forked from javadev/LeetCode-in-Kotlin
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
24 changed files
with
977 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
18 changes: 18 additions & 0 deletions
18
...1_3500/s3423_maximum_difference_between_adjacent_elements_in_a_circular_array/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3423_maximum_difference_between_adjacent_elements_in_a_circular_array | ||
|
|
||
| // #Easy #2025_01_19_Time_2_(100.00%)_Space_38.80_(100.00%) | ||
|
|
||
| import kotlin.math.abs | ||
| import kotlin.math.max | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun maxAdjacentDistance(nums: IntArray): Int { | ||
| var maxDiff = 0 | ||
| for (i in nums.indices) { | ||
| val nextIndex = (i + 1) % nums.size | ||
| val diff = abs((nums[i] - nums[nextIndex])) | ||
| maxDiff = max(maxDiff, diff) | ||
| } | ||
| return maxDiff | ||
| } | ||
| } |
32 changes: 32 additions & 0 deletions
32
...3423_maximum_difference_between_adjacent_elements_in_a_circular_array/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ | ||
| 3423\. Maximum Difference Between Adjacent Elements in a Circular Array | ||
|
|
||
| Easy | ||
|
|
||
| Given a **circular** array `nums`, find the **maximum** absolute difference between adjacent elements. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note**: In a circular array, the first and last elements are adjacent. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [1,2,4] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 3 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| Because `nums` is circular, `nums[0]` and `nums[2]` are adjacent. They have the maximum absolute difference of `|4 - 1| = 3`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** nums = [-5,-10,-5] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 5 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The adjacent elements `nums[0]` and `nums[1]` have the maximum absolute difference of `|-5 - (-10)| = 5`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * `2 <= nums.length <= 100` | ||
| * `-100 <= nums[i] <= 100` |
28 changes: 28 additions & 0 deletions
28
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3424_minimum_cost_to_make_arrays_identical/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,28 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3424_minimum_cost_to_make_arrays_identical | ||
|
|
||
| // #Medium #Array #Sorting #Greedy #2025_01_23_Time_38_(100.00%)_Space_64.36_(97.14%) | ||
|
|
||
| import kotlin.math.abs | ||
| import kotlin.math.min | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun minCost(arr: IntArray, brr: IntArray, k: Long): Long { | ||
| val n = arr.size | ||
| var sum1: Long = 0 | ||
| var sum2: Long | ||
| for (i in 0..<n) { | ||
| sum1 = sum1 + abs((arr[i] - brr[i])) | ||
| } | ||
| if (k < sum1) { | ||
| arr.sort() | ||
| brr.sort() | ||
| sum2 = k | ||
| for (i in 0..<n) { | ||
| sum2 = sum2 + abs((arr[i] - brr[i])) | ||
| } | ||
| } else { | ||
| return sum1 | ||
| } | ||
| return min(sum1, sum2) | ||
| } | ||
| } |
43 changes: 43 additions & 0 deletions
43
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3424_minimum_cost_to_make_arrays_identical/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,43 @@ | ||
| 3424\. Minimum Cost to Make Arrays Identical | ||
|
|
||
| Medium | ||
|
|
||
| You are given two integer arrays `arr` and `brr` of length `n`, and an integer `k`. You can perform the following operations on `arr` _any_ number of times: | ||
|
|
||
| * Split `arr` into _any_ number of **contiguous** **non-empty subarrays** and rearrange these subarrays in _any order_. This operation has a fixed cost of `k`. | ||
| * Choose any element in `arr` and add or subtract a positive integer `x` to it. The cost of this operation is `x`. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Return the **minimum** total cost to make `arr` **equal** to `brr`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** arr = [-7,9,5], brr = [7,-2,-5], k = 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 13 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| * Split `arr` into two contiguous subarrays: `[-7]` and `[9, 5]` and rearrange them as `[9, 5, -7]`, with a cost of 2. | ||
| * Subtract 2 from element `arr[0]`. The array becomes `[7, 5, -7]`. The cost of this operation is 2. | ||
| * Subtract 7 from element `arr[1]`. The array becomes `[7, -2, -7]`. The cost of this operation is 7. | ||
| * Add 2 to element `arr[2]`. The array becomes `[7, -2, -5]`. The cost of this operation is 2. | ||
|
|
||
| The total cost to make the arrays equal is `2 + 2 + 7 + 2 = 13`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** arr = [2,1], brr = [2,1], k = 0 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 0 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| Since the arrays are already equal, no operations are needed, and the total cost is 0. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>1 <= arr.length == brr.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * <code>0 <= k <= 2 * 10<sup>10</sup></code> | ||
| * <code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= arr[i] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * <code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= brr[i] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> |
91 changes: 91 additions & 0 deletions
91
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3425_longest_special_path/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,91 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3425_longest_special_path | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #2025_01_19_Time_106_(100.00%)_Space_187.68_(100.00%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| private lateinit var adj: Array<ArrayList<IntArray>> | ||
| private lateinit var nums: IntArray | ||
| private lateinit var dist: IntArray | ||
| private lateinit var lastOccur: IntArray | ||
| private lateinit var pathStack: ArrayList<Int> | ||
| private var minIndex = 0 | ||
| private var maxLen = 0 | ||
| private var minNodesForMaxLen = 0 | ||
|
|
||
| fun longestSpecialPath(edges: Array<IntArray>, nums: IntArray): IntArray { | ||
| val n = nums.size | ||
| this.nums = nums | ||
| adj = Array<ArrayList<IntArray>>(n) { ArrayList<IntArray>() } | ||
| for (i in 0..<n) { | ||
| adj[i] = ArrayList<IntArray>() | ||
| } | ||
| for (e in edges) { | ||
| val u = e[0] | ||
| val v = e[1] | ||
| val w = e[2] | ||
| adj[u].add(intArrayOf(v, w)) | ||
| adj[v].add(intArrayOf(u, w)) | ||
| } | ||
| dist = IntArray(n) | ||
| buildDist(0, -1, 0) | ||
| var maxVal = 0 | ||
| for (`val` in nums) { | ||
| if (`val` > maxVal) { | ||
| maxVal = `val` | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| lastOccur = IntArray(maxVal + 1) | ||
| lastOccur.fill(-1) | ||
| pathStack = ArrayList<Int>() | ||
| minIndex = 0 | ||
| maxLen = 0 | ||
| minNodesForMaxLen = Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE | ||
| dfs(0, -1) | ||
| return intArrayOf(maxLen, minNodesForMaxLen) | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private fun buildDist(u: Int, parent: Int, currDist: Int) { | ||
| dist[u] = currDist | ||
| for (edge in adj[u]) { | ||
| val v = edge[0] | ||
| val w = edge[1] | ||
| if (v == parent) { | ||
| continue | ||
| } | ||
| buildDist(v, u, currDist + w) | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| private fun dfs(u: Int, parent: Int) { | ||
| val stackPos = pathStack.size | ||
| pathStack.add(u) | ||
| val `val` = nums[u] | ||
| val oldPos = lastOccur[`val`] | ||
| val oldMinIndex = minIndex | ||
| lastOccur[`val`] = stackPos | ||
| if (oldPos >= minIndex) { | ||
| minIndex = oldPos + 1 | ||
| } | ||
| if (minIndex <= stackPos) { | ||
| val ancestor = pathStack[minIndex] | ||
| val pathLength = dist[u] - dist[ancestor] | ||
| val pathNodes = stackPos - minIndex + 1 | ||
| if (pathLength > maxLen) { | ||
| maxLen = pathLength | ||
| minNodesForMaxLen = pathNodes | ||
| } else if (pathLength == maxLen && pathNodes < minNodesForMaxLen) { | ||
| minNodesForMaxLen = pathNodes | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| for (edge in adj[u]) { | ||
| val v = edge[0] | ||
| if (v == parent) { | ||
| continue | ||
| } | ||
| dfs(v, u) | ||
| } | ||
| pathStack.removeAt(pathStack.size - 1) | ||
| lastOccur[`val`] = oldPos | ||
| minIndex = oldMinIndex | ||
| } | ||
| } |
48 changes: 48 additions & 0 deletions
48
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3425_longest_special_path/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,48 @@ | ||
| 3425\. Longest Special Path | ||
|
|
||
| Hard | ||
|
|
||
| You are given an undirected tree rooted at node `0` with `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1`, represented by a 2D array `edges` of length `n - 1`, where <code>edges[i] = [u<sub>i</sub>, v<sub>i</sub>, length<sub>i</sub>]</code> indicates an edge between nodes <code>u<sub>i</sub></code> and <code>v<sub>i</sub></code> with length <code>length<sub>i</sub></code>. You are also given an integer array `nums`, where `nums[i]` represents the value at node `i`. | ||
|
|
||
| A **special path** is defined as a **downward** path from an ancestor node to a descendant node such that all the values of the nodes in that path are **unique**. | ||
|
|
||
| **Note** that a path may start and end at the same node. | ||
|
|
||
| Return an array `result` of size 2, where `result[0]` is the **length** of the **longest** special path, and `result[1]` is the **minimum** number of nodes in all _possible_ **longest** special paths. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** edges = [[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,5],[1,4,4],[2,5,6]], nums = [2,1,2,1,3,1] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [6,2] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| #### In the image below, nodes are colored by their corresponding values in `nums` | ||
|
|
||
| 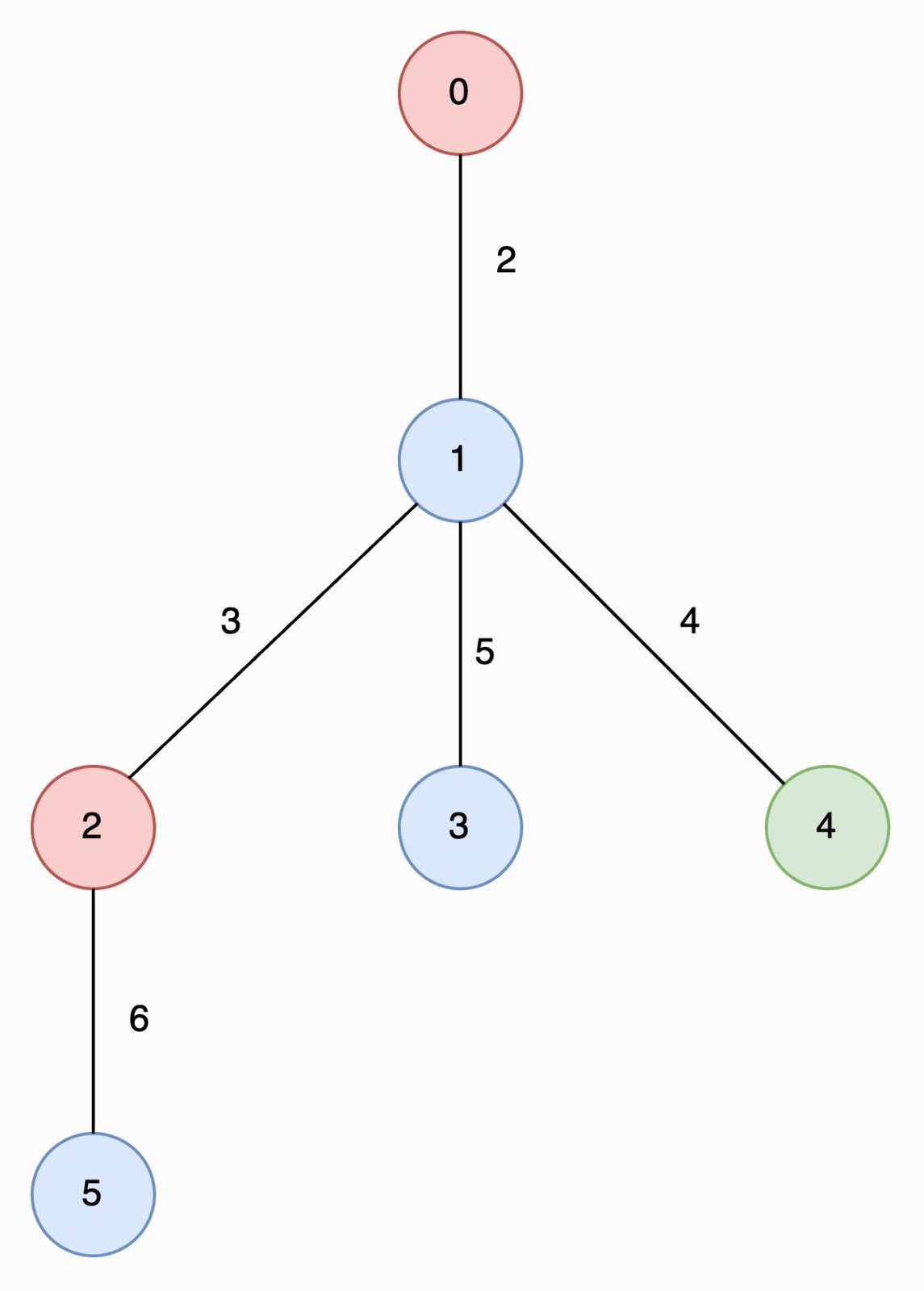 | ||
|
|
||
| The longest special paths are `2 -> 5` and `0 -> 1 -> 4`, both having a length of 6. The minimum number of nodes across all longest special paths is 2. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** edges = [[1,0,8]], nums = [2,2] | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** [0,1] | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| 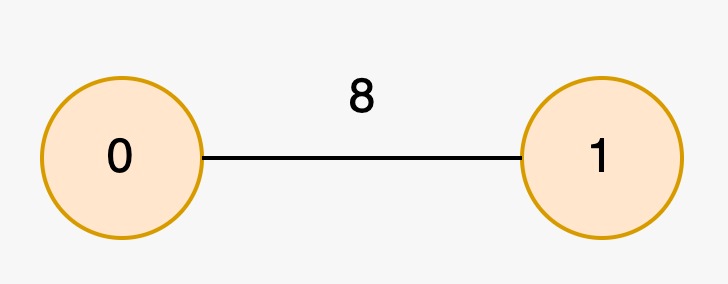 | ||
|
|
||
| The longest special paths are `0` and `1`, both having a length of 0. The minimum number of nodes across all longest special paths is 1. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>2 <= n <= 5 * 10<sup>4</sup></code> | ||
| * `edges.length == n - 1` | ||
| * `edges[i].length == 3` | ||
| * <code>0 <= u<sub>i</sub>, v<sub>i</sub> < n</code> | ||
| * <code>1 <= length<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>3</sup></code> | ||
| * `nums.length == n` | ||
| * <code>0 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 10<sup>4</sup></code> | ||
| * The input is generated such that `edges` represents a valid tree. |
40 changes: 40 additions & 0 deletions
40
...ain/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3426_manhattan_distances_of_all_arrangements_of_pieces/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,40 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3426_manhattan_distances_of_all_arrangements_of_pieces | ||
|
|
||
| // #Hard #2025_01_19_Time_21_(100.00%)_Space_34.61_(100.00%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| private fun comb(a: Long, b: Long, mod: Long): Long { | ||
| if (b > a) { | ||
| return 0 | ||
| } | ||
| var numer: Long = 1 | ||
| var denom: Long = 1 | ||
| for (i in 0..<b) { | ||
| numer = numer * (a - i) % mod | ||
| denom = denom * (i + 1) % mod | ||
| } | ||
| var denomInv: Long = 1 | ||
| var exp = mod - 2 | ||
| while (exp > 0) { | ||
| if (exp % 2 > 0) { | ||
| denomInv = denomInv * denom % mod | ||
| } | ||
| denom = denom * denom % mod | ||
| exp /= 2 | ||
| } | ||
| return numer * denomInv % mod | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| fun distanceSum(m: Int, n: Int, k: Int): Int { | ||
| var res: Long = 0 | ||
| val mod: Long = 1000000007 | ||
| val base = comb(m.toLong() * n - 2, k - 2L, mod) | ||
| for (d in 1..<n) { | ||
| res = (res + d.toLong() * (n - d) % mod * m % mod * m % mod) % mod | ||
| } | ||
| for (d in 1..<m) { | ||
| res = (res + d.toLong() * (m - d) % mod * n % mod * n % mod) % mod | ||
| } | ||
| return (res * base % mod).toInt() | ||
| } | ||
| } |
53 changes: 53 additions & 0 deletions
53
...in/g3401_3500/s3426_manhattan_distances_of_all_arrangements_of_pieces/readme.md
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ | ||
| 3426\. Manhattan Distances of All Arrangements of Pieces | ||
|
|
||
| Hard | ||
|
|
||
| You are given three integers `m`, `n`, and `k`. | ||
|
|
||
| There is a rectangular grid of size `m × n` containing `k` identical pieces. Return the sum of Manhattan distances between every pair of pieces over all **valid arrangements** of pieces. | ||
|
|
||
| A **valid arrangement** is a placement of all `k` pieces on the grid with **at most** one piece per cell. | ||
|
|
||
| Since the answer may be very large, return it **modulo** <code>10<sup>9</sup> + 7</code>. | ||
|
|
||
| The Manhattan Distance between two cells <code>(x<sub>i</sub>, y<sub>i</sub>)</code> and <code>(x<sub>j</sub>, y<sub>j</sub>)</code> is <code>|x<sub>i</sub> - x<sub>j</sub>| + |y<sub>i</sub> - y<sub>j</sub>|</code>. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 1:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** m = 2, n = 2, k = 2 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 8 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The valid arrangements of pieces on the board are: | ||
|
|
||
| 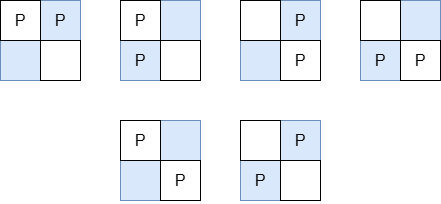 | ||
|
|
||
| * In the first 4 arrangements, the Manhattan distance between the two pieces is 1. | ||
| * In the last 2 arrangements, the Manhattan distance between the two pieces is 2. | ||
|
|
||
| Thus, the total Manhattan distance across all valid arrangements is `1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 8`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Example 2:** | ||
|
|
||
| **Input:** m = 1, n = 4, k = 3 | ||
|
|
||
| **Output:** 20 | ||
|
|
||
| **Explanation:** | ||
|
|
||
| The valid arrangements of pieces on the board are: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| * The first and last arrangements have a total Manhattan distance of `1 + 1 + 2 = 4`. | ||
| * The middle two arrangements have a total Manhattan distance of `1 + 2 + 3 = 6`. | ||
|
|
||
| The total Manhattan distance between all pairs of pieces across all arrangements is `4 + 6 + 6 + 4 = 20`. | ||
|
|
||
| **Constraints:** | ||
|
|
||
| * <code>1 <= m, n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * <code>2 <= m * n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> | ||
| * `2 <= k <= m * n` |
15 changes: 15 additions & 0 deletions
15
src/main/kotlin/g3401_3500/s3427_sum_of_variable_length_subarrays/Solution.kt
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ | ||
| package g3401_3500.s3427_sum_of_variable_length_subarrays | ||
|
|
||
| // #Easy #Array #Prefix_Sum #2025_01_22_Time_0_(100.00%)_Space_43.77_(58.41%) | ||
|
|
||
| class Solution { | ||
| fun subarraySum(nums: IntArray): Int { | ||
| var res = nums[0] | ||
| for (i in 1..<nums.size) { | ||
| val j = i - nums[i] - 1 | ||
| nums[i] += nums[i - 1] | ||
| res += nums[i] - (if (j < 0) 0 else nums[j]) | ||
| } | ||
| return res | ||
| } | ||
| } |
Oops, something went wrong.