-
Logistic Classification
: 정해진 2가지의 카테고리에 분류(Classify)하는 방식 (예 : 이메일 스팸 검출 / 페이스북 피드에 띄울 글 정하기 / 신용카드 도용 검출 / 주식 동향 등)
-
Cost Function
-
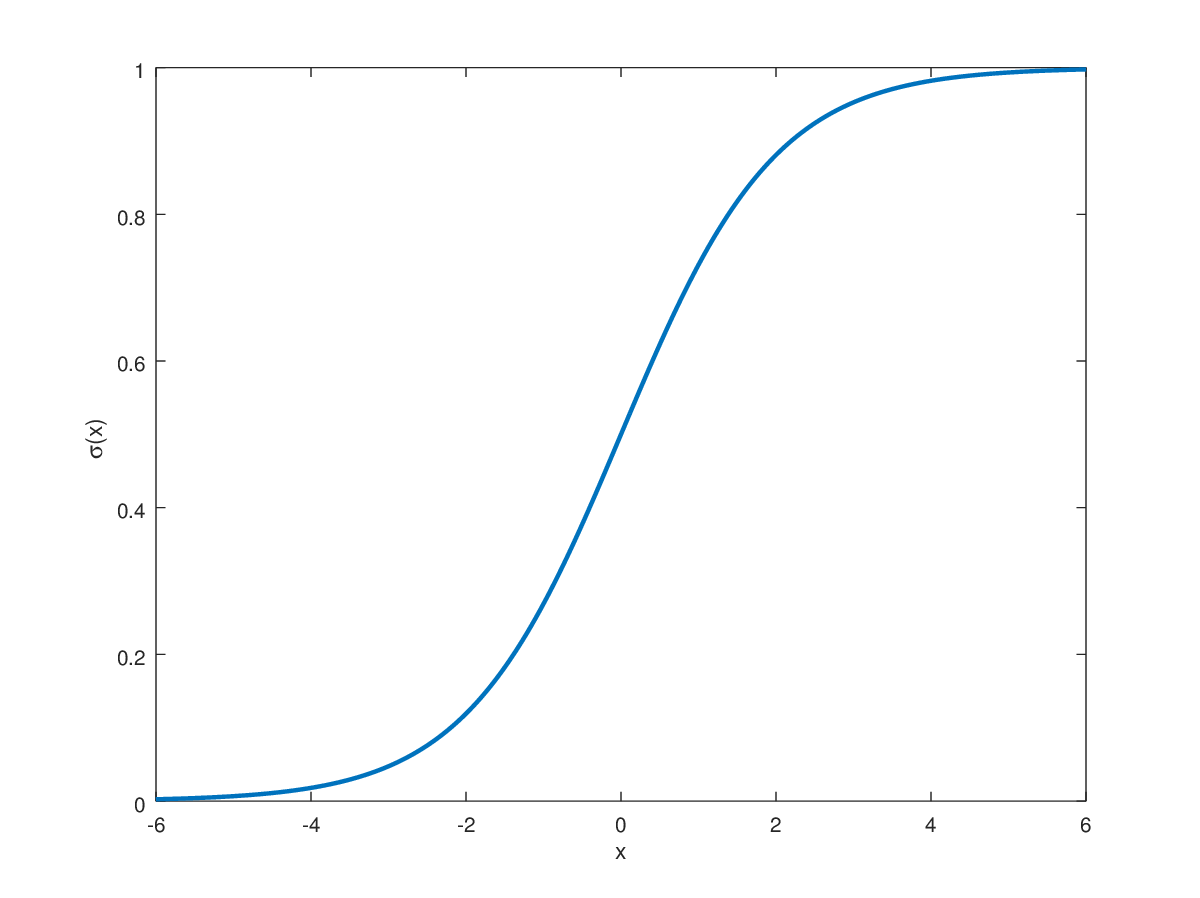
Linear로 hypothesis를 주었을 땐 cost(w) 모양은 2차함수였음. 하지만 sigmoid 모양으로 cost를 기존의 제곱을 써버리면 굉장히 난해한 곡선이 나온다. 따라서 경사하강법을 사용할 경우 시작점에 따라 local minimum을 찾게 된다.
-
Hypothesis에 맞춰 새로 도입하는 cost function: $$ cost(W) = \frac{1}{m} \sum c(H(x), y) $$
$$ c(H(x),y) = \begin{cases} -\log(H(x)) &\mbox{if y = 1} \\ -\log(1-H(x)) &\mbox{if y = 0} \end{cases} $$ -
Understanding Cost function
Hypothesis에 exponential 함수가 들어갔기 때문에 log를 쓴다. 함수 구조상, 예측을 맞출 경우 cost가 0이고 틀릴 경우 cost 거의 무한대로 커진다.
자세한 설명은 서술하기 힘드니 모딥 lec 5-2 참조
-
Minimize (Gradient Descent)
역시나 경사하강법을 쓴다. 이전과 비슷하게 $$ W := W - \alpha {\partial \over\partial W} cost(W) $$ 이다.
이 공식은 실전에선 그냥 라이브러리를 쓰면 된다.
-
-
Hypothesis
- H(x)는 주어진 x값에 대한 예측... 이자 X 가 1일 확률.
- cost(W,b)는 H(x)가 얼마나 잘 예측했는지 나타내는 지표 (작을 수록 좋다)
$$ H(X) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-W^TX}} $$
$$ cost(W) =- \frac{1}{m}\sum y \log((H(x) + (1-y)(\log(1-H(x)) $$
-
In code
-
Settings
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim # Torch Seed 부여 torch.manual_seed(1)
-
Training data
# Training Data x_data = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1],[4,3],[5,3],[6,2]] # |x_data| = 6X2 y_data = [[0], [0], [0], [1], [1], [1]] # |y_data| = 6X1 x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_data) y_train = torch.FloatTensor(y_data)
-
Hypothesis
# Hypothesis W = torch.zeros((2,1), requires_grad = True) b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad = True) # 수식 그대로 표현 hypothesis = 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-(x_train.matmul(W) + b))) # torch 제공함수로 계산 hypothesis = torch.sigmoid(x_train.matmul(W)+ b)
-
Cost Function
# 수식 그대로 표현 losses = -(y_train[0]*torch.log(hypothesis[0]) + (1-y_train) * torch.log(1-hypothesis[0])) cost = losses.mean() # torch 제공함수로 계산 : BCE(Binary Cross Entropy) cost = F.binary_cross_entropy(hypothesis, y_train)
-
-
Whole Training Process
# 모델 초기화 W = torch.zeros((2,1), require_grad = True) b = torch.zeros(1, require_grad = True) # Optimizer 설정 optimizer = optim.SGD([W,b], lr = 1) nb_epochs = 1000 for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1): # Cost 계산 hypothesis = torch.sigmoid(x_train.matmul(W) + b) cost = F.binary_cross_entropy(hypothesis, y_train) # Calculate H(x) optimizer.zero_grad() cost.backward() optimizer.step() # 100번마다 로그 출력하게 if epoch % 100 == 0: print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format( epoch,nb_epochs, cost.item()))
-
Evaluation (내가 만든 모델의 성능이 얼마나 좋을까?)
hypothesis = torch.sigmoid(x_train.matmul(W) + b) print(hypothesis[:5])
를 실행하면 몇의 확률로 1이 될지 알 수 있음.
prediction = hypothesis >= torch.FloatTensor([0.5]) print(prediction[:5]) # prediction은 ByteTensor
이렇게 하면 확률이 0.5 이상 되는 애들을 1로 예측하도록 찍을 수 있음.
이후에는 prediction과 y_train값을 비교하면 된다.
correct_prediction = prediction.float() == y_train
으로 예측과 train 값이 일치하는지 확인할 수 있음.
-
클래스 선언
class BinaryClassifier(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.linear = nn.Linear(8,1) self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self,x): return self.sigmoid(self.linear(x)) model = BinaryClassifier()
-
Full Code
# optimizer 설정 optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1) nb_epochs = 100 for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1): # H(x) 계산 hypothesis = model(x_train) # 돌려보면 여기서 오류가 나는데... size가 6x2와 8x1로 안 맞는다고 함 # 뭔갈 빠트린 걸까? # cost 계산 cost = F.binary_cross_entropy(hypothesis, y_train) # cost로 H(x) 개선 optimizer.zero_grad() cost.backward() optimizer.step() # 20번마다 로그 출력 if epoch % 10 == 0: prediction = hypothesis >= torch.FloatTensor([0.5]) correct_prediction = prediction.float() == y_train accuracy = correct_prediction.sum().item() / len(correct_prediction) print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f} Accuracy {:2.2f}%'.format( epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item(), accuracy * 100, ))