Batch ingestion involves extracting metadata from a source system in bulk. Typically, this happens on a predefined schedule using the Metadata Ingestion framework. The metadata that is extracted includes point-in-time instances of dataset, chart, dashboard, pipeline, user, group, usage, and task metadata.
:::note Required Python Version Installing DataHub CLI requires Python 3.6+. :::
Run the following commands in your terminal:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel setuptools
python3 -m pip install --upgrade acryl-datahub
python3 -m datahub version
Your command line should return the proper version of DataHub upon executing these commands successfully.
Check out the CLI Installation Guide for more installation options and troubleshooting tips.
Our CLI follows a plugin architecture. You must install connectors for different data sources individually.
For a list of all supported data sources, see the open source docs.
Once you've found the connectors you care about, simply install them using pip install.
For example, to install the mysql connector, you can run
pip install --upgrade 'acryl-datahub[mysql]'Check out the alternative installation options for more reference.
Create a Recipe yaml file that defines the source and sink for metadata, as shown below.
# example-recipe.yml
# MySQL source configuration
source:
type: mysql
config:
username: root
password: password
host_port: localhost:3306
# Recipe sink configuration.
sink:
type: "datahub-rest"
config:
server: "https://<your domain name>.acryl.io/gms"
token: <Your API key>The source configuration block defines where to extract metadata from. This can be an OLTP database system, a data warehouse, or something as simple as a file. Each source has custom configuration depending on what is required to access metadata from the source. To see configurations required for each supported source, refer to the Sources documentation.
The sink configuration block defines where to push metadata into. Each sink type requires specific configurations, the details of which are detailed in the Sinks documentation.
To configure your instance of DataHub as the destination for ingestion, set the "server" field of your recipe to point to your DataHub Cloud instance's domain suffixed by the path /gms, as shown below.
A complete example of a DataHub recipe file, which reads from MySQL and writes into a DataHub instance:
For more information and examples on configuring recipes, please refer to Recipes.
In DataHub Cloud deployments, only the datahub-rest sink is supported, which simply means that metadata will be pushed to the REST endpoints exposed by your DataHub instance. The required configurations for this sink are
- server: the location of the REST API exposed by your instance of DataHub
- token: a unique API key used to authenticate requests to your instance's REST API
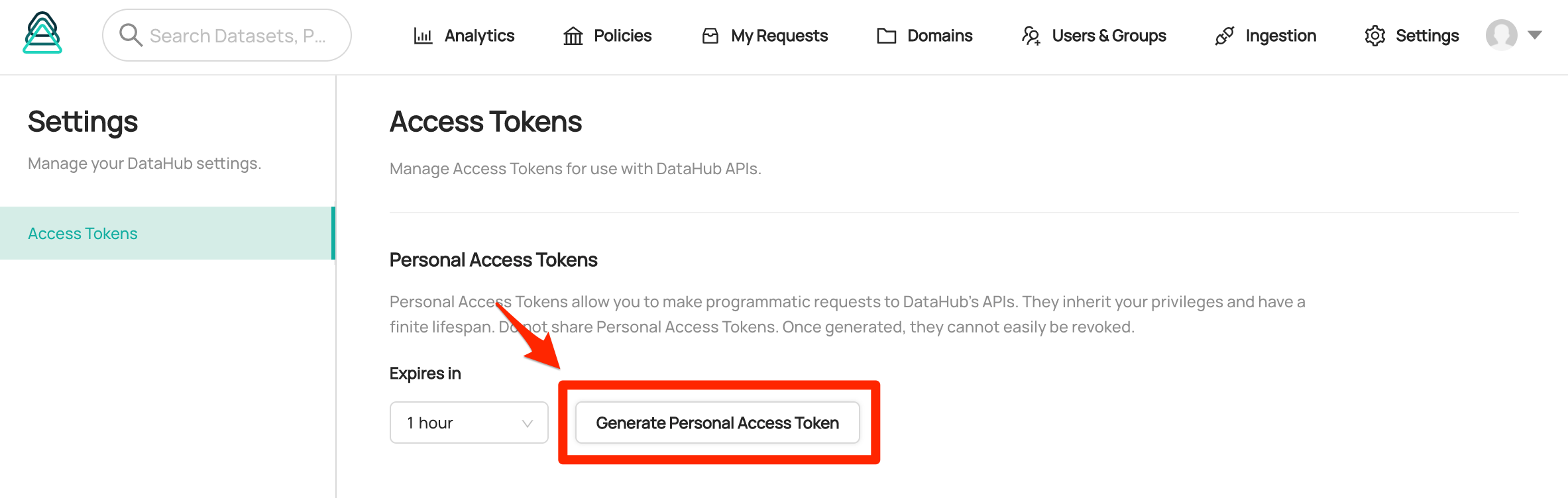
The token can be retrieved by logging in as admin. You can go to Settings page and generate a Personal Access Token with your desired expiration date.
:::info Secure Your API Key Please keep Your API key secure & avoid sharing it. If you are on DataHub Cloud and your key is compromised for any reason, please reach out to the Acryl team at [email protected]. :::
The final step requires invoking the DataHub CLI to ingest metadata based on your recipe configuration file.
To do so, simply run datahub ingest with a pointer to your YAML recipe file:
datahub ingest -c <path/to/recipe.yml>Ingestion can either be run in an ad-hoc manner by a system administrator or scheduled for repeated executions. Most commonly, ingestion will be run on a daily cadence. To schedule your ingestion job, we recommend using a job schedule like Apache Airflow. In cases of simpler deployments, a CRON job scheduled on an always-up machine can also work. Note that each source system will require a separate recipe file. This allows you to schedule ingestion from different sources independently or together. Learn more about scheduling ingestion in the Scheduling Ingestion Guide.
Please refer the following pages for advanced guids on CLI ingestion.
:::tip Compatibility
DataHub server uses a 3 digit versioning scheme, while the CLI uses a 4 digit scheme. For example, if you're using DataHub server version 0.10.0, you should use CLI version 0.10.0.x, where x is a patch version. We do this because we do CLI releases at a much higher frequency than server releases, usually every few days vs twice a month.
For ingestion sources, any breaking changes will be highlighted in the release notes. When fields are deprecated or otherwise changed, we will try to maintain backwards compatibility for two server releases, which is about 4-6 weeks. The CLI will also print warnings whenever deprecated options are used. :::
.png)