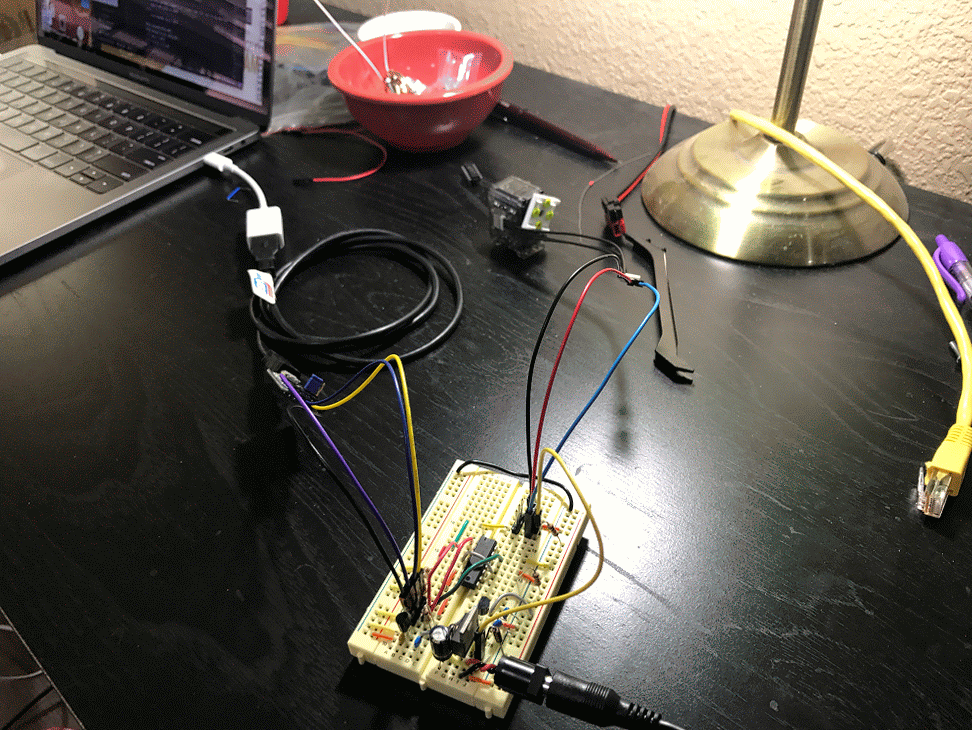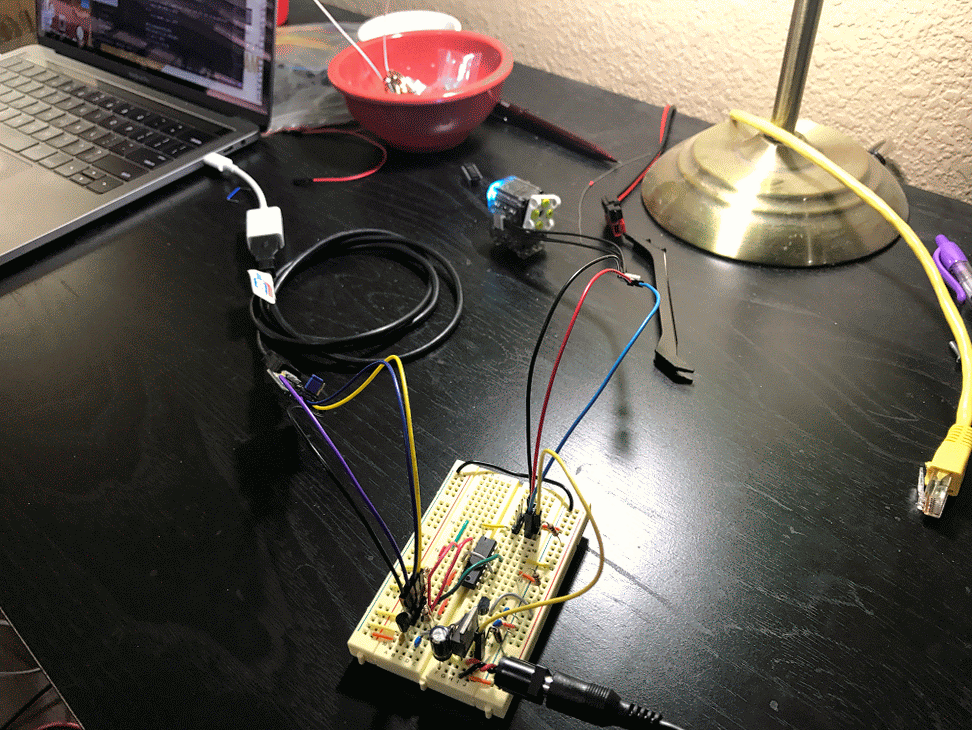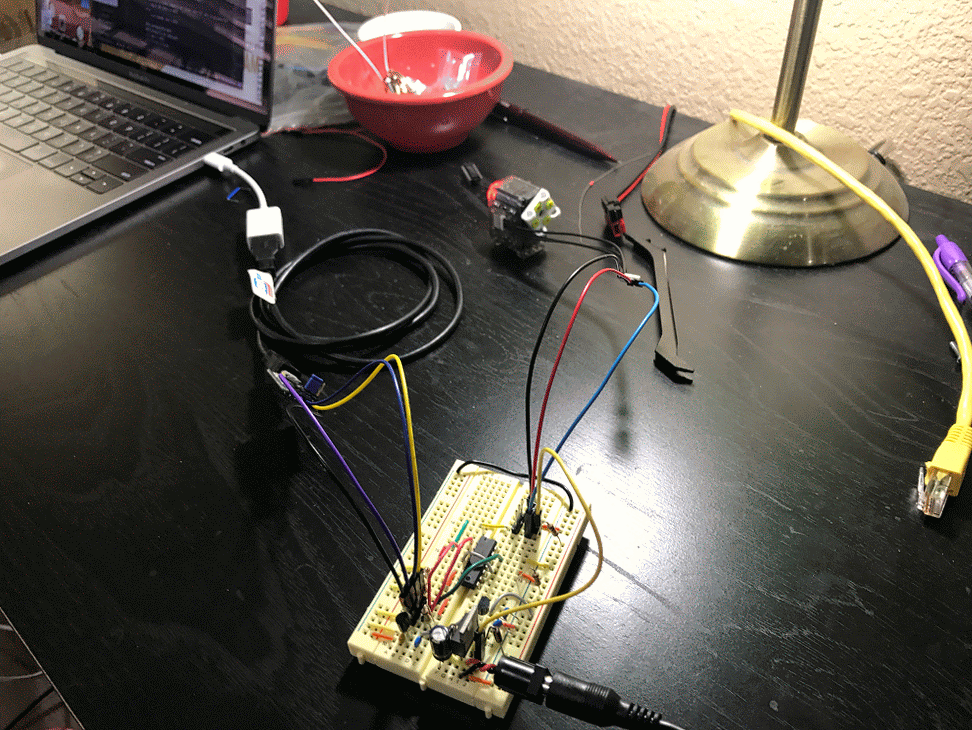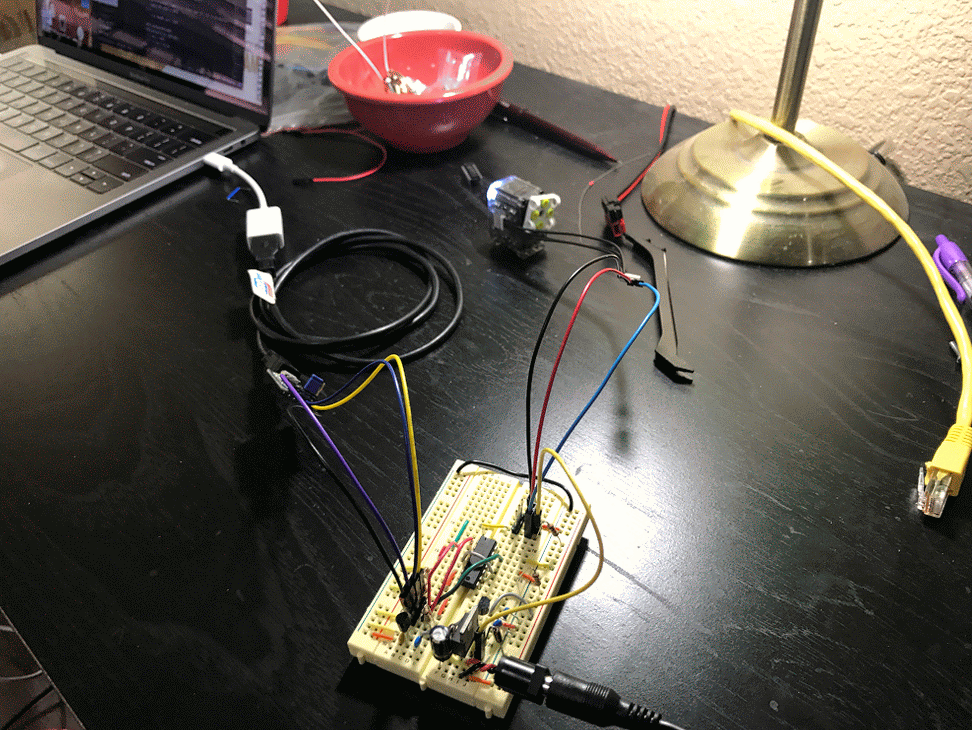


This is still a work in progress and only supports XL-320 and only version 2.0 of their protocol. The library is divided up as follows:
- pyxl320
- ServoSerial - half duplex hardware serial interface
- Packet - creates packets to talk to the servo
- utils - misc
- xl320 - register/command/error definitions for Dynamixel's XL-320 servo
New: pyXL320 now supports python2 and python3.
The suggested way to install this is via the pip command as follows:
pip install pyxl320
To submit git pulls, clone the repository and set it up as follows:
git clone https://github.com/walchko/pyxl320 cd pyxl320 pip install -r requirements pip install -e .
The \bin directory has a number of useful programs to set servo position or ID number. Just
run the command with the --help flag to see how to use it.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
servo_ping.py |
pings one or all of the servos |
servo_reboot.py |
reboots one or all servos |
servo_reset.py |
resets one or all servos to a specified level |
set_angle.py |
sets the angle of a given servo |
set_baud_rate.py |
change the baud rate of the servos |
set_id.py |
changes the ID number for a given servo |
The documents are stored in markdown files in the repo here and cover hardware interface and software development. However, a simple example to turn the servo and turn the LED to green using a USB serial converter:
from pyxl320 import xl320
from pyxl320 import ServoSerial, Packet, utils
serial = ServoSerial('/dev/tty.usbserial') # tell it what port you want to use
# serial = ServoSerial('/dev/tty.usbserial', fake=True) # use a dummy serial interface for testing
serial.open()
pkt = Packet.makeServoPacket(1, 158.6) # move servo 1 to 158.6 degrees
ret = serial.sendPkt(pkt) # send packet, I don't do anything with the returned status packet
pkt = packet.makeLEDPacket(1, pyxl320.XL320_LED_GREEN)
ret = serial.sendPkt(pkt)
print('Status packet:', ret) # here I print out the status packet returnedAlthough I have made some packet creators (like LED and Servo), you can make
your own using the basic makeWritePacket and makeReadPacket.
from pyxl320 import Packet, xl320
from pyxl320.Packet import le # creates little endian numbers
# let's make our own servo packet that sends servo 3 to 220.1 degrees
ID = 3
reg = xl320.XL320_GOAL_POSITION
params = le(int(220.1/300*1023)) # convert 220.1 degrees to an int between 0-1023
pkt = Packet.makeWritePacket(ID, reg, params)Here are some example robots
| 2017-04-01 | 0.9.0 | added python3 support |
| 2017-03-26 | 0.8.0 | major overhaul and removed the GPIO stuff |
| 2017-03-19 | 0.7.7 | can switch between GPIO pin and pyserial.setRTS() |
| 2017-02-20 | 0.7.6 | small fixes and added servo_reboot |
| 2017-01-16 | 0.7.5 | fixes some small errors |
| 2016-11-29 | 0.7.4 | add bulk write and small changes |
| 2016-10-11 | 0.7.1 | small changes/updates |
| 2016-09-12 | 0.7.0 | refactoring, still working on API |
| 2016-09-05 | 0.5.0 | published to PyPi |
| 2016-08-16 | 0.0.1 | init |
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2016 Kevin J. Walchko
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.