Struggling with automated testing?
Is writing reliable, maintainable tests for your Spring Boot applications more of an afterthought than an integrated part of your workflow?
Are you tired of:
- Spending countless hours debugging production issues that should have been caught in testing?
- Feeling anxious about deploying on Fridays because your test coverage isn't comprehensive?
- Wrestling with complex microservice architectures that are difficult to test properly?
- Copying and pasting test code from Stack Overflow without understanding the underlying principles?
- Missing deadlines because of unexpected bugs and regressions?
- Mindlessly applying cargo cult testing practices that don't fit your application's needs?
The Testing Spring Boot Applications Masterclass transforms you from feeling uncertain about your application's reliability to being confident in your testing strategy, making you a more productive, efficient, and valuable developer.
Automated testing is (unfortunately) often neglected, but it’s the key to building robust, reliable Spring Boot applications and shipping features with confidence.
This Masterclass will teach you everything you need to know about testing Spring Boot applications—from unit tests to end-to-end tests—so you can stop guessing and start delivering with peace of mind.
What You’ll Gain:
- Confidence in Every Deployment: Push to production—even on Fridays—without breaking a sweat.
- Master Testing Best Practices: Learn to test every layer: databases, messaging, HTTP communication, and more.
- Efficiency and Joy in Testing: Testing doesn’t have to be a frustrating chore. Let’s make it fun, fast, and effective!
- Production-Grade Application: You'll work with a real microservice architecture that mirrors actual business applications, not oversimplified examples.
- Comprehensive Coverage: From basic unit tests to complex integration scenarios, you'll learn testing strategies for every layer of your application.
- Practical Approach: Every concept is taught through hands-on examples that you can immediately apply to your projects.
Throughout the course you'll learn how to effectively use well-known testing libraries like JUnit 5, Mockito, Awaitility, LocalStack, Testcontainers, Selenide, WireMock, MockWebServer, and JsonPath.
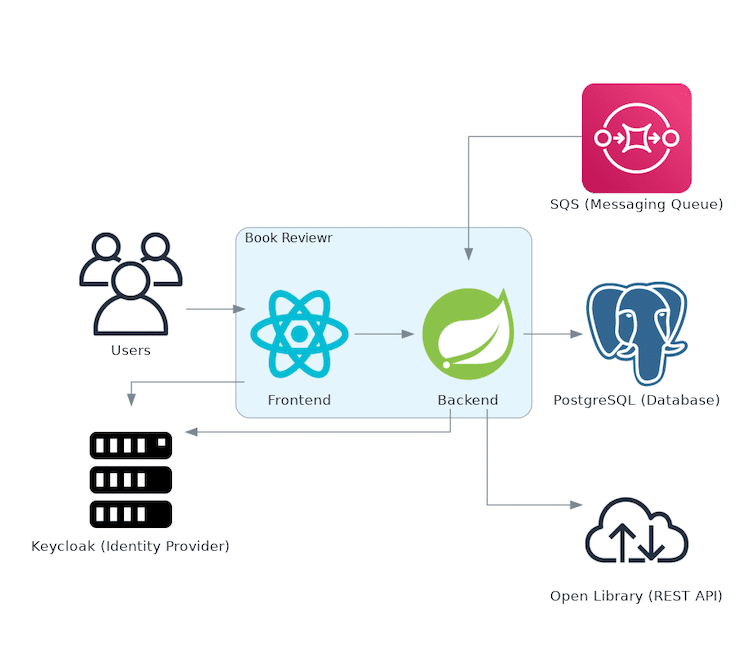
To mirror a typical modern microservice architecture, the demo application uses the following tech stack and infrastructure components:
- Keycloak (open source identity and access management solution) to secure parts of the frontend and backend with OpenID Connect/OAuth 2.0
- Amazon SQS (Simple Queuing Service) to demonstrate testing asynchronous message processing
- PostgreSQL (RDBMS) to demonstrate testing with a relational database
- Single Page Application Frontend with React and TypeScript
- Spring Boot backend with Java
- Dependency on a remote REST API to demonstrate testing HTTP communication
Even though the technical setup for your day-to-day projects might differ, the testing recipes you'll learn are generic, and you can easily apply them for your tech stacks.
From Wim Deblauwe:
Philip has made a fantastic overview of the full testing landscape of Spring. The videos are clear and explain details and common pitfalls in great depth. Looking forward to the rest of the course.
From Siva:
I got an opportunity to review the course I find it wonderful for learning how to test Spring Boot applications leveraging modern testing frameworks and libraries....
I would highly recommend Masterclass for anybody working with Spring Boot applications.
From Anton Ždanov:
For me testing a Spring application seemed like a challenge involving digging through numerous blog posts, documentation for JUnit, Mockito, and Spring Testing Reference which provide valuable information but are spread out and don't necessarily show the best practices.
After watching the Testing Spring Boot Applications Masterclass course I feel more confident in writing different types of tests for my apps. The course, videos, and the GitHub repository were of invaluable use to me demonstrating various testing mechanics the Spring ecosystem provides, and I will keep referencing the course materials in the future.
P.S. The application that is tested in the course is quite complex and covers a lot of real-world testing challenges one might encounter, which I found immensely useful for seeing the bigger picture.
» Enroll now for the Testing Spring Boot Applications Masterclass.
💡 Money-back guarantee: Not satisfied? Get a full refund within 60 days, no questions asked.
Mandatory requirements:
- Java 21 (JDK flavour (OpenJDK/Azul/Oracle) does not matter). For the correct Java version setup I can recommend JEnv (Mac/Linux) and the Maven Toolchains Plugin (Windows)
$ java -version
openjdk version "21.0.1" 2023-10-17 LTS
OpenJDK Runtime Environment Temurin-21.0.1+12 (build 21.0.1+12-LTS)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM Temurin-21.0.1+12 (build 21.0.1+12-LTS, mixed mode)
- Docker Engine (Community Edition is enough) and Docker Compose:
$ docker version
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 20.10.6
API version: 1.41
Go version: go1.13.15
Git commit: 370c289
Built: Fri Apr 9 22:47:17 2021
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Context: default
Experimental: true
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 20.10.6
API version: 1.41 (minimum version 1.12)
Go version: go1.13.15
Git commit: 8728dd2
Built: Fri Apr 9 22:45:28 2021
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
$ docker-compose version
docker-compose version 1.26.2, build eefe0d31
docker-py version: 4.2.2
CPython version: 3.7.7
OpenSSL version: OpenSSL 1.1.1g 21 Apr 2020
Optional requirements:
- Maven >= 3.6 (the project also includes the Maven Wrapper).
When using Maven from the command line, make sure ./mvnw -version reports the correct Java version:
$ ./mvnw -version
Apache Maven 3.8.4 (9b656c72d54e5bacbed989b64718c159fe39b537)
Maven home: /home/rieckpil/.m2/wrapper/dists/apache-maven-3.8.4-bin/52ccbt68d252mdldqsfsn03jlf/apache-maven-3.8.4
Java version: 17.0.1, vendor: Eclipse Adoptium, runtime: /usr/lib/jvm/jdk-17.0.1+12
Default locale: en_US, platform encoding: UTF-8
OS name: "linux", version: "5.4.0-92-generic", arch: "amd64", family: "unix"
- IntelliJ IDEA or any IDE/Code Editor (Eclipse, NetBeans, Code, Atom, etc.)
Assuming your local setups meets all requirements as stated above, you can now start the application:
- Make sure your Docker Engine is up- and running
- Start the required infrastructure components with
docker-compose up - Run the application with
./mvnw spring-boot:runor inside your IDE - Access http://localhost:8080 for the application frontend
- (Optional) Access http://localhost:8888 for the Keycloak Admin interface
Valid application users:
- duke (password
dukeduke) - mike (password
mikemike)
Replace ./mvnw with mvnw.cmd if you're running on Windows.
Run all unit tests (Maven Surefire Plugin): ./mvnw test
Run all integration & web tests (Maven Failsafe plugin):
- Make sure no conflicting Docker containers are currently running:
docker ps - Make sure the test classes have been compiled and the frontend has been build and is part of the
target/classes/publicfolder:./mvnw package -DskipTest - Execute
./mvnw failsafe:integration-test failsafe:verify
Run all tests together:
- Make sure no conflicting Docker container is currently running:
docker ps - Execute
./mvnw verify
Skip all tests (don't do this at home):
- Execute
./mvnw -DskipTests=true verify
See this GitHub issue for resolving it.
For skipping the frontend build, add -Dskip.installnodenpm -Dskip.npm to your Maven command, e.g., ./mvnw test -Dskip.installnodenpm -Dskip.npm.
You can pass -DskipTests to ./mvnw package if you experience test failures: ./mvnw package -DskipTests to build the application without running any unit test.
Next, make sure you have the latest version of this project (run git pull) and ensure the build status is green.
If you still encounter any test failures, please create an issue and include information about your environment.
Adjust the docker-compose.yml file and remove the setup to import Keycloak configuration on the startup:
version: '3.8'
services:
# ...
keycloak:
image: quay.io/keycloak/keycloak:18.0.0-legacy
environment:
- KEYCLOAK_USER=keycloak
- KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD=keycloak
- DB_VENDOR=h2
ports:
- "8888:8080"Next, start everything with docker-compose up and watch the following video to configure Keycloak manually.