# showing coefficients and stuff of a model in a nice way
model %>% tidy()# nice way to chqnge color aesthetic and do it for a log normal distributed data
scale_color_gradient2(low = "blue",
high = "red",
midpoint = log10(median(maryland_bridges$avg_daily_traffic)),
trans = "log10",
labels = comma_format()) +# replacing NA with something else
maryland_bridges %>%
replace_na(list(responsibility = "Other")u)# you can mutate things inside count
baltimore_bridges %>%
count(decade = 10 * (yr_built %/% 10))# showing correlation inside a column
# id: persons id
# value: here type of food
# what food types are correlated with other food types
library(widyr)
food_gathered %>%
pairwise_cor(value, id, sort = TRUE)# removes value entries that are in c()
df %>%
filter(!value %in% c("None", "Other (please specify)"))# removes any number inside "name"
df %>%
mutate(name = str_remove(name, "\\d+"))# filter every second year
filter(year %% 2 == 0) # filter only years like 1980, 1990 ...
filter(year %% 10 == 0) # THE WORLD
malaria_spread %>%
inner_join(maps::iso3166 %>%
# do we keep only mapname here
select(a3, mapname), by = c(code = "a3")) %>%
# this will keep all regions
# keeps all observations in y
right_join(world, by = c(mapname = "region")) %>%
ggplot(aes(long, lat, group = group, fill = Y2015)) +
geom_polygon() +
ltheme_void()# dispay the datasets contained in a packagedata(package = "datasets")
# selecting inside a join and keep only columns that are needed
malaria_spread %>%
inner_join(maps::iso3166 %>%
select(a3, mapname), by = c(code = "a3"))# not sure what this is but some geography sugar
tibble::as.tibble(map_data("world"))# remove only a specified file
for (fl in list.files(getwd(), recursive = TRUE)) {
if (grepl(pattern = ".icloud", x = fl) == TRUE) {
file.remove(fl)
}
}kenya_pr %>%
# %/% truncates the last digit
mutate(decade = 10 * (year_start %/% 10))malaria_in_process %>%
# grabbing 6 unique countries
filter(country %in% sample(unique(country), 6))
# ggplot2::map_data("world") %>% tibble() %>% filter(region == "Kenya")
kenya_pr %>%
# %/% truncates the last digit
mutate(decade = 10 * (year_start %/% 10)) %>%
# niiiice! This will show the highest pr´s on top of the graph
# this will arrange from lowest to highest and plot highest last
arrange(pr) %>%
ggplot(aes(longitude, latitude, colour = pr)) +
geom_point() +
borders("world", regions = "Kenya") +
scale_color_gradient2(low = "blue",
high = "red",
midpoint = .5,
labels = percent_format()) +
facet_wrap(~ decade) +
theme_void() +
coord_map() +
# changes the name of the legend
labs(color = "Prevalence")Change all numeric values in a dataframe to NA if they are equal to -9999
us_wind <- us_wind %>%
mutate_if(is.numeric, ~ ifelse(. == -9999, NA, .))To the color aesthetic and see the 6 lumped categories we need some R magic. Without arranging the data, the Other category would be on top and will overlay the other categories in the plot.
us_wind %>%
filter(!t_state %in% c("AK", "HI", "GU", "PR")) %>%
# FALSE comes before TRUE (in this case Other is on top)
# fct_lumped data needs to be arranged so that TRUE comes on the top of the table
mutate(p_name = fct_lump(p_name, 6)) %>%
arrange(p_name != "Other") %>%
filter(xlong < 100) %>%
ggplot(aes(xlong, ylat, color = p_name)) +
borders("state") +
geom_point() +
coord_map() +
theme_void()Not useful but interesting. How many times a package was downloaded from CRAN in the last week
cranlogs::cran_downloads(packages = "tidyverse", when = "last-week")Displaying time on the x axis TidyTuesday (minute 40:00)
# gap was produced by the line
# mutate(gap = datetime - lag(datetime))
# lag in seconds between downloads
r_downloads_gaps %>%
count(country, gap) %>%
# filter(country == "United States") %>%
ggplot(aes(gap)) +
geom_histogram() +
# clear bimodal log normal distribution
# scale_x_log10()
scale_x_log10(breaks = 60 ^ (0:4),
labels = c("Second", "Minute", "Hour", "2.5 Days", "120 Days"))Another TidyTuesday pearl (minute 9:00)
# this is a biggy!
# cool way to display weekdays
# not sure what group argument does but without it doesnt work
# AAAAAND mutate things inside group_by method is really cool
r_downloads_year %>%
count(date) %>%
# there will be a lot data for every weekday
group_by(weekday = wday(date, label = TRUE)) %>%
mutate(average = mean(n)) %>%
ggplot(aes(weekday, average)) +
geom_line(group = 1) +
expand_limits(y = 0)One lm smooth line for all genres vs. separate lm line for every group
# one line
movie_profit %>%
filter(release_date >= "1990-01-01",
profit_ratio >= .01) %>%
ggplot(aes(release_date, profit_ratio)) +
geom_point(aes(color = genre)) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", group = 1) +
geom_text(aes(label = movie), vjust = 1, hjust = 1, check_overlap = TRUE) +
scale_y_log10(labels = function(x) paste0(x, "X"), breaks = c(.1, 1, 10, 100))
# many lines
movie_profit %>%
filter(release_date >= "1990-01-01",
profit_ratio >= .01) %>%
ggplot(aes(release_date, profit_ratio)) +
geom_point(aes(color = genre)) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm") +
geom_text(aes(label = movie), vjust = 1, hjust = 1, check_overlap = TRUE) +
scale_y_log10(labels = function(x) paste0(x, "X"), breaks = c(.1, 1, 10, 100))Converting a random year to a corresponding decade
yrs <- tribble(~year,
1234,
1345,
1235,
1344,
1899)
# first we divide the year by 10 and floor it
# this way we get rid of the year and keep the integer of the decade
# by multiplying by 10 we get the decade
yrs_decade <- yrs %>%
mutate(decade = 10 * floor(year/10))# reversing the order of rows
# row_number() should be used inside mutate, filter or some other dplyr verb (I forgot which one)
# otherwise it returns numbers I don´t understand
arrange(desc(row_number())) This video is the best example of merging and pulling that I have seen so far.
I am stuck again while trying to move a cloned repository that I found on the internet (a copy of a book coded in bookdown) to a repository I created on Github. First of all I deleted the remotes that came with the cloned repository (didn`t know that remotes need to be deleted) and added new remote "pointer" that where the url of my new repository.
# shows the remotes
git remote -vI created a new branch brach_test with the git branch branch_test command. And checked out into it with git checkout brach_test. I pushed the branch with git push branch_test but needed to set the remote as upstream, with git push --set-upstream origin branch_test. Not entirely sure why I needed to do this and not but ok let´s where this will go.
UPDATE (05.08.24)
I don´t thing the steps above are helful. I decided to clone my own new repository and edits its remotes with this command.
# here I add to my local repository an additional remote poiter and give it a short name `book`
git remote add book https://github.com/rstudio/bookdown-demo.git
# now we see two remotes in my local repository
git remote -v
# book https://github.com/rstudio/bookdown-demo.git (fetch)
# book https://github.com/rstudio/bookdown-demo.git (push)
# origin https://github.com/GrigorijSchleifer/Medizinische-Informatik.git (fetch)
# origin https://github.com/GrigorijSchleifer/Medizinische-Informatik.git (push)Next, I fetched the content from the bookdown-demo to my local repository.
# the pointer to the remote of the bookdown-demo is named book
# this brings content, branches, commits from this repository to my local ropositors
git fetch bookThe next step that solved the headache was to merge the bookdown-demo on main. Or the other way around (main from my own repository on the tip of book/main). I am still confused what the correct order of git merge should be. And another important step was to allow the merge of unrelated histories. I think I know what the meaning of this flag is. Becaus my own, and freshly created repository is unrelated to the bookdown-demo repo, the histories are absolutely unrelated and git´s default behaviour is to prevent the merge of unrelated histories. The command I used is:
# because we have different conten in README there is a conflict
git merge main book/main --allow-unrelated-histories
# Auto-merging README.md
# CONFLICT (add/add): Merge conflict in README.md
# Recorded preimage for 'README.md'
# Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.# NOT CLEAR
git commit -m "fatal: You have not concluded your merge (MERGE_HEAD exists)"
# Recorded preimage for 'README.md'
# [main 3af470e] fatal: You have not concluded your merge (MERGE_HEAD exists)
# NOT CLEAR
git merge main book --allow-unrelated-histories
# merge: book - not something we can merge` This code creates two plots: one with a normal y-axis and another with a logarithmic y-axis. The logarithmic scale helps to better visualize the exponential relationship by compressing the y-axis.
# Create data frame with exponential relationship
df_exp <- data.frame(
normal = c(1:100),
exp = exp(1:100)
)# Plot with normal y-axis
df_exp %>%
ggplot(aes(normal, exp)) +
geom_point()# Plot with logarithmic y-axis
df_exp %>%
ggplot(aes(normal, exp)) +
geom_point() +
scale_y_log10()First encounter of the pipe operator behaving weirdly (something with left and right)
major_processed |>
select(Major, Total, ShareWomen, Sample_size, Median) %>%
lm(Median ~ ShareWomen, data = ., weights = Sample_size)# facet_grid() forms a matrix of panels defined by row and column faceting variables. It is most useful when you have two discrete variables,
ggplot(mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_grid(drv ~ cyl)# This vignette summarises the various formats that grid drawing functions take. Most of this information is available scattered throughout the R documentation. This appendix brings it all together in one place.
vignette("ggplot2-specs")# Load built-in datasets and show what is available
data()# move new column before existing column 1
mutate(new_column = x - y, .before = 1)
# move new column before specified column by name
mutate(new_column = x - y, .before = soneColumnName)
# Example
nycflights13::flights |>
mutate(
gain = dep_delay - arr_delay,
speed = distance / air_time * 60,
.before = 1,
.keep = "used"
)# modulo: result is the remainder 1
7 %% 2
# regular division: result is 3.5
7 / 2
# integer division: result is 3
7 %/% 2# returns the directory (all parts) of a file path, but not the file name
dirname(file.path("","p1","p2","p3", "filename"))
# "/p1/p2/p3"
# returns the base (last part) of a file path
basename(file.path("","p1","p2","p3", "filename"))
# "filename"RStudio: Switching between the console and the code editor without using your mouse (Mac)
ctrl 1 (for code editor)
ctrl 2 (for console)Visualising exponential relationships
# exponential relationship
df_exp <- data.frame(
normal = c(1:100),
exp = exp(1:100)
)
# normal logs view
df_exp %>%
ggplot(aes(normal, exp)) +
geom_point()
# y axis log10
df_exp %>%
ggplot(aes(normal, exp)) +
geom_point() +
scale_y_log10()

First encounter of the pipe operator behaving weirdly (something with left and right)
major_processed |>
select(Major, Total, ShareWomen, Sample_size, Median) %>%
lm(Median ~ ShareWomen, data = ., weights = Sample_size)# facet_grid() forms a matrix of panels defined by row and column faceting variables. It is most useful when you have two discrete variables,
ggplot(mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
facet_grid(drv ~ cyl)# This vignette summarises the various formats that grid drawing functions take. Most of this information is available scattered throughout the R documentation. This appendix brings it all together in one place.
vignette("ggplot2-specs")When you specify a color within aes(), ggplot2 interprets it as a mapping to a variable in the data, not a fixed color. Since there is no variable named "blue", ggplot2 defaults to a standard color (pink).
# will not work
ggplot(mpg) +
geom_point(aes(x = displ, y = hwy, color = "blue"))
# will not work
ggplot(mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point(aes(color = "blue"))
# will work
ggplot(mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point(color = "blue")
# will work
ggplot(mpg) +
geom_point(aes(x = displ, y = hwy), color = "blue")
# will work
ggplot(mpg, aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point(color = "blue")Shows all current libraries on my machine
# https://rstudio.github.io/renv/articles/renv.html
.libPaths()
# list all packages in libraries on my machine
lapply(.libPaths(), list.files)
# which repositories are currently set up in your session
getOption("repos")
# will create a snapshot of all packages and their versions
renv::snapshot()
# if called later, it will restore all packages from the last snapshot
# this way you can share a script and all packages will be the same
renv::restore()Error messages in German in RStudio ... nice and useless :)
Sys.setenv(LANGUAGE = "de")If you see X1-Xn in the table output, it means that the header rows are not recognized as header columns.`
X1 X2 X3
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 2 3
2 4 5 6
If you want to fix this, you can use the col_names argument set to TRUE. The output will be a data frame with the column names as the first row.
# A tibble: 1 × 3
`1` `2` `3`
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 4 5 6
read_csv2() reads semicolon-separated files. These use ; instead of , to separate fields and are common in countries that use , as the decimal marker.
For reading a file delimited with |, use read_delim() with argument delim = "|"
Columns that contain spaces are breaking R's usual rules for variable names; they're non-syntactic names. To refer to these variables, you need to surround them with backticks, `
Regular expression "(.)(.)" is used to split the column names into two parts:
The first part "(.)" captures the first character of the column name into a group. The second part "(.)" captures the second character of the column name into another group.
So, for example, if the column name is "x1", the first group "(.)" will capture "x", and the second group "(.)" will capture "1".# Load built-in datasets and show what is available
data()# move new column before existing column 1
mutate(new_column = x - y, .before = 1)
# move new column before specified column by name
mutate(new_column = x - y, .before = soneColumnName)
`
# 02.05.24
<a href="https://github.com/GrigorijSchleifer/codeNewbie/tree/main/R">R</a>
```R
# modulo: result is the remainder 1
7 %% 2
# regular division: result is 3.5
7 / 2
# integer division: result is 3
7 %/% 2# returns the directory (all parts) of a file path, but not the file name
dirname(file.path("","p1","p2","p3", "filename"))
# "/p1/p2/p3"
# returns the base (last part) of a file path
basename(file.path("","p1","p2","p3", "filename"))
# "filename"Quit R inside the terminal
quit()I want to install DOOM Emacs but can't do it because it requires Emacs version 27 or above. My problem is that I can't upgrade my version of Emacs. Now I am trying to delete Emacs from my server and install a newer version from source (for the first time in my life).
sudo apt remove emacsInstallation of Emacs 28 from source
1: Dependencies (needed for installation)
sudo apt-get install build-essential texinfo libx11-dev li bxpm-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libgif-dev libtiff-dev libgtk2.0-dev libncurses-dev automake autoconf2: Download and extract source code
wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/emacs/emacs-28.1.tar.xz3: Compile and install
cd emacs-28.1
./configure
make
sudo make install4: Doom needs a more recent version of Git. Installed Git from source using the tutorial from this link
# Install Emacs
sudo apt install emacsCreate .config file inside your home directory. Inside .config create a emacs directory and inside that create an init.el file.
In the init.el file add the following:
# telling the system that the config file will be config.org and not init.el
# config.org will be an org document containing emacs configuration blocks
(org-babel-load-file
(expand-file-name
"config.org" │
user-emacs-directory))Create a config.org file in ~/.config/emacs location (same as the config.el)
control x and control s: saving
control x and control f: finding files
Finding my Macs processor architecture
uname -mOther options are
-a -- print all basic information
-m -- print hardware class
-n -- print network node hostname
-p -- print processor type
-r -- print operating system release level
-s -- print name of the operating system
-v -- print detailed operating system version
Showing all postgres processes running on my machine
ps aux | grep postgresFinding the postgresql.conf file
cd /usr/local/var/postgresRestarting postgresql
brew services restart postgresql@14 Loading postgresql
brew services load postgresql@14Showing configuration of plist
cat ~/Library/LaunchAgents/[email protected]CREATE TABLE transactions (
id INTEGER,
recipient_id INTEGER,
sender_id INTEGER,
note TEXT,
amount INTEGER
);- Rename table, rename column, add column
ALTER TABLE people
RENAME TO users;
ALTER TABLE users
RENAME COLUMN handle TO username;
ALTER TABLE users
ADD COLUMN password TEXT;
ALTER TABLE transactions
ADD COLUMN was_successful BOOLEAN;
ALTER TABLE transactions
ADD COLUMN transaction_type TEXT;- Jumping from method to method.
[mjump to the method above.]mjump to the method below.
- Git stores folders as trees and files as blobs (binary large object: object type used to store the contents of each file in a repository plus the SHA-1 computed hash).
git ls-tree <commit hash>shows that. - A blob represents file contents without metadata.
- There are three kinds of objects in git (commits, trees and blobs). All of them are stored in gits object datadase.
- A commit is a snapshot of the project with a SHA1 hash ID
- A branch is a reference to a commits ID !!!
- Check this amazing Git tutorial for more ...

git commit -avm "message"nice way to skip the staging area (aflag includes all changed files), include (thevflag) the code differences in a commit and add a message (mflag)git rm --cached <filename>will remove a specified file from the staging area and move it bacj to the working areagit log -p -2shows the difference (-pthe patch output) introduced in each commit and limits the number of log entries displayed (-2flag)
ctrl rRedo Changes. The redo feature is the oposite of undo (allows you to reverse the previous action)
Sourcing the ~/.tmux.conf file requires a different command compared to other dotfiles (configuration files with a leading dot in their names).
tmux source-file ~/.tmux.confTMUX basic commands (MAC)
-
ctrl aorctrl tprefix (needed for all command to follow) -
ctrl b+shift %splitting panes left and right -
ctrl b+shift "splitting panes top and down -
ctrl b+arrow keysnavigating between panes down -
ctrl dclose a pane or typeexit -
ctrl b+ccreating a new window (window contains pains) -
ctrl b+nswitch to the next window -
ctrl b+pswitch to the previous window -
ctrl b+oswitch between panes -
ctrl b+ddetach from a session (everything will still run in the background) -
tmux lsList the currently running sessions -
tmux attach -t <sessionNumber>attacht to a specific session number (presented bytmux ls¡¡¡) -
tmux new -s <sessionName>attacht to a specific session -
tmux rename-session -t 0 <sessionName>rename a session using its number
Terminal Keybindings
ctrl amoves the cursor at the beginning of the linectrl emoves the cursor at the end of the linectrl bmoves the cursor to the leftctrl fmoves the cursor to the right
In Java, directly printing an array with System.out.println() will not print the contents of the array but will print its hashcode instead. To print the contents of the array, you need to use Arrays.toString() method from the java.util.Arrays class.
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));SSH learning session and some bulletpoints for me to remember.
- SSH connection is implemented using a client-server model
- remote machine must be running a piece of software called an SSH daemon
- The user’s computer must have an SSH client
- passwords (less secure and not recommended) or SSH keys, which are very secure
- always setting up SSH key-based authentication for most configurations
- user must have an SSH key pair locally.
- public key must be copied to
~/.ssh/authorized_keyson remote server
ctrl a moves the curser to the end of the line and ctrl e moves it to the beginning of the line.
MAC
Reverse delete. Or some other name for deleting stuff to the right of the cursor. By typing cntr d ... baaaam!
GIT
The .gitignore file contains names of folders and other files that Git ignores. These files are not automatically added to the staging area or included in commits. However, entries starting with an exclamation mark ("!") are an exception. These files will be included in a commit even though they are inside a folder that is otherwise ignored.
# file in out/ are excluded except `**/src/main/**/out/` and `**/src/test/**/out/`
out/
!**/src/main/**/out/
!**/src/test/**/out/VIM
This one is amazing! Enter the command mode by pressing : and use up or down keys to see your old commands. This will save me so much time!!!
Terminal
Amazing way to use the last command. Just type !! and hit tab or enter. Even better if you like to use the command befor your last entry just type !-2. Or !-4 and so on. Cool right!
IntelliJ
- Typing
/**+ then pressingEnterabove a method signature will create Javadoc stubs - 'live templates' to generate several types of code snippets.
forifor a for loop. Similar tosoutfor the print statement.
VSCode
Adding code snippets. Handy!
# open command palette
shift option PPaste configure user snippets. Amazing video HERE

lazygit "commit message"https://rahuldkjain.github.io/gh-profile-readme-generator/
Holy cow! This code when placed in vscodes settings.json will let you move lines vertically in normal mode
"vim.normalModeKeyBindingsNonRecursive": [
{
"before": ["J"],
"commands": ["editor.action.moveLinesDownAction"]
}, // moveLineDown
{
"before": ["K"],
"commands": ["editor.action.moveLinesUpAction"]
} // moveLineUp
],hostnamectl
# Show information about the host (server)
Static hostname: vps40009.alfahosting-vps.de
Icon name: computer-container
Chassis: container
Machine ID: ***
Boot ID: ***
Virtualization: openvz
Operating System: Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)
Kernel: Linux 4.19.0
Architecture: x86-64
SSH configuration on my blink app
Victor Geislinger - Setting up SSH keys for GitHub - Video
# -t ed25519 is the newest type of encryption that will be used to generate the key
# the key will be stored in ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 (default location)
# https://www.ssh.com/academy/ssh/keygen (nice tutorial)
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C your-git-mail
# starting the ssh agent
# Here we let computers ssh agent know about the key (like a wallet thes stores the key)
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
# adding private key to the ssh agent (like putting the id into the wallet)
touch ~/.ssh/config
# adding that file to ssh
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
# showing the public key that will be added to githubs
cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
# check if authentication was successful
# Hi GrigorijSchleifer! You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not provide shell access.
ssh -T [email protected]
ssh -T [email protected]Create a user on remote server and grand superuser privileges
# following this tutorial
# https://linuxize.com/post/how-to-add-user-to-sudoers-in-ubuntu/
# create a new user
createuser name_of_user
# Adding user to the sudoers group (root). This will avoid having to log out of our normal user and log back in as the root account.
# This will give or user superuser or root privileges allow our normal user to run commands with administrative privileges by putting the word sudo before the command.
# To add these privileges to our new user, we need to add the user to the sudo group.
usermod -aG sudo name_of_user
# see where linux stores the passwords
vim ect/passwd>> Run shell session as root# -s flag tells sudo to run shell as root
sudo -s# Installing venv on Debian (like my remote server) or Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install python3-venv# command to intall and upgrade the "pip" package manager to the latest version only for the current user
# -m: This option is used to run a module (pip in this case) as a script
# !!! Only ever use your system package manager to upgrade the system pip !!!
python3 -m pip install --user --upgrade pip
# installing virtualenv
python3 -m pip install --user virtualenv
# creating virtual environment for jekyll static web page development
python3 -m virtualenv jekyll_envFinding manuals to a certain terminal command by keyword lookup
$ man -k 'keyword'
# when command is found and manual is open use /MANUALSECTION to open up this explicit sectionReverse search for terminal commands you have typed so far
ctrl r
!!Hey, what's up fellas. I'm trying to install Jekyll for running my own technical blog for doctors, but unfortunately
I'm not able to update Ruby ... somehow I am stuck on an older version and don't know why I get a bunch of errors ...
So while I'm trying to stay calm instead of throwing my Mac out of the OR, I found this little snippet that shows my PATH
in a nice, concise way. Check it out ... and yes, my PATH <br> is messed up ... the next ToDo is already planned ...
see you later ... and as always ... sorry for my gebrochen english
Link to a similar but more sophisticated tutorial
echo $PATH | sed 's/:/\n/g' | uniq -cI am still new to virtual environment world but I already know that you must use virtual environments for your project
to separatte stuff ... so I was wondering where I should create all my environments ... I know I have only a few but it
turns out you should store the env's in ~ (your homne directory) ... oh Meister I hope it is true ...
# step I
mkdir ~/virtualenvs
# step 2
python -m virtualenv venv_name
# step 3
source venv_name/bin/activateBut the coolest thing ever ... you can save time by adding a function to your .zshrc and just use the funciton name plus the name of the environment to activate it ... niiiice
# add this to your .zshrc or .bashrc
export WORKON_HOME=~/virtualenvs # this is where you will store all your environments
function workon {
source "$WORKON_HOME/$1/bin/activate"
}# to activate a environment just type
workon env_nameDisplay avalable functions in iterm (zsh)
``` Hey, what is cookin ... I am adding some more functions to my bash. A neat new way to display all avalable function inside terminal is: ```
declare -fThis command will show a huge amount of functions and if you would like to limit the output to only one terminal page than pipe the output
of declare into less
declare -f | lessYou can move to the next matched pattern by pressing the n key or move back to the previous match by pressing the N (shift+n) key.
Get the newest ruby version (Jekyll static webpage installation)
``` I want a static webpage where I write about coding and collect my thougts. But, somehow I was not able to get Jekyll installd. And this was because of my ruby environment on Mac. I spent almost a day figuring out why I was not able to install the bundler gem (not sure yet what gem and bundler are) and found this amazing tutorial: ```
The fastest and easiest way to install Ruby on a Mac in 2023
Stopwords
This is a link to a page with a collection of stopwords for 40 different languages.
Quots do matter in bash
Hey, this is a cool one. I thougut that double quotes and single quote can be used interchangeably in bash but no! BASH does not expand variables inside single quotes ... what a nice pearl!
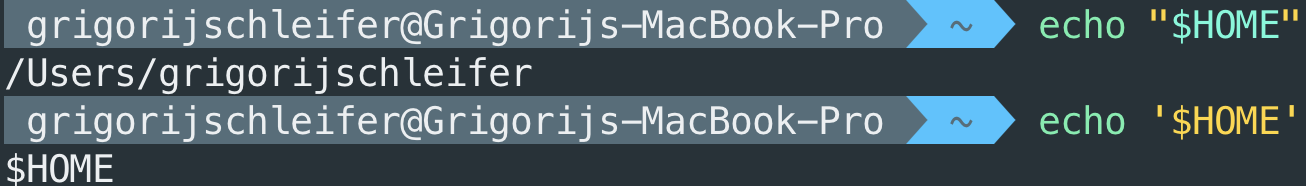
Declaring environment variables
Environment variables are useful, even for me. Often I need to check the home directory (HOME) or the shell
that is actually running (SHELL) and being able to modify this environment variables is important.
# this will change the default list of options for the less command
declare -x LESS="-iqM"Restart terminal session
Sometimes I would like to terminate my zsh session. To do so, just type:
Fastest way to insert google docstrins so far. Install autoDocstring extension for vsCode. Press cmd-shift-2 below your funcition definition

Terminal > Homebrew: I didn't know that homebrew doesn't automatically uninstall old packages, so you'll need to do it yourself.
brew cleanup
I use agnoster theme for my iTerm2 terminal and settings to that theme can be found at this location ~/.oh-my-zsh/themes/agnoster.zsh-theme
My goal was to get rid of the user and hostname display and replace it with some fancy emojis.
Before that the settings looked like this.

After the edit:

Don't forget to include the source ~/.oh-my-zsh/themes/agnoster.zsh-theme command in your .zshrc. Otherwise, after the terminal session is closed, your changes will disappear.
# press : to switch to command mode then type
:imap kj <Esc># press : to switch to command mode then type
:imap kj <Esc>Fastest way to insert google docstrins so far. Install autoDocstring extension for vsCode. Press cmd-shift-2 below your funcition definition

Terminal > Homebrew: I didn't know that homebrew doesn't automatically uninstall old packages, so you'll need to do it yourself.
brew cleanup
I use agnoster theme for my iTerm2 terminal and settings to that theme can be found at this location ~/.oh-my-zsh/themes/agnoster.zsh-theme
My goal was to get rid of the user and hostname display and replace it with some fancy emojis.
Before that the settings looked like this.

After the edit:

Don't forget to include the source ~/.oh-my-zsh/themes/agnoster.zsh-theme command in your .zshrc. Otherwise, after the terminal session is closed, your changes will disappear.


