annotations
- Data augmentation
- Assigning samples
- Evaluation
Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to learn more about MMRotate:
-
For installation instructions, please see install.
-
get_started is for the basic usage of MMRotate.
-
Refer to the below tutorials to dive deeper: