- Reference
- Basic structure
- Selector
- Good to know
- Font
- Background
- Image
- Display
- Box
- Coding Standard
- Repaint/Reflow
- Misc
- Visual guide to CSS: http://cssreference.io
- 中文文案排版指北: https://github.com/sparanoid/chinese-copywriting-guidelines
<!DOCTYPE html>
html
head
body
header
nav
section
article
aside
footer
html
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="assets/css/my.css">
<link href="mysite-mobile.css" rel="stylesheet" media="screen and (max-device-width: 480px)">
//- nav
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">About</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
css
// usually split in this way: layout.css color.css typography.css
// use one parent css to include them:
@import url(layout.css);
@import url(color.css);
@import url(typography.css);
@media print {
body {
/* css text */
}
}viewport <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width">
Prefer class over id: id is only faster when id is the key selector, it's slower when #home a, because browser read from right to left so #home a is read as finding all a then pick #home.
div pwinp- same style, last one win
- you give every ID selector (“#whatever”) a value of 100, every class selector (“.whatever”) a value of 10 and every HTML selector (“whatever”) a value of 1. Then you add them all up and hey presto, you have the specificity value
descendant selector
#id-name h2 { } /* it means select h2 under the id 'id-name' */- by default, it selects all nested chilren no matter how deep they are.
- to select the direct child:
#id-name > h2
select sibling using '+'
h1+p{} // select all p comes after h1the pattern of the selector: context + element + pseudo-class/elements
div#greentea > blockquote p:first-line // p is the element.pseudo-class :hover
- Style for specific state:
a:link { color: green; }, :hover, :visited - Style for specific position:
p:nth-child(2n) { color: green; }
pseudo-elements ::before
- Style for certain parts of a element. It's applied to content.
- Input elements have no content, that's why ::before is not applied.
-
strongvsemvsbememphasisstrongadded importanceb(style only)
-
dldd -
List: the only element we can place as a direct child of the
<ul>and<ol>elements is the<li>element -
audio<audio controls> <source src="jazz.ogg" type="audio/ogg"> <source src="jazz.mp3" type="audio/mpeg"> <source src="jazz.wav" type="audio/wav"> Please <a href="jazz.mp3" download>download</a> the audio file. </audio> -
figure+figcaption -
markfor highlight -
<progress value="70" max="100">70 %</progress> -
<ruby>and<rt>for 中文注音: http://codepen.io/hamxiaoz/pen/Nbjjjm -
You can live editing CSS by using
<style contenteditable>: https://codepen.io/GiorgioMalvone/pen/vHCds
font-family: Verdana, Arial, "Courier New", sans-serif;
// how to use web font (web open font format 'WOFF')?
@font-face { font-family: "name"; src: url("font.woff"), url("font.ttf"); }px(old IE doesn't support it!)%(relative to the parent element)em(scaling to the parent element) or keywords (small/medium etc.)rem(scaling relative to the root elment 'html')
to use it properly: (so it can be really easy to adjust whole font by just changing the base font)
- choose a keyword for body to define the whole page size as a basement.
- use em or %
- use rem
line-height: it can use number only to specify the size to its own size.
#gift { line-height: 1em; } // all elements inside gift is the same size of the element of gift, h1 size will be the same as h2! (which inherits from body)
#gift { line-height: 1; } // all elements inside gift is the same size as their own size. So h1 will be h1's size and h2 will be h2's size.text-decoration: no need to use , for multiple value: text-decoration: underline line-through;
-
DO NOT USE Background shortcut:
background-color,background-image,background-positionandbackground-repeatas you might overridediv { background: #b2b2b2 url("alert.png") 20px 10px no-repeat; } -
Linear gradient is background-image
-
{background-size: cover/curtain/etc}background-image: url(https://example.com); background-size: cover;
- By default it's inline element
display: none: means the browser will render the page as the element doesn't exist.visibility: hidden: means it renders as it's there but not visible, like invisibe cloak.opacity:0: Similar tovisibility: hiddenbut when focus on it, iOS will show keyboard. The other two won't.
display:block will stretch the element to left/right as far as possible.
width: browser will create scrollbar if viewport is smaller, in this case, use max-width instead of width.
Read: https://blog.coding.net/blog/css-margin
Order matters! The last one takes precedence, overriding anyone specified before:
margin: 30px;
margin-left: 50px; // margin left will be 50px instead of 30px
// or
margin-left: 50px;
margin: 30px; // margin left will be 30pxShortcuts:
margin: 30px 20px 30px 20px; // top right bottom left (think as a clockwise direction: from 12 to 11)
margin: 30px 20px; // top/bottom right/left
margin: 30px // means all sides have the same padding of 30px- Use margin to separate the block from things outside it.
- Use padding to move the contents away from the edges of the block.
- Margin collapse on vertical: http://codepen.io/hamxiaoz/pen/mRyeXp
- When styling typography and arbitrary sequences of paragraphs, headings and lists it's almost always better to space the elements with margins because of the adjacent margin collapsing behaviour.
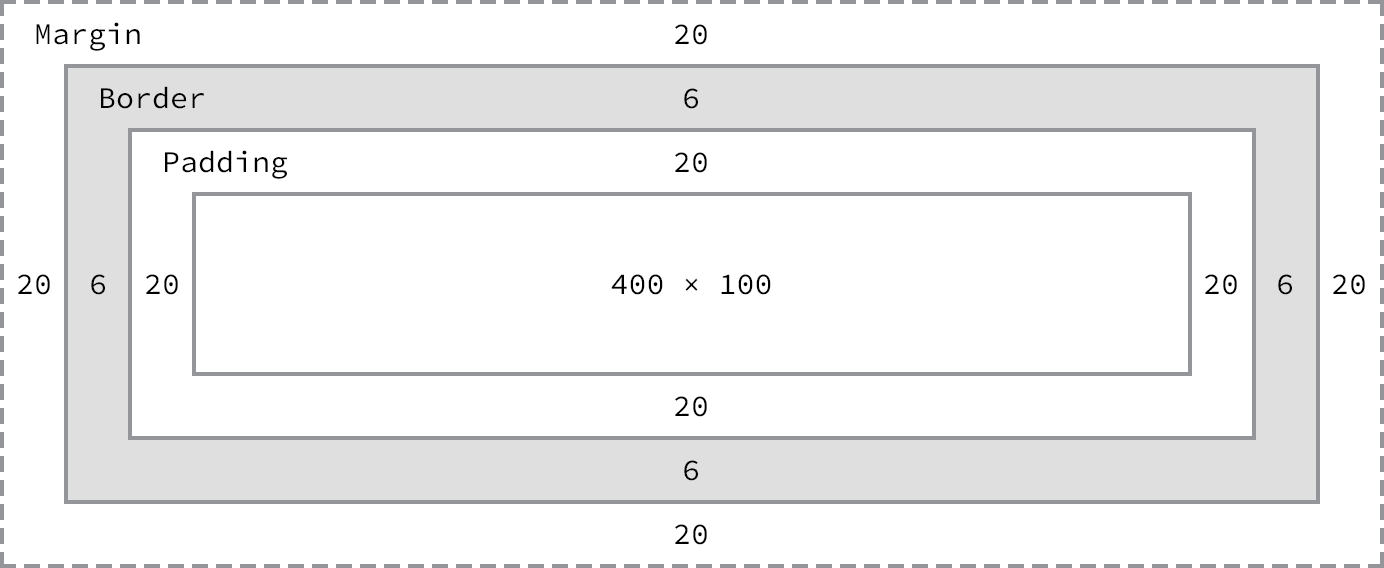
border: solid #009302 thin; // ... and border-width
background: white url(images/gift.gif) repeat-x; // color image repeatBy default, Box model is box-sizing: content-box, means the width specifies the the content only, not including padding and border.
So if you have width: 100% and padding, the item will display out of the container.
If you want the width to be the real width of the box, use box-sizing: border-box;
div {
border: 6px solid #949599;
height: 100px;
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
width: 400px;
}By default, it's
vertical-alignCSS property specifies the vertical alignment of an inline or table-cell box.text-align: it will align all inline content inside a block element.
-
try to avoid id in css
-
remove units for 0
-
When using vendor prefixes we need to make sure to place an unprefixed version of our property and value last, after any prefixed versions.
div { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(#a1d3b0, #f6f1d3); background: -moz-linear-gradient(#a1d3b0, #f6f1d3); background: linear-gradient(#a1d3b0, #f6f1d3); -webkit-box-sizing: border-box; -moz-box-sizing: border-box; box-sizing: border-box; }
To check:
因此,我们在写动画的时候因该规避这些属性:width, height, margin, padding, border, display, top, right, bottom ,left, position, float, overflow等。
不会出发重新布局的属性有:transform(其中的translate, rotate, scale), color, background等。
所以,我们平时在写css动画时,应该优先使用不触发重新布局的属性,这样可以使我们所展示动画效果的更加流畅。
- what's semantic css: code what you mean, think about the structure. if it's important, put it as H1.
- read last comment from: http://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=3653540
- use less can solve the problem.
- other css framework: blueprint, 960.
You need to set it to the object in Javascript or using inline style
element.style is just a conversion of the element's style attribute into a scriptable object. If you haven't set any inline style on the element, you won't get anything back.
document.getElementById("convert").style.display = "block" or <a style="display: block;"></a>