Deniz Engin, Anıl Genc, Hazım Kemal Ekenel
This paper proposes an end-to-end network for single-image dehazing problems, which is an enhanced version of the cycleGAN method, i.e, this also works on unpaired images in the datasets. The provided method is better than the state of the art methods for single-image dehazing which use the atmospheric scattering model.
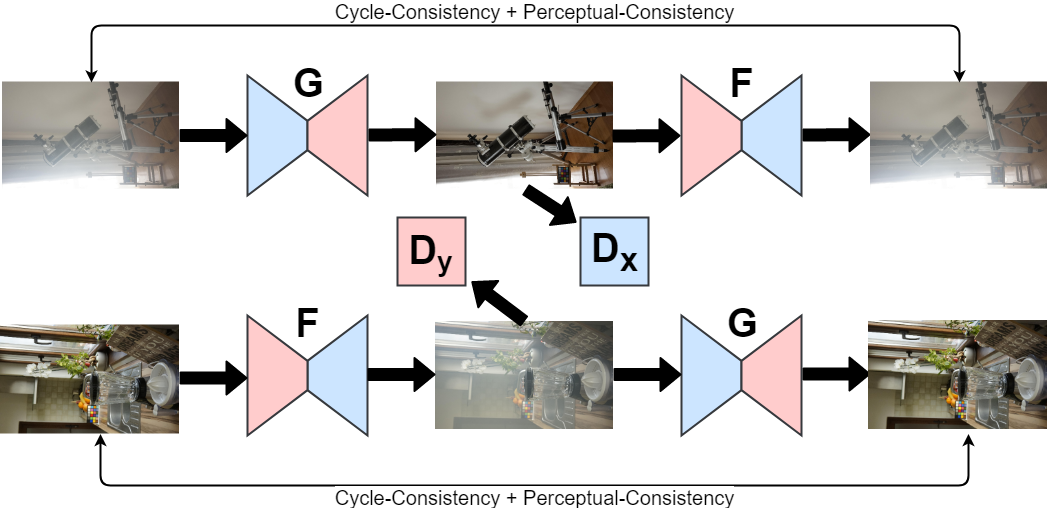
- The addition of perceptual cycle loss in the original cycleGAN architecture, which compares images in a feature space rather than the pixel space.
-
Since the paper is adopting the original cycleGAN architecture, hence dataset of unpaired images is used.
-
This method does not rely on calculating the parameters of the atmospheric scattering model (which is used in the earlier methods).
-
To upscale the output images, Laplacian pyramid is used instead of the bicubic-upscaling method to get a higher resolution and sharp image for better haze free images.
-
Due to its cyclic structure, the model turns out to be generalized and can be used for other datasets.
- The CycleGAN model architecture is adapted from the original CycleGAN paper, with the addition of a cycle perceptual loss inspired by the EnhanceNet paper. To achieve high-resolution output images, the model utilizes the Laplacian pyramid method.
-
The model achieves very significant results even in the absence of the ground-truth images, unlike the state of the art methods.
-
The is a generalizable model as it learns the dehazing task rather than overfitting on the data.
-
Higher weightage is given to cycle consistency loss as compared to perceptual cycle loss, as higher weightage to the perceptual cycle loss causes loss of color information after dehazing.
-
Implementation:- https://github.com/engindeniz/Cycle-Dehaze/