HTTP IS STATELESS
To overcome this, we can use either a session (stateful) or a token (stateless).
Firstly, what is it that is stateless or stateful ??
| x | Stateful | Stateless |
|---|---|---|
| Browser | ✅ | ✅ |
| Web server | ✅ | ❌ |
| Database | ✅ | ✅ |
The web server!
Many web applications use JSON Web Token (JWT) instead of sessions for authentication. In the token based application:
- The server creates a JWT with a secret and sends the JWT to the client.
- The client stores the JWT (usually in local storage) and includes JWT in the header with every request.
- The server would then validate the JWT with every request from the client and sends a response.
// Token Based Authentication (stateless): JSON Web Token:
const secret = "shhhhh";
let tokenResult = "";
const token = jwt.sign(userInfo, secret, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
tokenResult = res;
}
});
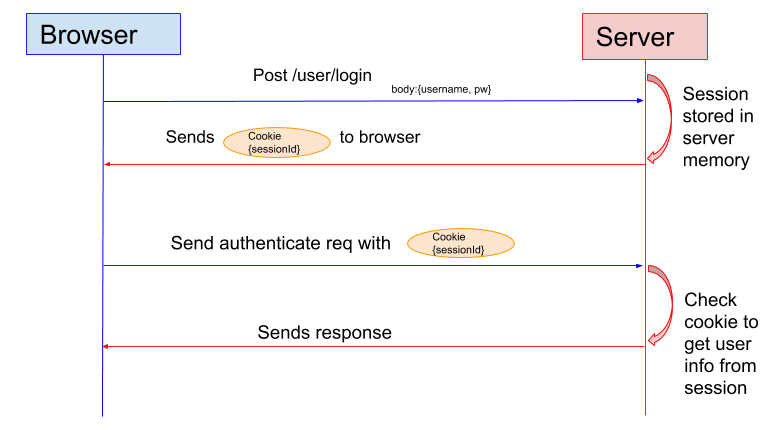
1. In the session based authentication, the server will create a session for the user after the user logs in
2. The session id is then stored on a cookie on the user’s browser. While the user stays logged in, the cookie would be sent along with every subsequent request.
3. The server can then compare the session id stored on the cookie against the session information stored in the memory to verify user’s identity and sends response with the corresponding state!
NB. You can revoke the authentication session on the IdP (Identity Provider) any time!
You log in to a site with your user and password.
The web server then does some things...
// Make a new, unique session id using some kind of generator
sessionId = sessionCounter();
// Store a session id in a cookie on the client's browser
res.writeHead{200, {'set-cookie': `sessionId=${sessionId}; HttpOnly; Max-Age=86400`})
// Associate session id with user in a 'sessions' JSON stored on server
sessions[sessionId] = username;Well done, you've initiated a new session!
| Stateless | Stateful |
|---|---|
| SCALABILITY: | |
| PRO: There is no issue with scaling because token is stored on the client side. | CON: Because the sessions are stored in the server’s memory, scaling becomes an issue when there is a huge number of users using the system at once. |
| Stateless | Stateful |
|---|---|
| MULTIPLE DEVICE | |
| PRO: There is no issue with cookies as the JWT is included in the request header. | CON: Cookies normally work on a single domain or subdomains and they are normally disabled by browser if they work cross-domain (3rd party cookies). It poses issues when APIs are served from a different domain to mobile and web devices. |
Real life examples
Facebook ASOS