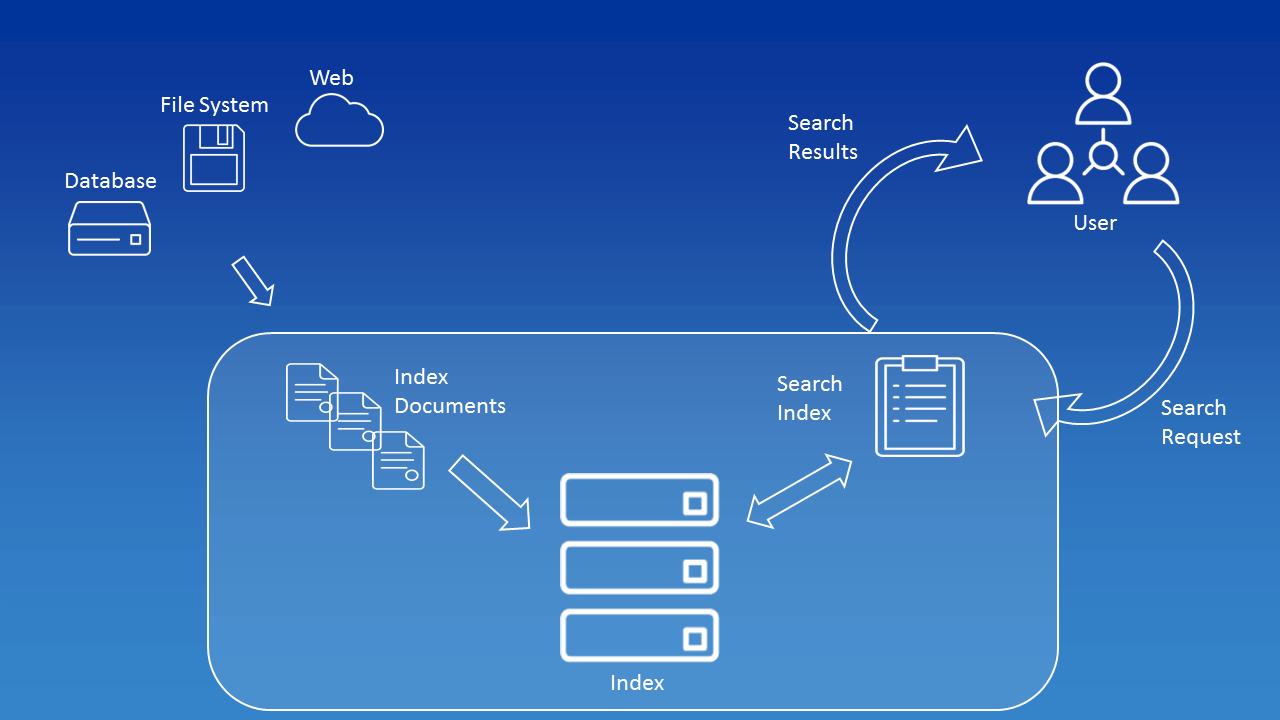
With the rapid development of the Internet and the explosive growth of Web information, Internet users' ability to filter out the impurities and retain the essence quickly and easily in order to obtain the information they require in the vast ocean of data has become a hot research topic in this field.
The full-text retrieval technology lies at the heart of information search. Full-text search technology gave us a tool for retrieving information based on the substance of data rather than external attributes based on a variety of computer data such as text, voice, and image as a processing object.
- Build a Text Database
- Create Indexing
- Search
- Filter and Sort the Results
When it came to the implementation, the following options were examined.
- Use built-in search-functionality in the currently used database management systems.
- Use an open-source library to build a separate, independent, search component.
PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, and Microsoft SQL Server are the database management systems now in use by various clients. All of them provide indexing and full-text search capabilities in some way. Despite this, and without taking into account their effectiveness, the issue of re-usability persists. That example, if a prototype or full implementation for one of the DMBSs was created, the ability to search the others would not have improved. There's also nothing stopping a user from switching to a different DBMS or a new customer from showing up with a different DBMS. As a result, the project will not use any built-in search functions from a database management system, instead focusing on developing a distinct, independent search component.
Because they had a commercial licence or had a restricted free version, the search engines Splunk, MarkLogic, Microsoft Azure Search, Algolia, Google Search Appliance, and Amazon CloudSearch were all removed. Below is a list of the remaining five contestants.
- Lucene
- Elasticsearch (ES)
- Solr
- Sphinx
- Xapian Sphinx and Xapian are both written in C++ but have support for programming in Java. Apache Lucene, Elasticsearch and Solr are all written in Java.
Lucene Core is a Java package that offers enhanced indexing and search capabilities, as well as spellchecking, hit highlighting, and advanced analysis/tokenization. Python bindings for Lucene Core are provided by the PyLucene subproject.
Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine that can handle a wide range of scenarios. As the heart of the Elastic Stack, it saves your data centrally for lightning fast search, fine-tuned relevancy, and scalable analytics.
Solr is a search platform that is open-source and may be used to create search apps. It was constructed on top of Lucene (full text search engine). Solr is an enterprise-ready, fast, and scalable search engine. Solr-based applications are smart and provide excellent performance.
Solr is a wrap around Lucene’s Java API. Therefore, using Solr, you can leverage all the features of Lucene. Let us take a look at some of most prominent features of Solr-
- Restful APIs
- Full text search
- Enterprise ready
- Flexible and Extensible
- NoSQL database
- Admin Interface
- Highly Scalable
- Text-Centric and Sorted by Relevance