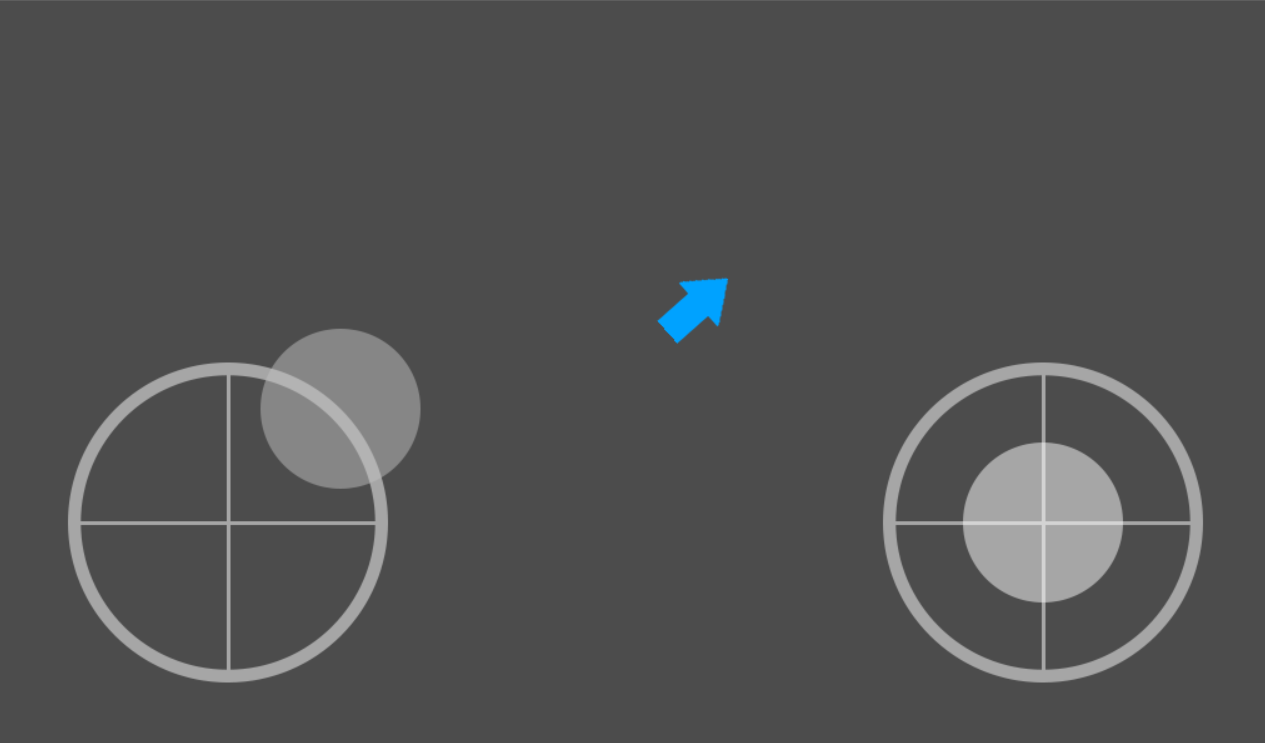
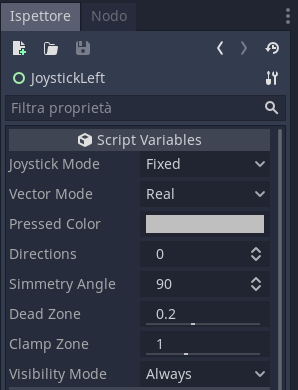
A simple virtual joystick for touchscreens, for both 2D and 3D games, with useful options.
Made with Godot Engine: https://godotengine.org
-
Joystick mode:
- Fixed: The joystick doesn't move.
- Dynamic: Every time the joystick area is pressed, the joystick position is set on the touched position.
- Following: If the finger moves outside the joystick background, the joystick follows it.
-
Vector mode:
- Real: return a vector with a lenght beetween 0 and 1; useful for implementing different velocity or acceleration.
- Normalized: return a normalized vector.
-
Directions: The number of directions, e.g. a D-pad is joystick with 4 directions, keep 0 for a free joystick.
-
Simmetry Angle: the angle of simmetry of the directions.
-
Dead zone: If the handle is inside this range, in proportion to the background size, the output is zero.
-
Clamp zone: The max distance the handle can reach, in proportion to the background size.
- The Control parent of the joystick is the area in which the joystick can move in Dynamic or Following mode.
- For moving the joystick inside is area, select it, right click and turn on "Editable Children" and simply move the 'Background' node. - With "Editable Children" turned on you can also edit the joystick textures and colors.
- An example scene is provided in the "Test" folder.
- To be able to use the joystick with the mouse, you have to go to Project settings -> Input Devices -> Pointing, and turn on the option "emulate touch from mouse".
Create a CanvasLayer node and name it "UI", it'll contain all the UI elements, then add the Joystick scene as a child of the UI node and move it where you prefer (remember to turn on "Editable Children").