TrustKit is an open source framework that makes it easy to deploy SSL public key pinning in any iOS 7+, macOS 10.9+, tvOS 10+ or watchOS 3+ App; it supports both Swift and Objective-C Apps.
TrustKit provides the following features:
- Simple API to configure an SSL pinning policy and enforce it within an App. The policy settings are heavily based on the HTTP Public Key Pinning specification.
- Auto-pinning functionality by swizzling the App's NSURLConnection and NSURLSession delegates in order to automatically add pinning validation to the App's HTTPS connections; this allows deploying TrustKit without even modifying the App's source code.
- Sane implementation by pinning the certificate's Subject Public Key Info, as opposed to the certificate itself or the public key bits.
- Reporting mechanism to notify a server about pinning validation failures happening within the App, when an unexpected certificate chain is detected. This is similar to the report-uri directive described in the HPKP specification. The reporting mechanism can also be customized within the App by leveraging pin validation notifications sent by TrustKit.
TrustKit was open-sourced at Black Hat 2015 USA.
- Read the Getting Started guide.
- Check out the API documentation.
- Have a look at the Black Hat USA 2015 presentation and the significant changes that subsequently happened with iOS 9.
- TrustKit was featured on PayPal's engineering blog.
TrustKit can be deployed using CocoaPods, by adding the following line to your Podfile:
pod 'TrustKit'Then run:
$ pod installAlternatively, Carthage can be used by adding the following line to your Cartfile:
github "datatheorem/TrustKit"
Then run:
carthage build --platform iOSThen, deploying SSL pinning in the App requires initializing TrustKit with a pinning policy (domains, Subject Public Key Info hashes, and additional settings).
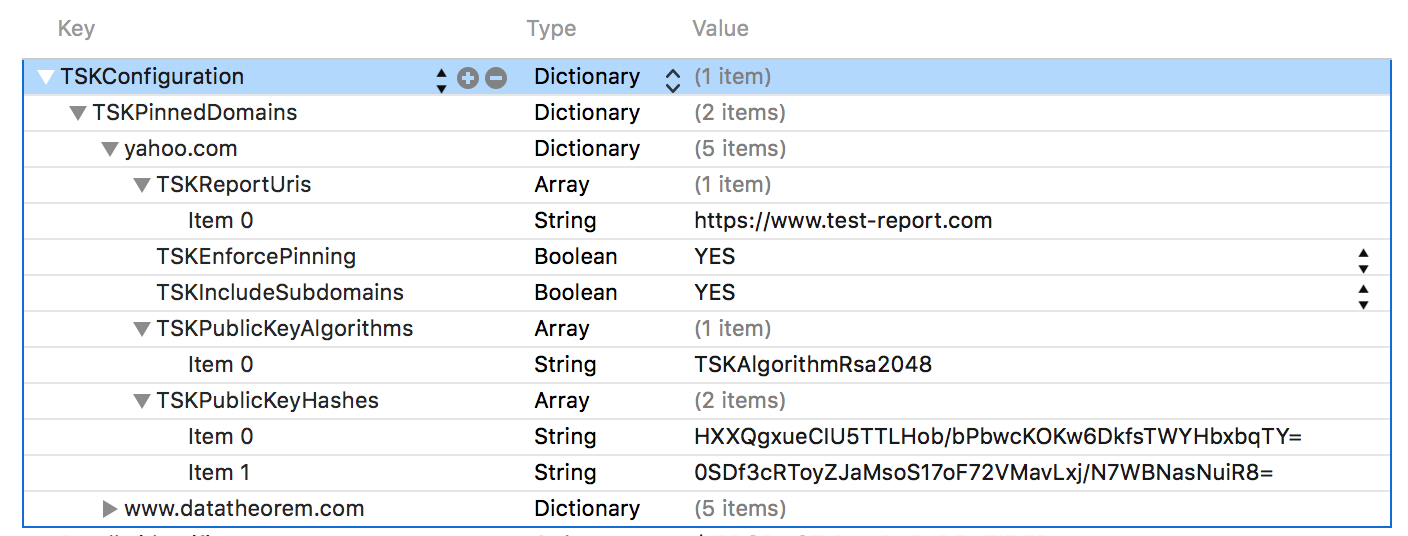
The policy can be configured within the App's Info.plist:
Alternatively, the pinning policy can be set programmatically:
NSDictionary *trustKitConfig =
@{
kTSKSwizzleNetworkDelegates: @YES,
kTSKPinnedDomains : @{
@"www.datatheorem.com" : @{
kTSKPublicKeyAlgorithms : @[kTSKAlgorithmRsa2048],
kTSKPublicKeyHashes : @[
@"HXXQgxueCIU5TTLHob/bPbwcKOKw6DkfsTWYHbxbqTY=",
@"0SDf3cRToyZJaMsoS17oF72VMavLxj/N7WBNasNuiR8="
],
kTSKEnforcePinning : @NO,
kTSKReportUris : @[@"http://report.datatheorem.com/log_report"],
},
@"yahoo.com" : @{
kTSKPublicKeyAlgorithms : @[kTSKAlgorithmRsa4096],
kTSKPublicKeyHashes : @[
@"TQEtdMbmwFgYUifM4LDF+xgEtd0z69mPGmkp014d6ZY=",
@"rFjc3wG7lTZe43zeYTvPq8k4xdDEutCmIhI5dn4oCeE=",
],
kTSKIncludeSubdomains : @YES
}
}};
[TrustKit initializeWithConfiguration:trustKitConfig];The policy can also be set programmatically in Swift Apps:
let trustKitConfig = [
kTSKPinnedDomains: [
"yahoo.com": [
kTSKPublicKeyAlgorithms: [kTSKAlgorithmRsa2048],
kTSKPublicKeyHashes: [
"JbQbUG5JMJUoI6brnx0x3vZF6jilxsapbXGVfjhN8Fg=",
"WoiWRyIOVNa9ihaBciRSC7XHjliYS9VwUGOIud4PB18="
],]]]
TrustKit.initializeWithConfiguration(config)Once TrustKit has been initialized and if kTSKSwizzleNetworkDelegates is enabled in the policy, TrustKit will automatically swizzle the App's NSURLSession and NSURLConnection delegates to verify the server's certificate against the configured pinning policy, whenever an HTTPS connection is initiated. If report URIs have been configured, the App will also send reports to the specified URIs whenever a pin validation failure occurred.
The swizzling behavior should only be used for simple Apps. When swizzling is disabled, a server's certificate chain can easily be manually checked against the App's SSL pinning policy using the TSKPinningValidator class, for example to implement an authentication handler.
For more information, see the Getting Started guide.
TrustKit is a joint-effort between the security teams at Data Theorem and Yahoo. See AUTHORS for details.
TrustKit is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.