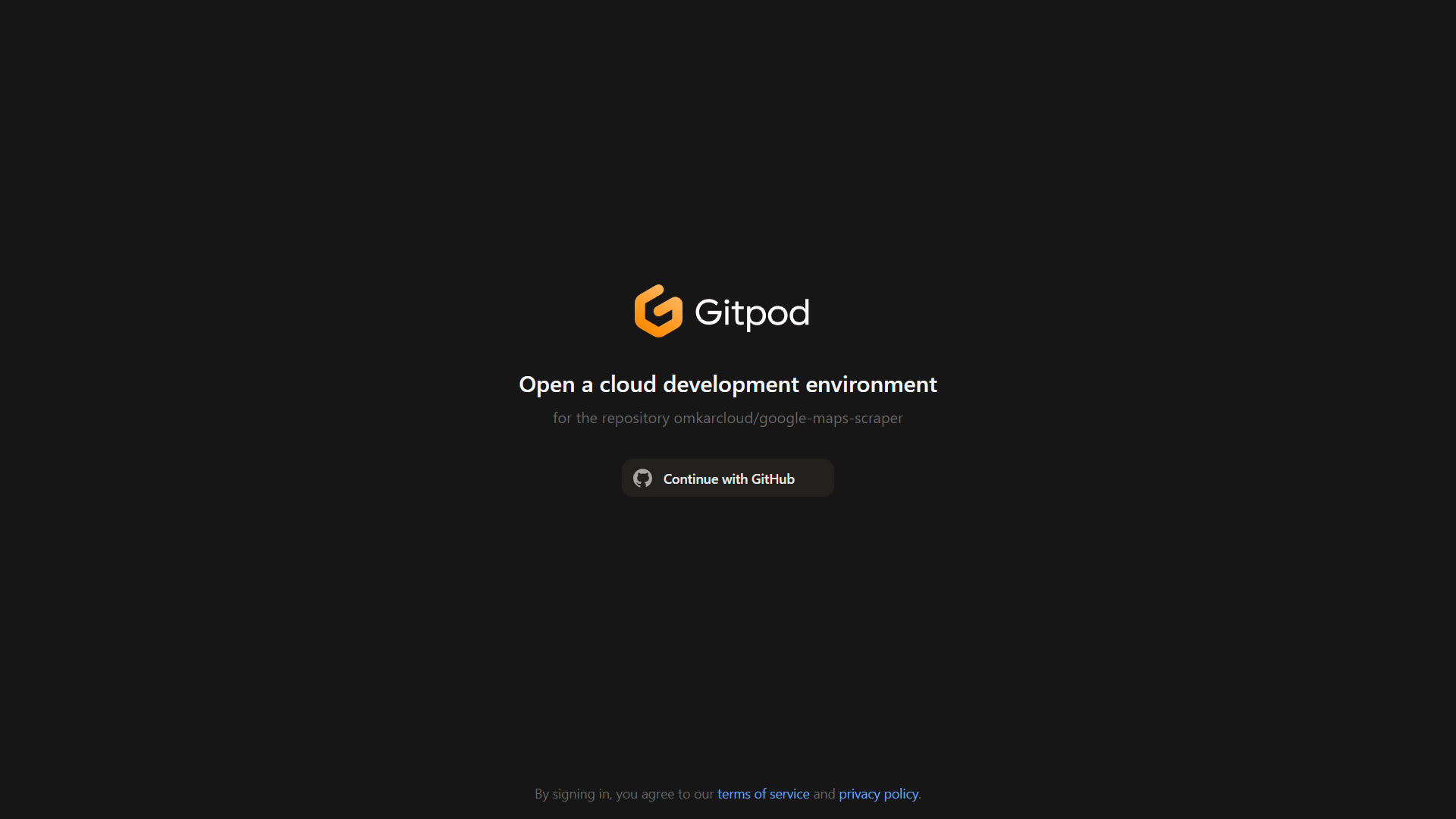
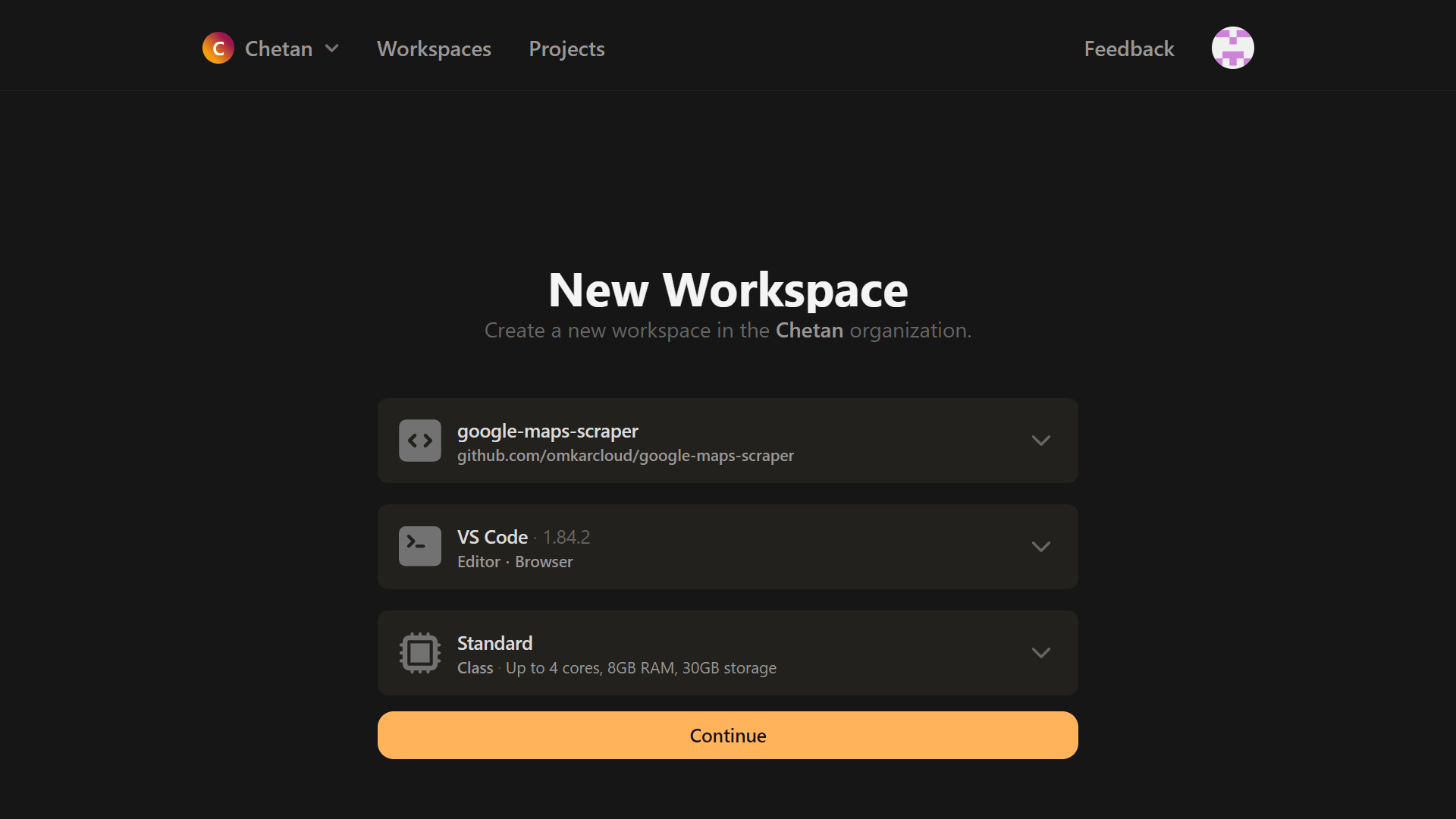
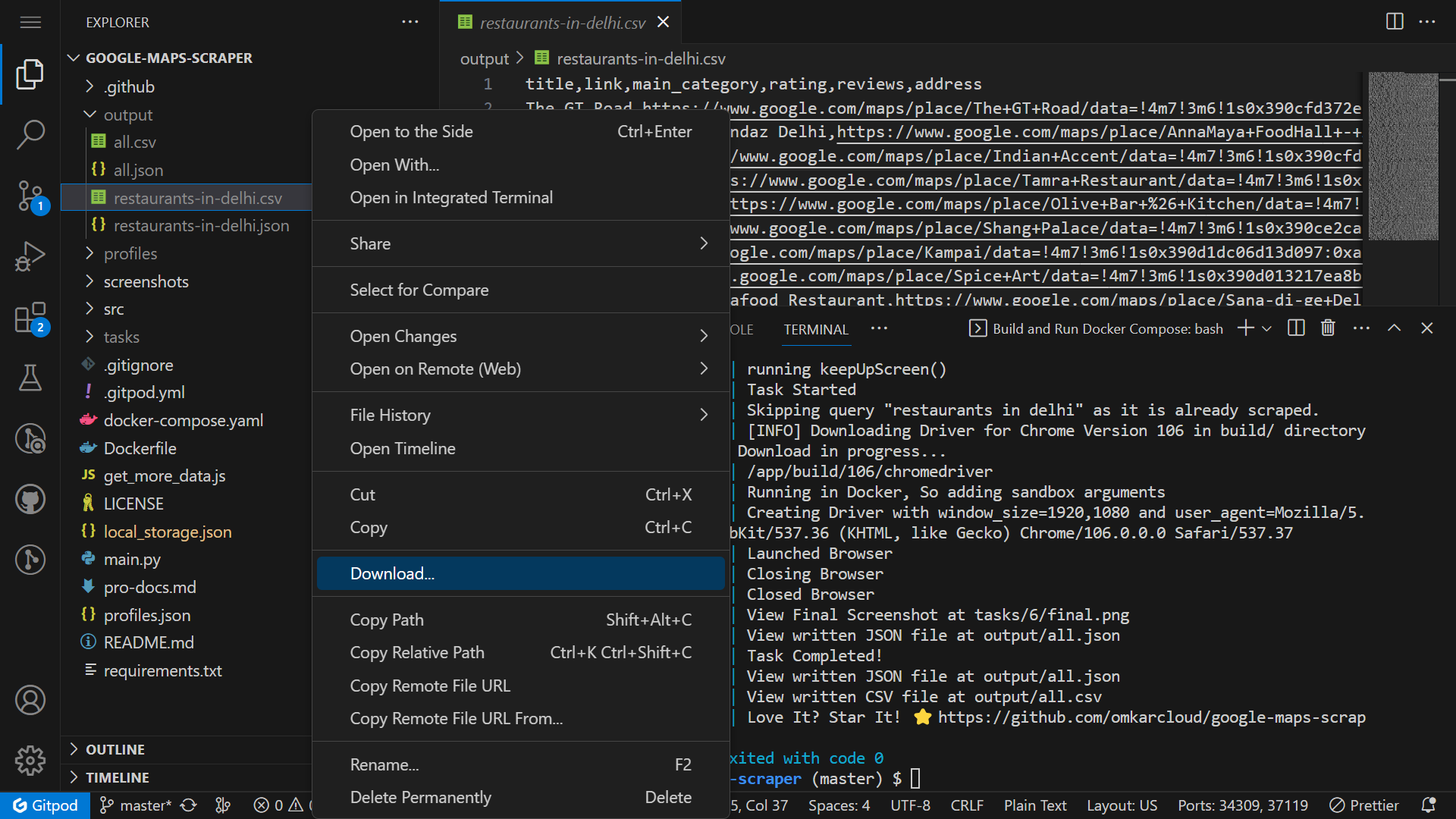
You can easily run the scraper in Gitpod, a browser-based development environment. Set it up in just 5 minutes by following these steps:
-
Visit this link and sign up using your GitHub account.
-
Once Signed Up, Open it in Gitpod.
-
In the terminal, run the following command to start scraping:
python main.py
-
Once the scraper has finished running, download the leads from the
outputfolder.
Just like with a local setup, you can configure the scraper in Gitpod by editing the main.py file and running the scraper using the python main.py command.
Also, it's important to regularly interact with the Gitpod environment, such as clicking within it every 30 minutes, to keep the machine active and prevent automatic shutdown.
If you don't want to click every 30 minutes, then we encourage to install Python on PC and run the scraper locally.
No, the scraper is very light on resources, so there won't be any noticeable difference whether you run it on an Intel Pentium processor with 4GB of RAM or an Intel i7 processor with 16GB of RAM.
Set the scrape_reviews argument to true.
queries = [
"web developers in bangalore"
]
Gmaps.places(queries, scrape_reviews=True, max=5)You can also configure the following options:
- reviews_max (Defaults: 20)
- reviews_sort (Defaults: Newest)
- Options are Most Relevant, Newest, Highest Rating, Lowest Rating
Here is an example that scrapes the Lowest Rated, 100 Reviews.
queries = [
"web developers in bangalore"
]
Gmaps.places(queries, scrape_reviews=True, reviews_max=100, reviews_sort=Gmaps.LOWEST_RATING, max=5)To scrape all reviews without any limit, you can set reviews_max to Gmaps.ALL_REVIEWS.
queries = [
"web developers in bangalore"
]
Gmaps.places(queries, scrape_reviews=True, reviews_max=Gmaps.ALL_REVIEWS, max=5)Please understand that some places may have thousands of reviews, so scraping all reviews may take a long time.
It's best to limit the number of reviews to scrape to a number like 100 or 1000.
Important: If you are a Data Scientist focused on scraping reviews for Data Analysis, we encourage you to use our Google Maps Reviews Scraper, as it is specially tailored for Data Scientists.
- Scrape 100 Newest Google Maps Places Reviews of a Country and Store the result as JSON.
from botasaurus import bt
queries = Gmaps.Cities.India("your_target in")
scraped_places = Gmaps.places(queries, scrape_reviews=True, reviews_max=100, max=5)
bt.write_json(result, "scraped_places.json")- Read the Data for Panda Analysis
from botasaurus import bt
scraped_places = bt.read_json("scraped_places.json")
# Do whatever you want with scraped_placesPass the lang argument.
For example, if you want to scrape results in Spanish, you can do so by passing lang="Gmaps.Lang.Spanish".
queries = [
"web developers in bangalore"
]
Gmaps.places(queries, lang=Gmaps.Lang.Spanish)All Google Maps languages are supported. Some popular languages you may want to use are:
- Gmaps.Lang.Spanish
- Gmaps.Lang.English
- Gmaps.Lang.Chinese
- Gmaps.Lang.Japanese
- And of course Gmaps.Lang.Hindi 😊
See the list of all supported languages here
Use the links method to scrape information from specific Google Maps place links. Here's an example:
links = [
"https://www.google.com/maps/place/Zinavo-+Web+Development,+Web+Design+Company+in+Bangalore,+SEO+Services,+Digital+Marketing+Agency,+eCommerce+Web+Development/@13.01443,77.6480612,17z/data=!3m1!4b1!4m6!3m5!1s0x3bae172f3e7069f1:0xbcac5b2d393c2aa2!8m2!3d13.01443!4d77.6480612!16s%2Fg%2F11h0l3y9l?authuser=0&hl=en&entry=ttu",
"https://www.google.com/maps/place/SeekNEO+-+Web+Development,+Web+Design+Company+in+Bangalore,+eCommerce+Web+Development,+SEO+Services,+Digital+Marketing+Agency/@12.9863763,77.5473899,17z/data=!3m1!4b1!4m6!3m5!1s0x3bae13ac4bcc6641:0x1bf48a7dee3d5a51!8m2!3d12.9863763!4d77.5473899!16s%2Fg%2F11g2338zrl?authuser=0&hl=en&entry=ttu"
]
output_folder = "my-awesome-places"
Gmaps.links(links, output_folder)Provide the coordinates to the scraper as follows:
queries = [
"web developers in bangalore"
]
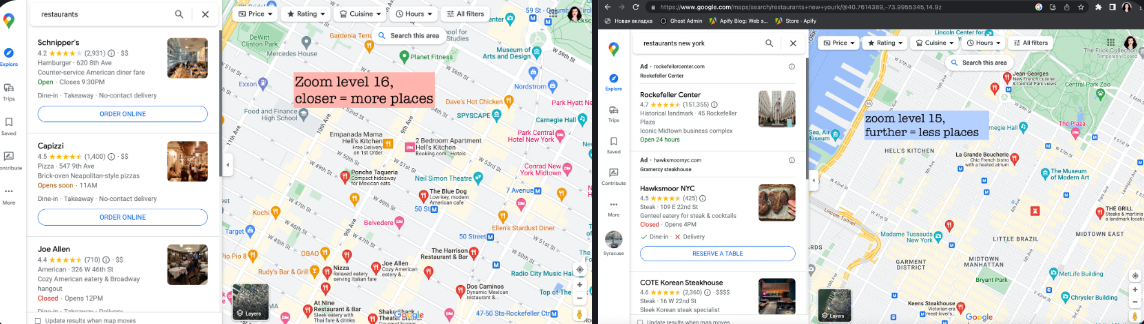
Gmaps.places(queries, geo_coordinates="12.900490, 77.571466", max=5)You can also adjust the zoom level, which will zoom in to the location before scraping:
- 1 (Whole Planet)
- 21 (House Level)
Zooming results in more places being scraped within a smaller area. Below is the same map at different zoom levels, yielding different numbers of results.
Image Credits: Apify
For example, to scrape places in Bangalore at zoom level 16:
queries = [
"web developers in bangalore"
]
Gmaps.places(queries, geo_coordinates="12.900490, 77.571466", zoom=16, max=5)We randomize cities for each user to increase the chances of sales.
If multiple users are targeting the same leads in the same cities, it reduces the opportunity for each.
Randomizing cities spreads them among our users, giving each user a better chance to make a sale.
❓ When setting the Lang Attribute to Hindi/Japanese/Chinese, the characters are in English instead of the specified language. How to transform characters to the specified language?
By default, we convert any non-English characters to English characters. For example, "भारत" gets converted to "Bharat".
We do this because Excel can't render non-English characters properly.
If you want to retain the original characters and not convert them to English, then set the convert_to_english parameter to False as follows:
queries = [
"web developers in Bangalore"
]
Gmaps.places(queries, lang=Gmaps.Lang.Hindi, convert_to_english=False, max=5)Also, in case you are unable to view characters properly in Excel, then the easiest solution is to upload the CSV to Google Sheets, which should render the characters properly.
Through experimentation, we have found a scraping speed that doesn't trigger Google Maps' detection systems, so you do not need to use proxies for scraping Google Maps.
For further help, ask your question in GitHub Discussions. We'll be happy to help you out.
Love It? Star It ⭐!
Become one of our amazing stargazers by giving us a star ⭐ on GitHub!
It's just one click, but it means the world to me.