-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Run Client Examples
This tutorial will walk through the steps required to run the OpenDXL Python Client examples within the OpenDXL Environment.
- The OpenDXL Environment has been installed and is running.
- The OpenDXL Environment Console is accessible.
- One of the following DXL fabrics is available for connecting to:
- OpenDXL Broker
- ePO-Managed DXL Fabric with DXL Brokers and ePO Extensions (4.0 or later)
Throughout this tutorial commands will be pasted into the OpenDXL Environment terminal. The following table details how to perform paste operations within the terminal:
| Operating System | Paste |
|---|---|
| Windows | SHIFT+INSERT |
| Mac | COMMAND+V |
The first step is to connect to the OpenDXL Environment Console as shown below.
Next, click on the Terminal button as shown above to display a terminal for the environment.
Next, type the following command to switch to the /opendxl root directory.
cd /opendxl
The output should appear as follows:
In this step, a local clone of the OpenDXL Python Client GitHub repository will be created. This repository contains the examples that will be run in the subsequent steps of this tutorial.
To clone the repository execute the following command:
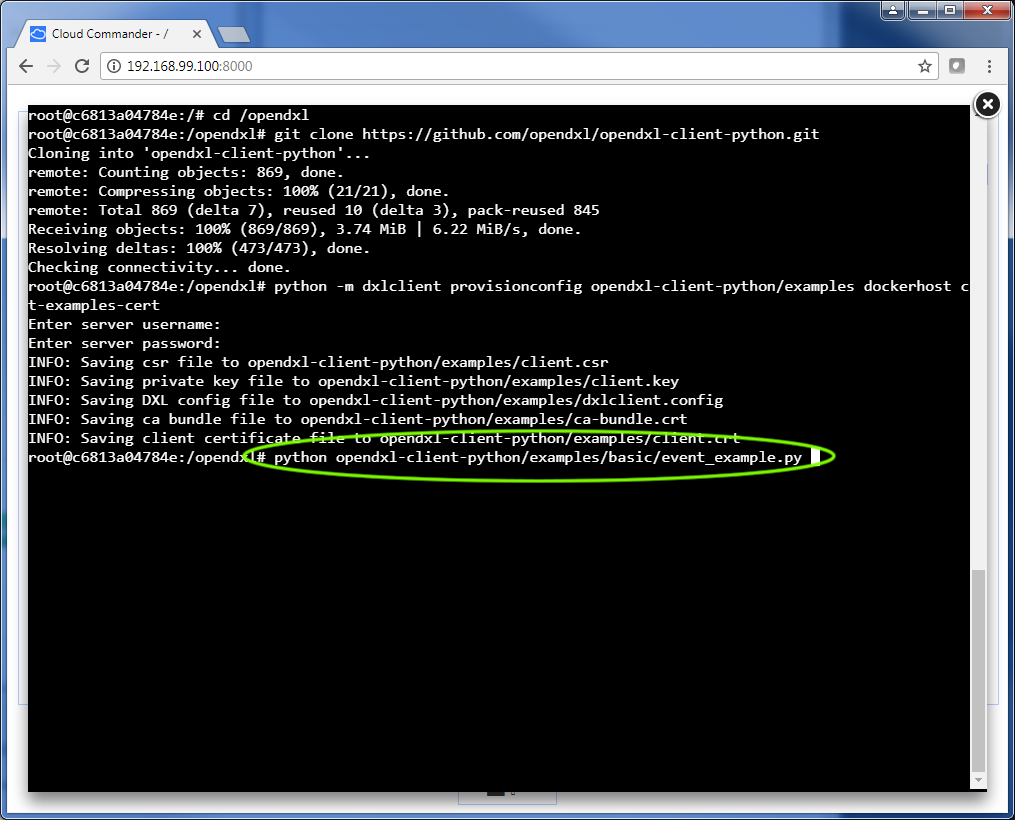
git clone https://github.com/opendxl/opendxl-client-python.git
The output should appear as follows:
The next step is to provision the OpenDXL client that will be used to run the examples that are included with the cloned OpenDXL Python Client repository. The OpenDXL Client that is included as part of the OpenDXL Environment will be used to provision the client.
The command to perform provisioning of the client has the following structure:
python -m dxlclient provisionconfig <client-config-dir> <provision-server> <cert-common-name>
The parameters are as follows:
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| client‑config‑dir | opendxl-client-python/examples |
The directory to contain the results of the provisioning operation. The generated files include the client's certificate and related private key along with information about the broker(s) to connect to. |
| provision‑server |
dockerhost for an OpenDXL Brokeror ePO IP address or host name for ePO-managed DXL environments. |
The server that will be used to provision the client. For an OpenDXL Broker, this will be the broker itself. However, since the broker is most likely running within the same Docker host as the OpenDXL Environment, the host name dockerhost should be specified (See Docker hostname resolution for more information).For ePO-managed environments, this will be the host name/IP address of the ePO server. If a non-standard port is being used, see NOTE regarding the -t parameter below. |
| cert‑common‑name | client-examples-cert |
The common name to associate with the generated certificate. |
NOTE: If a non-standard port (not 8443) is being used for ePO or the management interface of the OpenDXL Broker, an additional "port" argument must be specified.
For example-t 443could be specified as part of the provision command to connect to the provisioning server on port443.
Execute the following command to provision the client. The command below assumes the client is being provisioned for use with an OpenDXL Broker container that is running on the same host. If ePO is the target for the client provisioning, change dockerhost to reflect the IP address or host name of the ePO server.
python -m dxlclient provisionconfig opendxl-client-python/examples dockerhost client-examples-cert
When prompted, provide credentials for the OpenDXL Broker Management Console or ePO (the ePO user must be an administrator).
The output should appear as follows:
In this step, the OpenDXL Client "Basic Events Example" will be executed.
To run the example, execute the following command:
python opendxl-client-python/examples/basic/event_example.py
The output should appear as follows:
OpenDXL Environment
- Overview
-
Installation
- Graphical (Kitematic)
- Command Line
- FAQ
Tutorials
Web Console