This module installs and configures Bolt to use a local PuppetDB and the Puppet Communications Protocol (PCP) transport.
This module aims to configure a dedicated Puppet Enterprise (PE) compiler to become a Bolt server. The intention is to offload plan execution from Orchestrator on the Primary server to Bolt on the Bolt server. A compiler is ideal because it already has access to PE, Code Manager, and its local PuppetDB.
The puppet_bolt_server module performs these activities:
- Install Bolt on the node.
- Create the
/root/.puppetlabs/etc/bolt/bolt-defaults.yamlfile with custom configuration to:- Use the PCP transport.
- Use the local PuppetDB for queries.
- Consume a Puppet token.
-
apply_helpers- The
puppet_bolt_serverdepends on theapply_helpersmodule, it will install helper tasks that are used by theapply()function in Bolt.
To install it, make sure to add it to the Puppetfile in your control-repo
mod 'puppetlabs-apply_helpers', '0.3.0'
Note: you only need to install this module if you want to use
apply()in your plans. - The
-
taskplanWe recommend installing the
taskplanmodule. Thetaskplanmodule allows you to run a task that uses Bolt to run a plan.You can also create a task yourself or use any task that can run a bolt plan on the bolt server.
Quickstart: Use the PE console to configure the puppet_bolt_server in your existing PE server.
-
Add the puppetlabs-puppet_bolt_server to your control repo.
-
Add a new node group in the PE console:
Parent name: PE Infrastructure Group name: Bolt Server Environment: production -
Add the
puppet_bolt_serverclass to your Bolt Server node group. -
On the Rules tab, add the dedicated compiler (for running Bolt) to the group. This compiler must not be in the compiler pool for catalog compilation.
-
On the Configuration data tab, add your puppet token (sensitive string).
Class: puppet_bolt_server Parameter: puppet_token Value: '<PUPPET_TOKEN>'- We recommend creating a service user inside PE RBAC and choosing an appropriate lifetime for its token.
- Use this command to generate a token with a one-year lifetime:
puppet access login --lifetime 1y
-
Commit your changes.
-
Run Puppet on the Bolt Server node group.
After completing the installation steps, your Bolt server should have these files:
/root/.puppetlabs/etc/bolt/bolt-defaults.yaml/root/.puppetlabs/bolt/bolt-project.yaml/root/.puppetlabs/token
To test that everything is configured properly, you can run any Bolt plan that runs a PuppetDB query, such as this test plan:
# /root/Projects/local_plan/plans/test.pp
plan local_plan::test(
){
$query_results = puppetdb_query("nodes[]{}")
out::message("Hello world from the Bolt Server, query results: ${query_results}")
}Run the test plan with:
bolt plan run local_plan::test
You should get the PuppetDB query results in the terminal. If you inspect the puppetdb-access.log, you should find a log with a call to the local PuppetDB returning a 200 OK HTTP status. For example:
$ less /var/log/puppetlabs/puppetdb/puppetdb-access.log
127.0.0.1 - - [01/Nov/2022:15:56:21 +0000] "POST /pdb/query/v4 HTTP/1.1" 200 1793 "-" "HTTPClient/1.0 (2.8.3, ruby 2.7.6 (2022-04-12))" 99 21 -By default, this module will create the log file under /var/log/puppetlabs/bolt-server/bolt-server.log.
The log level is set to 'info' by default. For more information, please read the Bolt logs doc here
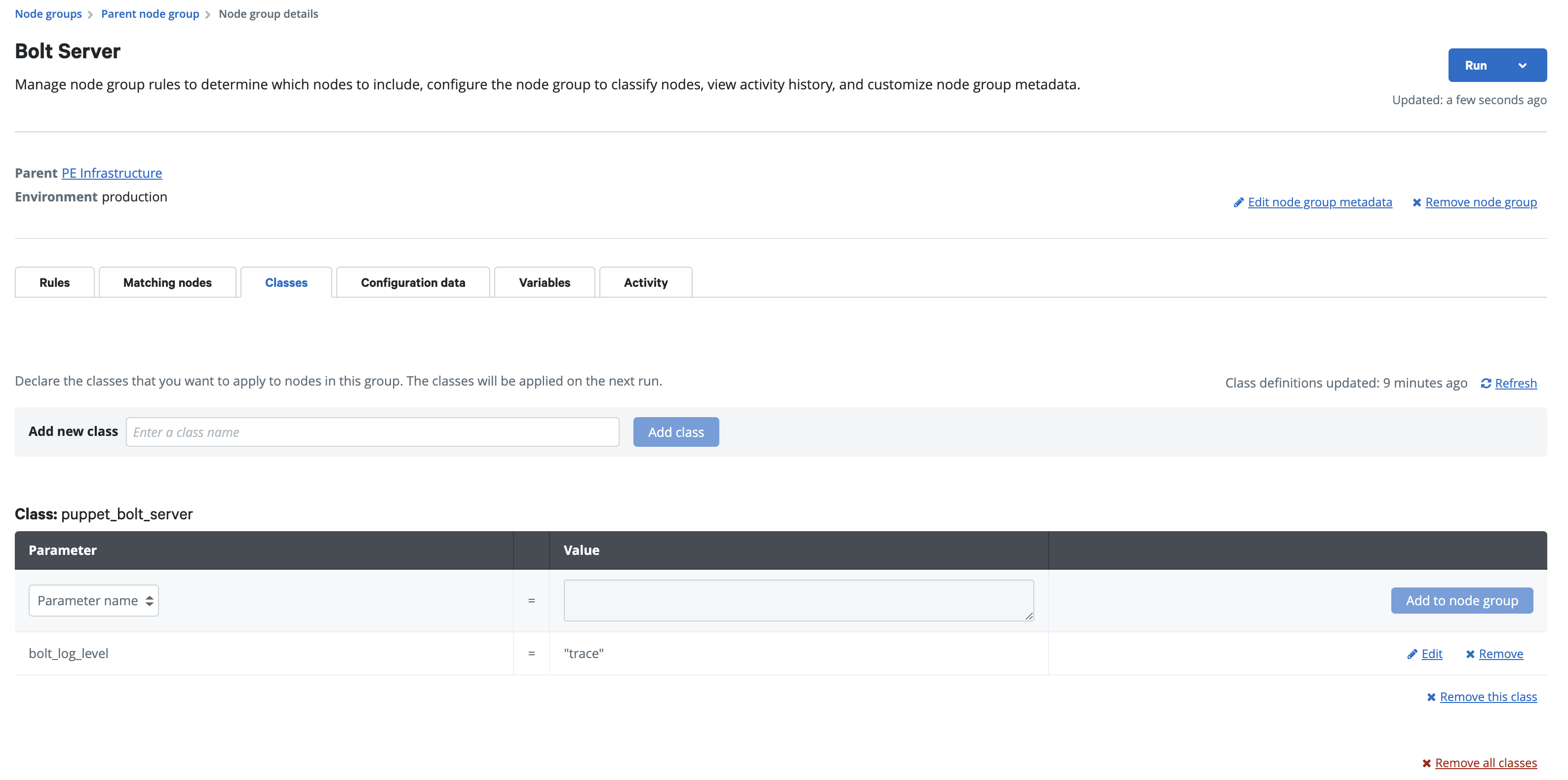
To change the log level you can go to the Bolt Server's node group, in the Classes tab add the bolt_log_level parameter as shown in the screenshot above, commit your changes and run Puppet on the node group.
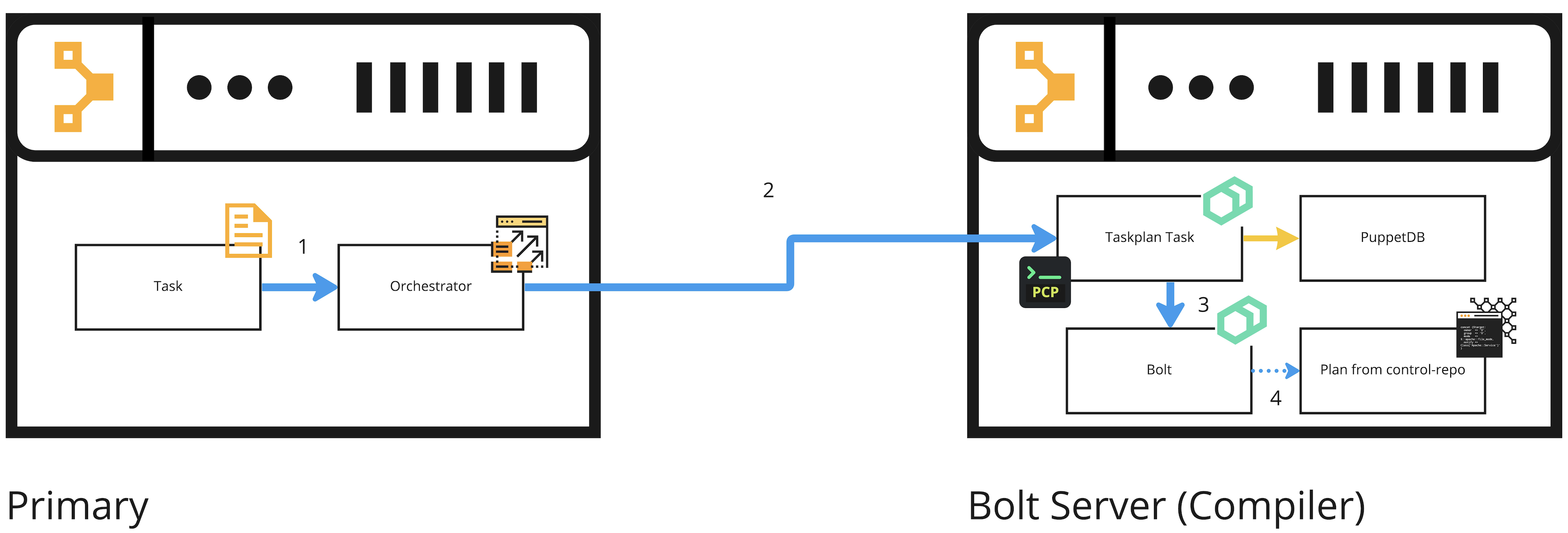
This is an overview of the internal process when you offload plan execution from your PE primary server to a Bolt server. Please note that we recommend using taskplan but it can also be a different task that starts a Bolt plan:
- Someone requests Orchestrator to run the
taskplantask on the Bolt server. - The
taskplantask runs on the Bolt server. - The task starts Bolt with the
bolt plan runcommand. - Bolt starts and runs the plan
This example uses puppet task run to run the taskplan task on the Bolt server.
Required parameters:
- Choose one of your existing, basic plans or create one that receives a parameter (such as
message). - Use your Bolt server's certname.
From the PE primary server CLI, run:
puppet task run taskplan --params '{"plan":"<PLAN_NAME>", "params":{"message": "Hello world!"}, "debug":true}' -n <BOLT_SERVER_CERTNAME>This triggers a taskplan task run, and the task runs the plan on the Bolt server according to the specified parameters.
This offloads plan execution from Orchestrator to a dedicated Bolt server, which alleviates CPU and memory load on the primary server.
This example uses the Orchestrator API to trigger a task run. You can do this from any system connected to your PE primary server (over port 8143) and that has a Puppet RBAC token.
Prepare a JSON body to run taskplan task, targetting the Bolt server. For example:
# test_params.json
{
"environment" : "production",
"task" : "taskplan",
"params" : {
"plan" : "<PLAN_NAME>",
"params" : { "message": "Hello world!" },
"debug" : true
},
"scope" : {
"nodes" : ["<BOLT_SERVER_CERTNAME"]
}
}Make sure to change the params.plan, params.params, and the scope.nodes according to your own test plan.
Use curl to trigger the Ochrestrator API and run the task:
auth_header="X-Authentication: $(puppet-access show)"
uri="https://$(puppet config print server):8143/orchestrator/v1/command/task"
curl -d "@test_params.json" --insecure --header "$auth_header" "$uri"puppet_bolt_serveris tested only on RHEL 7 and 8 based systems.- Requires Puppet >= 6.21.0 <= 7.20.0
- This module only supports running plans from the Production environment.
- Warning: There is no rate limit to run plans, and you need to pay attention to the VM specification since the available memory is directly related to how many concurrent plans you can run.
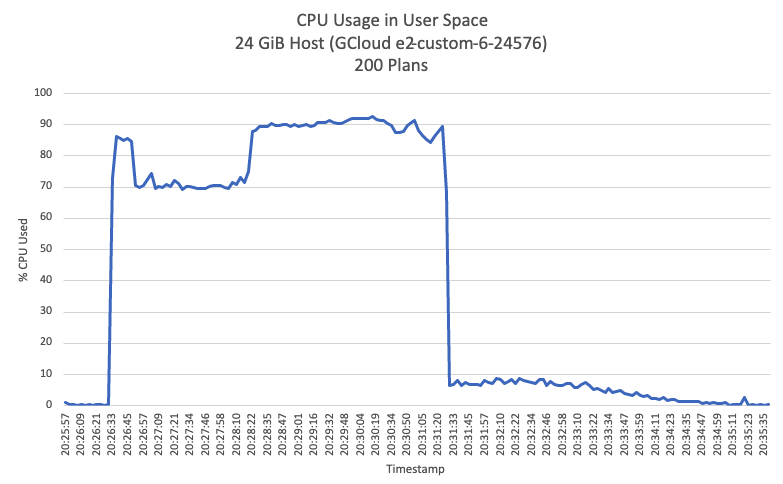
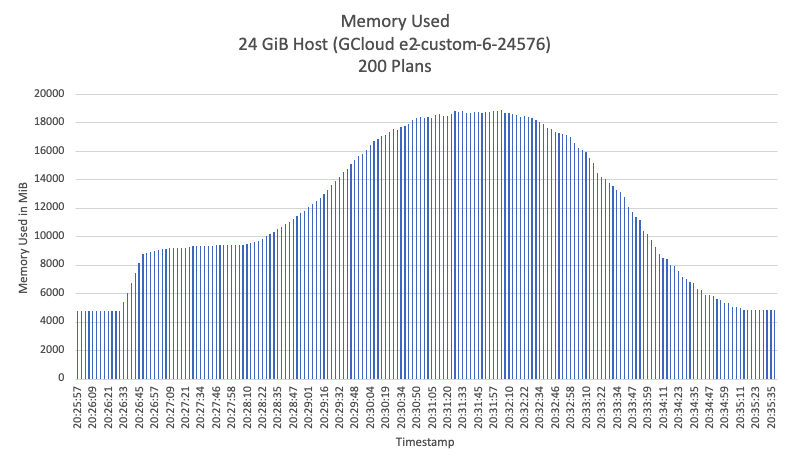
Based on the results of the load test, we know that each additional (concurrent) 50 plans require about 4 GiB to run successfully. As explained in the limitations section, in this early version puppet_bolt_server there are no limits on memory consumption, the bolt processes will continue to use more and more memory until the system becomes completely unresponsive. In our tests, we used 24 GiB of RAM but we noticed the thin margin of memory left during the test, this is dangerous since we could run out of memory.
These are the machine specs of our servers:
- 24 GiB RAM
- CPU Intel Broadwell x86/64, 6 cores
Our recommendation is to run a maximum of 200 concurrent plans, allocating 28 GiB RAM for it, this will give a bit of room in case of unexpected spikes of plans beyond 200.
For education purposes here are two charts that show how the Bolt server will behave in the scenario of running 200 concurrent plans: