just is a handy way to save and run project-specific commands.
This readme is also available as a book.
(中文文档在 这里, 快看过来!)
Commands, called recipes, are stored in a file called justfile with syntax inspired by make:
You can then run them with just RECIPE:
$ just test-all
cc *.c -o main
./test --all
Yay, all your tests passed!just has a ton of useful features, and many improvements over make:
-
justis a command runner, not a build system, so it avoids much ofmake's complexity and idiosyncrasies. No need for.PHONYrecipes! -
Linux, MacOS, and Windows are supported with no additional dependencies. (Although if your system doesn't have an
sh, you'll need to choose a different shell.) -
Errors are specific and informative, and syntax errors are reported along with their source context.
-
Recipes can accept command line arguments.
-
Wherever possible, errors are resolved statically. Unknown recipes and circular dependencies are reported before anything runs.
-
justloads.envfiles, making it easy to populate environment variables. -
Recipes can be listed from the command line.
-
Command line completion scripts are available for most popular shells.
-
Recipes can be written in arbitrary languages, like Python or NodeJS.
-
justcan be invoked from any subdirectory, not just the directory that contains thejustfile. -
And much more!
If you need help with just please feel free to open an issue or ping me on Discord. Feature requests and bug reports are always welcome!
just should run on any system with a reasonable sh, including Linux, MacOS, and the BSDs.
On Windows, just works with the sh provided by Git for Windows, GitHub Desktop, or Cygwin.
If you'd rather not install sh, you can use the shell setting to use the shell of your choice.
Like PowerShell:
# use PowerShell instead of sh:
set shell := ["powershell.exe", "-c"]
hello:
Write-Host "Hello, world!"…or cmd.exe:
# use cmd.exe instead of sh:
set shell := ["cmd.exe", "/c"]
list:
dirYou can also set the shell using command-line arguments. For example, to use PowerShell, launch just with --shell powershell.exe --shell-arg -c.
(PowerShell is installed by default on Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 S1 and later, and cmd.exe is quite fiddly, so PowerShell is recommended for most Windows users.)
| Operating System | Package Manager | Package | Command |
|---|---|---|---|
| Various | Cargo | just | cargo install just |
| Microsoft Windows | Scoop | just | scoop install just |
| Various | Homebrew | just | brew install just |
| macOS | MacPorts | just | port install just |
| Arch Linux | pacman | just | pacman -S just |
| Various | Nix | just | nix-env -iA nixpkgs.just |
| NixOS | Nix | just | nix-env -iA nixos.just |
| Solus | eopkg | just | eopkg install just |
| Void Linux | XBPS | just | xbps-install -S just |
| FreeBSD | pkg | just | pkg install just |
| Alpine Linux | apk-tools | just | apk add just |
| Fedora Linux | DNF | just | dnf install just |
| Gentoo Linux | Portage | dm9pZCAq/sys-devel/just |
eselect repository enable dm9pZCAqemerge --sync dm9pZCAqemerge sys-devel/just
|
| Various | Conda | just | conda install -c conda-forge just |
| Microsoft Windows | Chocolatey | just | choco install just |
| Various | Snap | just | snap install --edge --classic just |
| Various | asdf | just |
asdf plugin add justasdf install just <version>
|
| Debian and Ubuntu derivatives | MPR | just |
git clone 'https://mpr.makedeb.org/just'cd justmakedeb -si
|
| Debian and Ubuntu derivatives | Prebuilt-MPR | just |
You must have the Prebuilt-MPR set up on your system in order to run this command.sudo apt install just
|
Pre-built binaries for Linux, MacOS, and Windows can be found on the releases page.
You can use the following command on Linux, MacOS, or Windows to download the latest release, just replace DEST with the directory where you'd like to put just:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://just.systems/install.sh | bash -s -- --to DESTFor example, to install just to ~/bin:
# create ~/bin
mkdir -p ~/bin
# download and extract just to ~/bin/just
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://just.systems/install.sh | bash -s -- --to ~/bin
# add `~/bin` to the paths that your shell searches for executables
# this line should be added to your shells initialization file,
# e.g. `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/bin"
# just should now be executable
just --helpextractions/setup-just can be used to install just in a GitHub Actions workflow.
Example usage:
- uses: extractions/setup-just@v1
with:
just-version: 0.8 # optional semver specification, otherwise latestAn RSS feed of just releases is available here.
just-install can be used to automate installation of just in Node.js applications.
just is a great, more robust alternative to npm scripts. If you want to include just in the dependencies of a Node.js application, just-install will install a local, platform-specific binary as part of the npm install command. This removes the need for every developer to install just independently using one of the processes mentioned above. After installation, the just command will work in npm scripts or with npx. It's great for teams who want to make the set up process for their project as easy as possible.
For more information, see the just-install README file.
With the release of version 1.0, just features a strong commitment to backwards compatibility and stability.
Future releases will not introduce backwards incompatible changes that make existing justfiles stop working, or break working invocations of the command-line interface.
This does not, however, preclude fixing outright bugs, even if doing so might break justfiles that rely on their behavior.
There will never be a just 2.0. Any desirable backwards-incompatible changes will be opt-in on a per-justfile basis, so users may migrate at their leisure.
Features that aren't yet ready for stabilization are gated behind the --unstable flag. Features enabled by --unstable may change in backwards incompatible ways at any time.
justfile syntax is close enough to make that you may want to tell your editor to use make syntax highlighting for just.
The vim-just plugin provides syntax highlighting for justfiles.
Install it with your favorite package manager, like Plug:
call plug#begin()
Plug 'NoahTheDuke/vim-just'
call plug#end()Or with Vim's built-in package support:
mkdir -p ~/.vim/pack/vendor/start
cd ~/.vim/pack/vendor/start
git clone https://github.com/NoahTheDuke/vim-just.gitvim-just is also available from vim-polyglot, a multi-language Vim plugin.
tree-sitter-just is an Nvim Treesitter plugin for Neovim.
Vim's built-in makefile syntax highlighting isn't perfect for justfiles, but it's better than nothing. You can put the following in ~/.vim/filetype.vim:
if exists("did_load_filetypes")
finish
endif
augroup filetypedetect
au BufNewFile,BufRead justfile setf make
augroup ENDOr add the following to an individual justfile to enable make mode on a per-file basis:
# vim: set ft=make :
just-mode provides syntax highlighting and automatic indentation of justfiles. It is available on MELPA as just-mode.
justl provides commands for executing and listing recipes.
You can add the following to an individual justfile to enable make mode on a per-file basis:
# Local Variables:
# mode: makefile
# End:
An extension for VS Code by skellock is available here (repository), but is no longer actively developed.
You can install it from the command line by running:
code --install-extension skellock.justAn more recently active fork by sclu1034 is available here.
A plugin for JetBrains IDEs by linux_china is available here.
Kakoune supports justfile syntax highlighting out of the box, thanks to TeddyDD.
A syntax file for Sublime Text written by TonioGela is available in extras/just.sublime-syntax.
Feel free to send me the commands necessary to get syntax highlighting working in your editor of choice so that I may include them here.
See the installation section for how to install just on your computer. Try running just --version to make sure that it's installed correctly.
For an overview of the syntax, check out this cheatsheet.
Once just is installed and working, create a file named justfile in the root of your project with the following contents:
recipe-name:
echo 'This is a recipe!'
# this is a comment
another-recipe:
@echo 'This is another recipe.'When you invoke just it looks for file justfile in the current directory and upwards, so you can invoke it from any subdirectory of your project.
The search for a justfile is case insensitive, so any case, like Justfile, JUSTFILE, or JuStFiLe, will work. just will also look for files with the name .justfile, in case you'd like to hide a justfile.
Running just with no arguments runs the first recipe in the justfile:
$ just
echo 'This is a recipe!'
This is a recipe!One or more arguments specify the recipe(s) to run:
$ just another-recipe
This is another recipe.just prints each command to standard error before running it, which is why echo 'This is a recipe!' was printed. This is suppressed for lines starting with @, which is why echo 'This is another recipe.' was not printed.
Recipes stop running if a command fails. Here cargo publish will only run if cargo test succeeds:
publish:
cargo test
# tests passed, time to publish!
cargo publishRecipes can depend on other recipes. Here the test recipe depends on the build recipe, so build will run before test:
build:
cc main.c foo.c bar.c -o main
test: build
./test
sloc:
@echo "`wc -l *.c` lines of code"$ just test
cc main.c foo.c bar.c -o main
./test
testing… all tests passed!Recipes without dependencies will run in the order they're given on the command line:
$ just build sloc
cc main.c foo.c bar.c -o main
1337 lines of codeDependencies will always run first, even if they are passed after a recipe that depends on them:
$ just test build
cc main.c foo.c bar.c -o main
./test
testing… all tests passed!A variety of example justfiles can be found in the examples directory.
When just is invoked without a recipe, it runs the first recipe in the justfile. This recipe might be the most frequently run command in the project, like running the tests:
test:
cargo testYou can also use dependencies to run multiple recipes by default:
default: lint build test
build:
echo Building…
test:
echo Testing…
lint:
echo Linting…If no recipe makes sense as the default recipe, you can add a recipe to the beginning of your justfile that lists the available recipes:
default:
just --listRecipes can be listed in alphabetical order with just --list:
$ just --list
Available recipes:
build
test
deploy
lintjust --summary is more concise:
$ just --summary
build test deploy lintPass --unsorted to print recipes in the order they appear in the justfile:
test:
echo 'Testing!'
build:
echo 'Building!'$ just --list --unsorted
Available recipes:
test
build$ just --summary --unsorted
test buildIf you'd like just to default to listing the recipes in the justfile, you can use this as your default recipe:
default:
@just --listNote that you may need to add --justfile {{justfile()}} to the line above above. Without it, if you executed just -f /some/distant/justfile -d . or just -f ./non-standard-justfile, the plain just --list inside the recipe would not necessarily use the file you provided. It would try to find a justfile in your current path, maybe even resulting in a No justfile found error.
The heading text can be customized with --list-heading:
$ just --list --list-heading $'Cool stuff…\n'
Cool stuff…
test
buildAnd the indentation can be customized with --list-prefix:
$ just --list --list-prefix ····
Available recipes:
····test
····buildThe argument to --list-heading replaces both the heading and the newline following it, so it should contain a newline if non-empty. It works this way so you can suppress the heading line entirely by passing the empty string:
$ just --list --list-heading ''
test
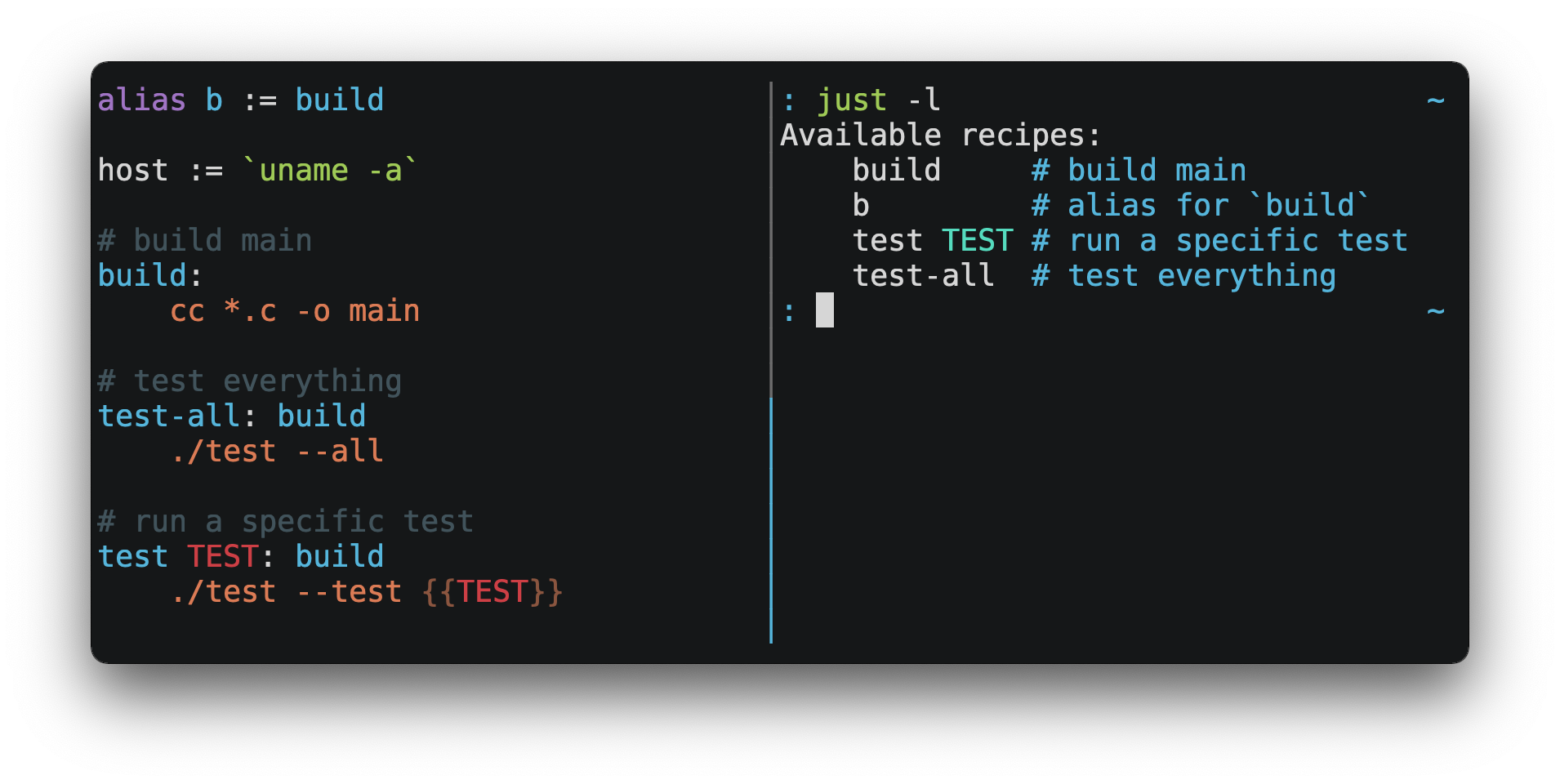
buildAliases allow recipes to be invoked with alternative names:
alias b := build
build:
echo 'Building!'$ just b
build
echo 'Building!'
Building!Settings control interpretation and execution. Each setting may be specified at most once, anywhere in the justfile.
For example:
set shell := ["zsh", "-cu"]
foo:
# this line will be run as `zsh -cu 'ls **/*.txt'`
ls **/*.txt| Name | Value | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
allow-duplicate-recipes |
boolean | False | Allow recipes appearing later in a justfile to override earlier recipes with the same name. |
dotenv-load |
boolean | False | Load a .env file, if present. |
export |
boolean | False | Export all variables as environment variables. |
fallback |
boolean | False | Search justfile in parent directory if the first recipe on the command line is not found. |
ignore-comments |
boolean | False | Ignore recipe lines beginning with #. |
positional-arguments |
boolean | False | Pass positional arguments. |
shell |
[COMMAND, ARGS…] |
- | Set the command used to invoke recipes and evaluate backticks. |
tempdir |
string | - | Create temporary directories in tempdir instead of the system default temporary directory. |
windows-powershell |
boolean | False | Use PowerShell on Windows as default shell. (Deprecated. Use windows-shell instead. |
windows-shell |
[COMMAND, ARGS…] |
- | Set the command used to invoke recipes and evaluate backticks. |
Boolean settings can be written as:
set NAMEWhich is equivalent to:
set NAME := trueIf allow-duplicate-recipes is set to true, defining multiple recipes with the same name is not an error and the last definition is used. Defaults to false.
set allow-duplicate-recipes
@foo:
echo foo
@foo:
echo bar$ just foo
barIf dotenv-load is true, a .env file will be loaded if present. Defaults to false.
The export setting causes all just variables to be exported as environment variables. Defaults to false.
set export
a := "hello"
@foo b:
echo $a
echo $b$ just foo goodbye
hello
goodbyeIf positional-arguments is true, recipe arguments will be passed as positional arguments to commands. For linewise recipes, argument $0 will be the name of the recipe.
For example, running this recipe:
set positional-arguments
@foo bar:
echo $0
echo $1Will produce the following output:
$ just foo hello
foo
helloWhen using an sh-compatible shell, such as bash or zsh, $@ expands to the positional arguments given to the recipe, starting from one. When used within double quotes as "$@", arguments including whitespace will be passed on as if they were double-quoted. That is, "$@" is equivalent to "$1" "$2"… When there are no positional parameters, "$@" and $@ expand to nothing (i.e., they are removed).
This example recipe will print arguments one by one on separate lines:
set positional-arguments
@test *args='':
bash -c 'while (( "$#" )); do echo - $1; shift; done' -- "$@"Running it with two arguments:
$ just test foo "bar baz"
- foo
- bar bazThe shell setting controls the command used to invoke recipe lines and backticks. Shebang recipes are unaffected.
# use python3 to execute recipe lines and backticks
set shell := ["python3", "-c"]
# use print to capture result of evaluation
foos := `print("foo" * 4)`
foo:
print("Snake snake snake snake.")
print("{{foos}}")just passes the command to be executed as an argument. Many shells will need an additional flag, often -c, to make them evaluate the first argument.
just uses sh on Windows by default. To use a different shell on Windows, use windows-shell:
set windows-shell := ["powershell.exe", "-NoLogo", "-Command"]
hello:
Write-Host "Hello, world!"See powershell.just for a justfile that uses PowerShell on all platforms.
set windows-powershell uses the legacy powershell.exe binary, and is no longer recommended. See the windows-shell setting above for a more flexible way to control which shell is used on Windows.
just uses sh on Windows by default. To use powershell.exe instead, set windows-powershell to true.
set windows-powershell := true
hello:
Write-Host "Hello, world!"set shell := ["python3", "-c"]set shell := ["bash", "-uc"]set shell := ["zsh", "-uc"]set shell := ["fish", "-c"]set shell := ["nu", "-c"]If you want to change the default table mode to light:
set shell := ['nu', '-m', 'light', '-c']Nushell was written in Rust, and has cross-platform support for Windows / macOS and Linux.
Comments immediately preceding a recipe will appear in just --list:
# build stuff
build:
./bin/build
# test stuff
test:
./bin/test$ just --list
Available recipes:
build # build stuff
test # test stuffIf dotenv-load is set, just will load environment variables from a file named .env. This file can be located in the same directory as your justfile or in a parent directory. These variables are environment variables, not just variables, and so must be accessed using $VARIABLE_NAME in recipes and backticks.
For example, if your .env file contains:
# a comment, will be ignored
DATABASE_ADDRESS=localhost:6379
SERVER_PORT=1337And your justfile contains:
set dotenv-load
serve:
@echo "Starting server with database $DATABASE_ADDRESS on port $SERVER_PORT…"
./server --database $DATABASE_ADDRESS --port $SERVER_PORTjust serve will output:
$ just serve
Starting server with database localhost:6379 on port 1337…
./server --database $DATABASE_ADDRESS --port $SERVER_PORTVariables, strings, concatenation, path joining, and substitution using {{…}} are supported:
tmpdir := `mktemp`
version := "0.2.7"
tardir := tmpdir / "awesomesauce-" + version
tarball := tardir + ".tar.gz"
publish:
rm -f {{tarball}}
mkdir {{tardir}}
cp README.md *.c {{tardir}}
tar zcvf {{tarball}} {{tardir}}
scp {{tarball}} [email protected]:release/
rm -rf {{tarball}} {{tardir}}The / operator can be used to join two strings with a slash:
foo := "a" / "b"$ just --evaluate foo
a/b
Note that a / is added even if one is already present:
foo := "a/"
bar := foo / "b"$ just --evaluate bar
a//b
Absolute paths can also be constructed1.5.0:
foo := / "b"$ just --evaluate foo
/b
The / operator uses the / character, even on Windows. Thus, using the / operator should be avoided with paths that use universal naming convention (UNC), i.e., those that start with \?, since forward slashes are not supported with UNC paths.
To write a recipe containing {{, use {{{{:
braces:
echo 'I {{{{LOVE}} curly braces!'(An unmatched }} is ignored, so it doesn't need to be escaped.)
Another option is to put all the text you'd like to escape inside of an interpolation:
braces:
echo '{{'I {{LOVE}} curly braces!'}}'Yet another option is to use {{ "{{" }}:
braces:
echo 'I {{ "{{" }}LOVE}} curly braces!'Double-quoted strings support escape sequences:
string-with-tab := "\t"
string-with-newline := "\n"
string-with-carriage-return := "\r"
string-with-double-quote := "\""
string-with-slash := "\\"
string-with-no-newline := "\
"$ just --evaluate
"tring-with-carriage-return := "
string-with-double-quote := """
string-with-newline := "
"
string-with-no-newline := ""
string-with-slash := "\"
string-with-tab := " "Strings may contain line breaks:
single := '
hello
'
double := "
goodbye
"Single-quoted strings do not recognize escape sequences:
escapes := '\t\n\r\"\\'$ just --evaluate
escapes := "\t\n\r\"\\"Indented versions of both single- and double-quoted strings, delimited by triple single- or triple double-quotes, are supported. Indented string lines are stripped of leading whitespace common to all non-blank lines:
# this string will evaluate to `foo\nbar\n`
x := '''
foo
bar
'''
# this string will evaluate to `abc\n wuv\nbar\n`
y := """
abc
wuv
xyz
"""Similar to unindented strings, indented double-quoted strings process escape sequences, and indented single-quoted strings ignore escape sequences. Escape sequence processing takes place after unindentation. The unindention algorithm does not take escape-sequence produced whitespace or newlines into account.
Normally, if a command returns a non-zero exit status, execution will stop. To continue execution after a command, even if it fails, prefix the command with -:
foo:
-cat foo
echo 'Done!'$ just foo
cat foo
cat: foo: No such file or directory
echo 'Done!'
Done!just provides a few built-in functions that might be useful when writing recipes.
arch()— Instruction set architecture. Possible values are:"aarch64","arm","asmjs","hexagon","mips","msp430","powerpc","powerpc64","s390x","sparc","wasm32","x86","x86_64", and"xcore".os()— Operating system. Possible values are:"android","bitrig","dragonfly","emscripten","freebsd","haiku","ios","linux","macos","netbsd","openbsd","solaris", and"windows".os_family()— Operating system family; possible values are:"unix"and"windows".
For example:
system-info:
@echo "This is an {{arch()}} machine".$ just system-info
This is an x86_64 machineThe os_family() function can be used to create cross-platform justfiles that work on various operating systems. For an example, see cross-platform.just file.
env_var(key)— Retrieves the environment variable with namekey, aborting if it is not present.
home_dir := env_var('HOME')
test:
echo "{{home_dir}}"$ just
/home/user1env_var_or_default(key, default)— Retrieves the environment variable with namekey, returningdefaultif it is not present.
invocation_directory()- Retrieves the absolute path to the current directory whenjustwas invoked, beforejustchanged it (chdir'd) prior to executing commands.
For example, to call rustfmt on files just under the "current directory" (from the user/invoker's perspective), use the following rule:
rustfmt:
find {{invocation_directory()}} -name \*.rs -exec rustfmt {} \;Alternatively, if your command needs to be run from the current directory, you could use (e.g.):
build:
cd {{invocation_directory()}}; ./some_script_that_needs_to_be_run_from_here-
justfile()- Retrieves the path of the currentjustfile. -
justfile_directory()- Retrieves the path of the parent directory of the currentjustfile.
For example, to run a command relative to the location of the current justfile:
script:
./{{justfile_directory()}}/scripts/some_scriptjust_executable()- Absolute path to thejustexecutable.
For example:
executable:
@echo The executable is at: {{just_executable()}}$ just
The executable is at: /bin/justquote(s)- Replace all single quotes with'\''and prepend and append single quotes tos. This is sufficient to escape special characters for many shells, including most Bourne shell descendants.replace(s, from, to)- Replace all occurrences offrominstoto.replace_regex(s, regex, replacement)- Replace all occurrences ofregexinstoreplacement.trim(s)- Remove leading and trailing whitespace froms.trim_end(s)- Remove trailing whitespace froms.trim_end_match(s, pat)- Remove suffix ofsmatchingpat.trim_end_matches(s, pat)- Repeatedly remove suffixes ofsmatchingpat.trim_start(s)- Remove leading whitespace froms.trim_start_match(s, pat)- Remove prefix ofsmatchingpat.trim_start_matches(s, pat)- Repeatedly remove prefixes ofsmatchingpat.
capitalize(s)1.7.0 - Convert first character ofsto uppercase and the rest to lowercase.kebabcase(s)1.7.0 - Convertstokebab-case.lowercamelcase(s)1.7.0 - ConvertstolowerCamelCase.lowercase(s)- Convertsto lowercase.shoutykebabcase(s)1.7.0 - ConvertstoSHOUTY-KEBAB-CASE.shoutysnakecase(s)1.7.0 - ConvertstoSHOUTY_SNAKE_CASE.snakecase(s)1.7.0 - Convertstosnake_case.titlecase(s)1.7.0 - ConvertstoTitle Case.uppercamelcase(s)1.7.0 - ConvertstoUpperCamelCase.uppercase(s)- Convertsto uppercase.
absolute_path(path)- Absolute path to relativepathin the working directory.absolute_path("./bar.txt")in directory/foois/foo/bar.txt.extension(path)- Extension ofpath.extension("/foo/bar.txt")istxt.file_name(path)- File name ofpathwith any leading directory components removed.file_name("/foo/bar.txt")isbar.txt.file_stem(path)- File name ofpathwithout extension.file_stem("/foo/bar.txt")isbar.parent_directory(path)- Parent directory ofpath.parent_directory("/foo/bar.txt")is/foo.without_extension(path)-pathwithout extension.without_extension("/foo/bar.txt")is/foo/bar.
These functions can fail, for example if a path does not have an extension, which will halt execution.
clean(path)- Simplifypathby removing extra path separators, intermediate.components, and..where possible.clean("foo//bar")isfoo/bar,clean("foo/..")is.,clean("foo/./bar")isfoo/bar.join(a, b…)- This function uses/on Unix and\on Windows, which can be lead to unwanted behavior. The/operator, e.g.,a / b, which always uses/, should be considered as a replacement unless\s are specifically desired on Windows. Join pathawith pathb.join("foo/bar", "baz")isfoo/bar/baz. Accepts two or more arguments.
path_exists(path)- Returnstrueif the path points at an existing entity andfalseotherwise. Traverses symbolic links, and returnsfalseif the path is inaccessible or points to a broken symlink.
error(message)- Abort execution and report errormessageto user.
sha256(string)- Return the SHA-256 hash ofstringas a hexadecimal string.sha256_file(path)- Return the SHA-256 hash of the file atpathas a hexadecimal string.uuid()- Return a randomly generated UUID.
Recipes may be annotated with attributes that change their behavior.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
[no-cd] |
Don't change directory before executing recipe. |
[no-exit-message] |
Don't print an error message if recipe fails. |
[linux] |
Enable recipe on Linux. |
[macos] |
Enable recipe on MacOS. |
[unix] |
Enable recipe on Unixes. |
[windows] |
Enable recipe on Windows. |
The [linux], [macos], [unix], and [windows] attributes are
configuration attributes. By default, recipes are always enabled. A recipe with
one or more configuration attributes will only be enabled when one or more of
those configurations is active.
This can be used to write justfiles that behave differently depending on
which operating system they run on. The run recipe in this justfile will
compile and run main.c, using a different C compiler and using the correct
output binary name for that compiler depending on the operating system:
[unix]
run:
cc main.c
./a.out
[windows]
run:
cl main.c
main.exejust normally executes recipes with the current directory set to the
directory that contains the justfile. This can be disabled using the
[no-cd] attribute. This can be used to create recipes which use paths
relative to the invocation directory, or which operate on the current
directory.
For exmaple, this commit recipe:
[no-cd]
commit file:
git add {{file}}
git commitCan be used with paths that are relative to the current directory, because
[no-cd] prevents just from changing the current directory when executing
commit.
Backticks can be used to store the result of commands:
localhost := `dumpinterfaces | cut -d: -f2 | sed 's/\/.*//' | sed 's/ //g'`
serve:
./serve {{localhost}} 8080Indented backticks, delimited by three backticks, are de-indented in the same manner as indented strings:
# This backtick evaluates the command `echo foo\necho bar\n`, which produces the value `foo\nbar\n`.
stuff := ```
echo foo
echo bar
```See the Strings section for details on unindenting.
Backticks may not start with #!. This syntax is reserved for a future upgrade.
if/else expressions evaluate different branches depending on if two expressions evaluate to the same value:
foo := if "2" == "2" { "Good!" } else { "1984" }
bar:
@echo "{{foo}}"$ just bar
Good!It is also possible to test for inequality:
foo := if "hello" != "goodbye" { "xyz" } else { "abc" }
bar:
@echo {{foo}}$ just bar
xyzAnd match against regular expressions:
foo := if "hello" =~ 'hel+o' { "match" } else { "mismatch" }
bar:
@echo {{foo}}$ just bar
matchRegular expressions are provided by the regex crate, whose syntax is documented on docs.rs. Since regular expressions commonly use backslash escape sequences, consider using single-quoted string literals, which will pass slashes to the regex parser unmolested.
Conditional expressions short-circuit, which means they only evaluate one of their branches. This can be used to make sure that backtick expressions don't run when they shouldn't.
foo := if env_var("RELEASE") == "true" { `get-something-from-release-database` } else { "dummy-value" }Conditionals can be used inside of recipes:
bar foo:
echo {{ if foo == "bar" { "hello" } else { "goodbye" } }}Note the space after the final }! Without the space, the interpolation will be prematurely closed.
Multiple conditionals can be chained:
foo := if "hello" == "goodbye" {
"xyz"
} else if "a" == "a" {
"abc"
} else {
"123"
}
bar:
@echo {{foo}}$ just bar
abcExecution can be halted with the error function. For example:
foo := if "hello" == "goodbye" {
"xyz"
} else if "a" == "b" {
"abc"
} else {
error("123")
}
Which produce the following error when run:
error: Call to function `error` failed: 123
|
16 | error("123")
Variables can be overridden from the command line.
os := "linux"
test: build
./test --test {{os}}
build:
./build {{os}}$ just
./build linux
./test --test linuxAny number of arguments of the form NAME=VALUE can be passed before recipes:
$ just os=plan9
./build plan9
./test --test plan9Or you can use the --set flag:
$ just --set os bsd
./build bsd
./test --test bsdAssignments prefixed with the export keyword will be exported to recipes as environment variables:
export RUST_BACKTRACE := "1"
test:
# will print a stack trace if it crashes
cargo testParameters prefixed with a $ will be exported as environment variables:
test $RUST_BACKTRACE="1":
# will print a stack trace if it crashes
cargo testExported variables and parameters are not exported to backticks in the same scope.
export WORLD := "world"
# This backtick will fail with "WORLD: unbound variable"
BAR := `echo hello $WORLD`# Running `just a foo` will fail with "A: unbound variable"
a $A $B=`echo $A`:
echo $A $BWhen export is set, all just variables are exported as environment variables.
Environment variables from the environment are passed automatically to the recipes.
print_home_folder:
echo "HOME is: '${HOME}'"$ just
HOME is '/home/myuser'just will load environment variables from a .env file if dotenv-load is set. The variables in the file will be available as environment variables to the recipes. See dotenv-integration for more information.
Environment variables can be propagated to just variables using the functions env_var() and env_var_or_default().
See environment-variables.
Recipes may have parameters. Here recipe build has a parameter called target:
build target:
@echo 'Building {{target}}…'
cd {{target}} && makeTo pass arguments on the command line, put them after the recipe name:
$ just build my-awesome-project
Building my-awesome-project…
cd my-awesome-project && makeTo pass arguments to a dependency, put the dependency in parentheses along with the arguments:
default: (build "main")
build target:
@echo 'Building {{target}}…'
cd {{target}} && makeVariables can also be passed as arguments to dependencies:
target := "main"
_build version:
@echo 'Building {{version}}…'
cd {{version}} && make
build: (_build target)A command's arguments can be passed to dependency by putting the dependency in parentheses along with the arguments:
build target:
@echo "Building {{target}}…"
push target: (build target)
@echo 'Pushing {{target}}…'Parameters may have default values:
default := 'all'
test target tests=default:
@echo 'Testing {{target}}:{{tests}}…'
./test --tests {{tests}} {{target}}Parameters with default values may be omitted:
$ just test server
Testing server:all…
./test --tests all serverOr supplied:
$ just test server unit
Testing server:unit…
./test --tests unit serverDefault values may be arbitrary expressions, but concatenations or path joins must be parenthesized:
arch := "wasm"
test triple=(arch + "-unknown-unknown") input=(arch / "input.dat"):
./test {{triple}}The last parameter of a recipe may be variadic, indicated with either a + or a * before the argument name:
backup +FILES:
scp {{FILES}} [email protected]:Variadic parameters prefixed with + accept one or more arguments and expand to a string containing those arguments separated by spaces:
$ just backup FAQ.md GRAMMAR.md
scp FAQ.md GRAMMAR.md [email protected]:
FAQ.md 100% 1831 1.8KB/s 00:00
GRAMMAR.md 100% 1666 1.6KB/s 00:00Variadic parameters prefixed with * accept zero or more arguments and expand to a string containing those arguments separated by spaces, or an empty string if no arguments are present:
commit MESSAGE *FLAGS:
git commit {{FLAGS}} -m "{{MESSAGE}}"Variadic parameters can be assigned default values. These are overridden by arguments passed on the command line:
test +FLAGS='-q':
cargo test {{FLAGS}}{{…}} substitutions may need to be quoted if they contain spaces. For example, if you have the following recipe:
search QUERY:
lynx https://www.google.com/?q={{QUERY}}And you type:
$ just search "cat toupee"just will run the command lynx https://www.google.com/?q=cat toupee, which will get parsed by sh as lynx, https://www.google.com/?q=cat, and toupee, and not the intended lynx and https://www.google.com/?q=cat toupee.
You can fix this by adding quotes:
search QUERY:
lynx 'https://www.google.com/?q={{QUERY}}'Parameters prefixed with a $ will be exported as environment variables:
foo $bar:
echo $barNormal dependencies of a recipes always run before a recipe starts. That is to say, the dependee always runs before the depender. These dependencies are called "prior dependencies".
A recipe can also have subsequent dependencies, which run after the recipe and are introduced with an &&:
a:
echo 'A!'
b: a && c d
echo 'B!'
c:
echo 'C!'
d:
echo 'D!'…running b prints:
$ just b
echo 'A!'
A!
echo 'B!'
B!
echo 'C!'
C!
echo 'D!'
D!just doesn't support running recipes in the middle of another recipe, but you can call just recursively in the middle of a recipe. Given the following justfile:
a:
echo 'A!'
b: a
echo 'B start!'
just c
echo 'B end!'
c:
echo 'C!'…running b prints:
$ just b
echo 'A!'
A!
echo 'B start!'
B start!
echo 'C!'
C!
echo 'B end!'
B end!This has limitations, since recipe c is run with an entirely new invocation of just: Assignments will be recalculated, dependencies might run twice, and command line arguments will not be propagated to the child just process.
Recipes that start with #! are called shebang recipes, and are executed by
saving the recipe body to a file and running it. This lets you write recipes in
different languages:
polyglot: python js perl sh ruby
python:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
print('Hello from python!')
js:
#!/usr/bin/env node
console.log('Greetings from JavaScript!')
perl:
#!/usr/bin/env perl
print "Larry Wall says Hi!\n";
sh:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
hello='Yo'
echo "$hello from a shell script!"
nu:
#!/usr/bin/env nu
let hello = 'Yo'
echo $"($hello) from a shell script!"
ruby:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
puts "Hello from ruby!"$ just polyglot
Hello from python!
Greetings from JavaScript!
Larry Wall says Hi!
Yo from a shell script!
Hello from ruby!On Unix-like operating systems, including Linux and MacOS, shebang recipes are
executed by saving the recipe body to a file in a temporary directory, marking
the file as executable, and executing it. The OS then parses the shebang line
into a command line and invokes it, including the path to the file. For
example, if a recipe starts with #!/usr/bin/env bash, the final command that
the OS runs will be something like /usr/bin/env bash /tmp/PATH_TO_SAVED_RECIPE_BODY. Keep in mind that different operating systems
split shebang lines differently.
Windows does not support shebang lines. On Windows, just splits the shebang
line into a command and arguments, saves the recipe body to a file, and invokes
the split command and arguments, adding the path to the saved recipe body as
the final argument.
If you're writing a bash shebang recipe, consider adding set -euxo pipefail:
foo:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euxo pipefail
hello='Yo'
echo "$hello from Bash!"It isn't strictly necessary, but set -euxo pipefail turns on a few useful features that make bash shebang recipes behave more like normal, linewise just recipe:
-
set -emakesbashexit if a command fails. -
set -umakesbashexit if a variable is undefined. -
set -xmakesbashprint each script line before it's run. -
set -o pipefailmakesbashexit if a command in a pipeline fails. This isbash-specific, so isn't turned on in normal linewisejustrecipes.
Together, these avoid a lot of shell scripting gotchas.
On Windows, shebang interpreter paths containing a / are translated from Unix-style paths to Windows-style paths using cygpath, a utility that ships with Cygwin.
For example, to execute this recipe on Windows:
echo:
#!/bin/sh
echo "Hello!"The interpreter path /bin/sh will be translated to a Windows-style path using cygpath before being executed.
If the interpreter path does not contain a / it will be executed without being translated. This is useful if cygpath is not available, or you wish to pass a Windows-style path to the interpreter.
Recipe lines are interpreted by the shell, not just, so it's not possible to set just variables in the middle of a recipe:
foo:
x := "hello" # This doesn't work!
echo {{x}}It is possible to use shell variables, but there's another problem. Every recipe line is run by a new shell instance, so variables set in one line won't be set in the next:
foo:
x=hello && echo $x # This works!
y=bye
echo $y # This doesn't, `y` is undefined here!The best way to work around this is to use a shebang recipe. Shebang recipe bodies are extracted and run as scripts, so a single shell instance will run the whole thing:
foo:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euxo pipefail
x=hello
echo $xEach line of each recipe is executed by a fresh shell, so it is not possible to share environment variables between recipes.
Some tools, like Python's venv, require loading environment variables in order to work, making them challenging to use with just. As a workaround, you can execute the virtual environment binaries directly:
venv:
[ -d foo ] || python3 -m venv foo
run: venv
./foo/bin/python3 main.pyEach recipe line is executed by a new shell, so if you change the working directory on one line, it won't have an effect on later lines:
foo:
pwd # This `pwd` will print the same directory…
cd bar
pwd # …as this `pwd`!There are a couple ways around this. One is to call cd on the same line as the command you want to run:
foo:
cd bar && pwdThe other is to use a shebang recipe. Shebang recipe bodies are extracted and run as scripts, so a single shell instance will run the whole thing, and thus a pwd on one line will affect later lines, just like a shell script:
foo:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euxo pipefail
cd bar
pwdRecipe lines can be indented with spaces or tabs, but not a mix of both. All of a recipe's lines must have the same indentation, but different recipes in the same justfile may use different indentation.
Recipes without an initial shebang are evaluated and run line-by-line, which means that multi-line constructs probably won't do what you want.
For example, with the following justfile:
conditional:
if true; then
echo 'True!'
fiThe extra leading whitespace before the second line of the conditional recipe will produce a parse error:
$ just conditional
error: Recipe line has extra leading whitespace
|
3 | echo 'True!'
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^To work around this, you can write conditionals on one line, escape newlines with slashes, or add a shebang to your recipe. Some examples of multi-line constructs are provided for reference.
conditional:
if true; then echo 'True!'; ficonditional:
if true; then \
echo 'True!'; \
ficonditional:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
if true; then
echo 'True!'
fifor:
for file in `ls .`; do echo $file; donefor:
for file in `ls .`; do \
echo $file; \
donefor:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
for file in `ls .`; do
echo $file
donewhile:
while `server-is-dead`; do ping -c 1 server; donewhile:
while `server-is-dead`; do \
ping -c 1 server; \
donewhile:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
while `server-is-dead`; do
ping -c 1 server
donejust supports a number of useful command line options for listing, dumping, and debugging recipes and variable:
$ just --list
Available recipes:
js
perl
polyglot
python
ruby
$ just --show perl
perl:
#!/usr/bin/env perl
print "Larry Wall says Hi!\n";
$ just --show polyglot
polyglot: python js perl sh rubyRun just --help to see all the options.
Recipes and aliases whose name starts with a _ are omitted from just --list:
test: _test-helper
./bin/test
_test-helper:
./bin/super-secret-test-helper-stuff$ just --list
Available recipes:
testAnd from just --summary:
$ just --summary
testThe [private] attributemaster may also be used to hide recipes without needing to change the name:
[private]
foo:
bar:$ just --list
Available recipes:
barThis is useful for helper recipes which are only meant to be used as dependencies of other recipes.
A recipe name may be prefixed with @ to invert the meaning of @ before each line:
@quiet:
echo hello
echo goodbye
@# all done!Now only the lines starting with @ will be echoed:
$ j quiet
hello
goodbye
# all done!Shebang recipes are quiet by default:
foo:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo 'Foo!'$ just foo
Foo!Adding @ to a shebang recipe name makes just print the recipe before executing it:
@bar:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo 'Bar!'$ just bar
#!/usr/bin/env bash
echo 'Bar!'
Bar!just normally prints error messages when a recipe line fails. These error
messages can be suppressed using the [no-exit-message] attribute. You may find
this especially useful with a recipe that recipe wraps a tool:
git *args:
@git {{args}}$ just git status
fatal: not a git repository (or any of the parent directories): .git
error: Recipe `git` failed on line 2 with exit code 128Add the attribute to suppress the exit error message when the tool exits with a non-zero code:
[no-exit-message]
git *args:
@git {{args}}$ just git status
fatal: not a git repository (or any of the parent directories): .gitThe --choose subcommand makes just invoke a chooser to select which recipes to run. Choosers should read lines containing recipe names from standard input and print one or more of those names separated by spaces to standard output.
Because there is currently no way to run a recipe that requires arguments with --choose, such recipes will not be given to the chooser. Private recipes and aliases are also skipped.
The chooser can be overridden with the --chooser flag. If --chooser is not given, then just first checks if $JUST_CHOOSER is set. If it isn't, then the chooser defaults to fzf, a popular fuzzy finder.
Arguments can be included in the chooser, i.e. fzf --exact.
The chooser is invoked in the same way as recipe lines. For example, if the chooser is fzf, it will be invoked with sh -cu 'fzf', and if the shell, or the shell arguments are overridden, the chooser invocation will respect those overrides.
If you'd like just to default to selecting recipes with a chooser, you can use this as your default recipe:
default:
@just --chooseIf the first argument passed to just contains a /, then the following occurs:
-
The argument is split at the last
/. -
The part before the last
/is treated as a directory.justwill start its search for thejustfilethere, instead of in the current directory. -
The part after the last slash is treated as a normal argument, or ignored if it is empty.
This may seem a little strange, but it's useful if you wish to run a command in a justfile that is in a subdirectory.
For example, if you are in a directory which contains a subdirectory named foo, which contains a justfile with the recipe build, which is also the default recipe, the following are all equivalent:
$ (cd foo && just build)
$ just foo/build
$ just foo/just looks for justfiles named justfile and .justfile, which can be used to keep a justfile hidden.
By adding a shebang line to the top of a justfile and making it executable, just can be used as an interpreter for scripts:
$ cat > script <<EOF
#!/usr/bin/env just --justfile
foo:
echo foo
EOF
$ chmod +x script
$ ./script foo
echo foo
fooWhen a script with a shebang is executed, the system supplies the path to the script as an argument to the command in the shebang. So, with a shebang of #!/usr/bin/env just --justfile, the command will be /usr/bin/env just --justfile PATH_TO_SCRIPT.
With the above shebang, just will change its working directory to the location of the script. If you'd rather leave the working directory unchanged, use #!/usr/bin/env just --working-directory . --justfile.
Note: Shebang line splitting is not consistent across operating systems. The previous examples have only been tested on macOS. On Linux, you may need to pass the -S flag to env:
#!/usr/bin/env -S just --justfile
default:
echo fooThe --dump command can be used with --dump-format json to print a JSON representation of a justfile. The JSON format is currently unstable, so the --unstable flag is required.
If a recipe is not found in a justfile and the fallback setting is set,
just will look for justfiles in the parent directory and up, until it
reaches the root directory. just will stop after it reaches a justfile in
which the fallback setting is false or unset.
This feature is currently unstable, and so must be enabled with the
--unstable flag.
As an example, suppose the current directory contains this justfile:
set fallback
foo:
echo fooAnd the parent directory contains this justfile:
bar:
echo bar$ just --unstable bar
Trying ../justfile
echo bar
barGiven this justfile:
foo argument:
touch {{argument}}The following command will create two files, some and argument.txt:
$ just foo "some argument.txt"The users shell will parse "some argument.txt" as a single argument, but when just replaces touch {{argument}} with touch some argument.txt, the quotes are not preserved, and touch will receive two arguments.
There are a few ways to avoid this: quoting, positional arguments, and exported arguments.
Quotes can be added around the {{argument}} interpolation:
foo argument:
touch '{{argument}}'This preserves just's ability to catch variable name typos before running, for example if you were to write {{argument}}, but will not do what you want if the value of argument contains single quotes.
The positional-arguments setting causes all arguments to be passed as positional arguments, allowing them to be accessed with $1, $2, …, and $@, which can be then double-quoted to avoid further splitting by the shell:
set positional-arguments
foo argument:
touch "$1"This defeats just's ability to catch typos, for example if you type $2, but works for all possible values of argument, including those with double quotes.
All arguments are exported when the export setting is set:
set export
foo argument:
touch "$argument"Or individual arguments may be exported by prefixing them with $:
foo $argument:
touch "$argument"This defeats just's ability to catch typos, for example if you type $argumant, but works for all possible values of argument, including those with double quotes.
There are a number of ways to configure the shell for linewise recipes, which are the default when a recipe does not start with a #! shebang. Their precedence, from highest to lowest, is:
- The
--shelland--shell-argcommand line options. Passing either of these will causejustto ignore any settings in the current justfile. set windows-shell := [...]set windows-powershell(deprecated)set shell := [...]
Since set windows-shell has higher precedence than set shell, you can use set windows-shell to pick a shell on Windows, and set shell to pick a shell for all other platforms.
A changelog for the latest release is available in CHANGELOG.md. Changelogs for previous releases are available on the releases page. just --changelog can also be used to make a just binary print its changelog.
Tools that pair nicely with just include:
watchexec— a simple tool that watches a path and runs a command whenever it detects modifications.
For lightning-fast command running, put alias j=just in your shell's configuration file.
In bash, the aliased command may not keep the shell completion functionality described in the next section. Add the following line to your .bashrc to use the same completion function as just for your aliased command:
complete -F _just -o bashdefault -o default jShell completion scripts for Bash, Zsh, Fish, PowerShell, and Elvish are available in the completions directory. Please refer to your shell's documentation for how to install them.
The just binary can also generate the same completion scripts at runtime, using the --completions command:
$ just --completions zsh > just.zshmacOS Note: Recent versions of macOS use zsh as the default shell. If you use Homebrew to install just, it will automatically install the most recent copy of the zsh completion script in the Homebrew zsh directory, which the built-in version of zsh doesn't know about by default. It's best to use this copy of the script if possible, since it will be updated whenever you update just via Homebrew. Also, many other Homebrew packages use the same location for completion scripts, and the built-in zsh doesn't know about those either. To take advantage of just completion in zsh in this scenario, you can set fpath to the Homebrew location before calling compinit. Note also that Oh My Zsh runs compinit by default. So your .zshrc file could look like this:
# Init Homebrew, which adds environment variables
eval "$(brew shellenv)"
fpath=($HOMEBREW_PREFIX/share/zsh/site-functions $fpath)
# Then choose one of these options:
# 1. If you're using Oh My Zsh, you can initialize it here
# source $ZSH/oh-my-zsh.sh
# 2. Otherwise, run compinit yourself
# autoload -U compinit
# compinitA non-normative grammar of justfiles can be found in GRAMMAR.md.
Before just was a fancy Rust program it was a tiny shell script that called make. You can find the old version in extras/just.sh.
If you want some recipes to be available everywhere, you have a few options.
First, create a justfile in ~/.user.justfile with some recipes.
If you want to call the recipes in ~/.user.justfile by name, and don't mind creating an alias for every recipe, add the following to your shell's initialization script:
for recipe in `just --justfile ~/.user.justfile --summary`; do
alias $recipe="just --justfile ~/.user.justfile --working-directory . $recipe"
doneNow, if you have a recipe called foo in ~/.user.justfile, you can just type foo at the command line to run it.
It took me way too long to realize that you could create recipe aliases like this. Notwithstanding my tardiness, I am very pleased to bring you this major advance in justfile technology.
If you'd rather not create aliases for every recipe, you can create a single alias:
alias .j='just --justfile ~/.user.justfile --working-directory .'Now, if you have a recipe called foo in ~/.user.justfile, you can just type .j foo at the command line to run it.
I'm pretty sure that nobody actually uses this feature, but it's there.
¯\_(ツ)_/¯
You can customize the above aliases with additional options. For example, if you'd prefer to have the recipes in your justfile run in your home directory, instead of the current directory:
alias .j='just --justfile ~/.user.justfile --working-directory ~'The following export statement gives just recipes access to local Node module binaries, and makes just recipe commands behave more like script entries in Node.js package.json files:
export PATH := "./node_modules/.bin:" + env_var('PATH')There is no shortage of command runners! Some more or less similar alternatives to just include:
- make: The Unix build tool that inspired
just. There are a few different modern day descendents of the originalmake, including FreeBSD Make and GNU Make. - task: A YAML-based command runner written in Go.
- maid: A Markdown-based command runner written in JavaScript.
- microsoft/just: A JavasScript-based command runner written in JavaScript.
- cargo-make: A command runner for Rust projects.
- mmake: A wrapper around
makewith a number of improvements, including remote includes. - robo: A YAML-based command runner written in Go.
- mask: A Markdown-based command runner written in Rust.
- makesure: A simple and portable command runner written in AWK and shell.
- haku: A make-like command runner written in Rust.
just welcomes your contributions! just is released under the maximally permissive CC0 public domain dedication and fallback license, so your changes must also be released under this license.
Janus is a tool that collects and analyzes justfiles, and can determine if a new version of just breaks or changes the interpretation of existing justfiles.
Before merging a particularly large or gruesome change, Janus should be run to make sure that nothing breaks. Don't worry about running Janus yourself, Casey will happily run it for you on changes that need it.
The minimum supported Rust version, or MSRV, is Rust 1.47.0.
New releases of just are made frequently so that users quickly get access to new features.
Release commit messages use the following template:
Release x.y.z
- Bump version: x.y.z → x.y.z
- Update changelog
- Update changelog contributor credits
- Update dependencies
- Update man page
- Update version references in readme
make has some behaviors which are confusing, complicated, or make it unsuitable for use as a general command runner.
One example is that under some circumstances, make won't actually run the commands in a recipe. For example, if you have a file called test and the following makefile:
test:
./testmake will refuse to run your tests:
$ make test
make: `test' is up to date.make assumes that the test recipe produces a file called test. Since this file exists and the recipe has no other dependencies, make thinks that it doesn't have anything to do and exits.
To be fair, this behavior is desirable when using make as a build system, but not when using it as a command runner. You can disable this behavior for specific targets using make's built-in .PHONY target name, but the syntax is verbose and can be hard to remember. The explicit list of phony targets, written separately from the recipe definitions, also introduces the risk of accidentally defining a new non-phony target. In just, all recipes are treated as if they were phony.
Other examples of make's idiosyncrasies include the difference between = and := in assignments, the confusing error messages that are produced if you mess up your makefile, needing $$ to use environment variables in recipes, and incompatibilities between different flavors of make.
cargo build scripts have a pretty specific use, which is to control how cargo builds your Rust project. This might include adding flags to rustc invocations, building an external dependency, or running some kind of codegen step.
just, on the other hand, is for all the other miscellaneous commands you might run as part of development. Things like running tests in different configurations, linting your code, pushing build artifacts to a server, removing temporary files, and the like.
Also, although just is written in Rust, it can be used regardless of the language or build system your project uses.
I personally find it very useful to write a justfile for almost every project, big or small.
On a big project with multiple contributors, it's very useful to have a file with all the commands needed to work on the project close at hand.
There are probably different commands to test, build, lint, deploy, and the like, and having them all in one place is useful and cuts down on the time you have to spend telling people which commands to run and how to type them.
And, with an easy place to put commands, it's likely that you'll come up with other useful things which are part of the project's collective wisdom, but which aren't written down anywhere, like the arcane commands needed for some part of your revision control workflow, install all your project's dependencies, or all the random flags you might need to pass to the build system.
Some ideas for recipes:
-
Deploying/publishing the project
-
Building in release mode vs debug mode
-
Running in debug mode or with logging enabled
-
Complex git workflows
-
Updating dependencies
-
Running different sets of tests, for example fast tests vs slow tests, or running them with verbose output
-
Any complex set of commands that you really should write down somewhere, if only to be able to remember them
Even for small, personal projects it's nice to be able to remember commands by name instead of ^Reverse searching your shell history, and it's a huge boon to be able to go into an old project written in a random language with a mysterious build system and know that all the commands you need to do whatever you need to do are in the justfile, and that if you type just something useful (or at least interesting!) will probably happen.
For ideas for recipes, check out this project's justfile, or some of the justfiles out in the wild.
Anyways, I think that's about it for this incredibly long-winded README.
I hope you enjoy using just and find great success and satisfaction in all your computational endeavors!
😸