The goal of this project is to:
Build a neural network model predicting a sentiment of a sentence.
where
Build - develop using Python with Keras API
neural network - a recurrence neural network called LSTM - Long Short Term Memory
predicting - after training the model can be used for predictions
sentiment - a label specifying if a sentence is either positive, neutral or negative.
sentence - the learning process is based on online reviews, so we can assume that we will achieve best results when predicting sentiment of a review.
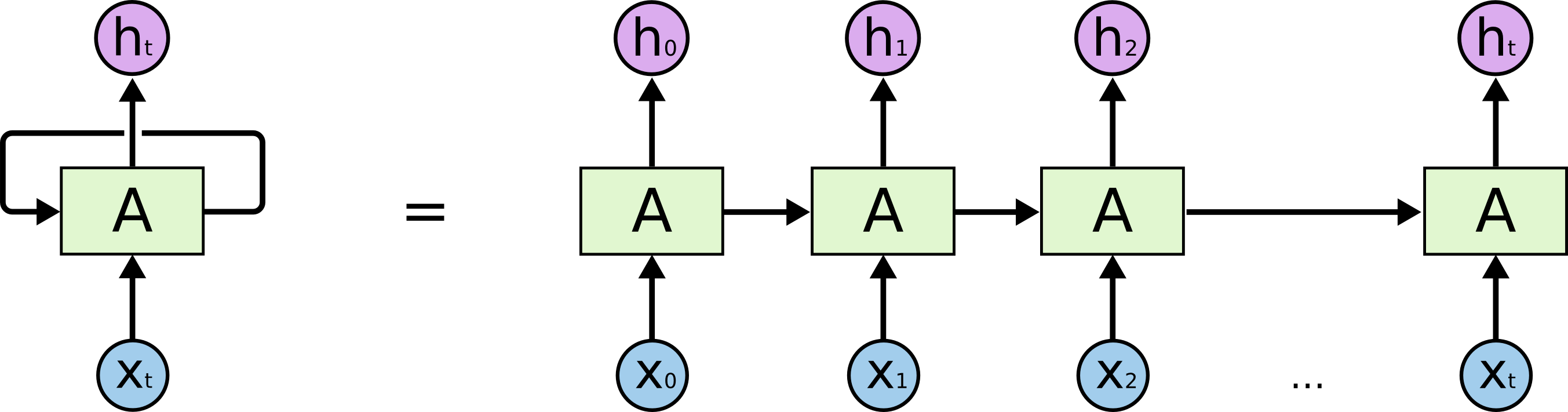
As you probably know, there are few different types of neural networks. One of them is RNN - Recurrent Neural Network. This group of neural networks form a sequence of nodes, where every node is dependent on previous node. The net takes its own an output and treats it as an input in iteration during the learning process. As you might expect it's a reason, why RNNs are aplicable when there is some importance in data order (e.g. time series or language processing).
LSTM - Long Short Term Memory - is a neural network of RNN class. It's just more powerful, more intelligent. It passes not only last memorised elements, but it keeps old ones as well, making an impression of understanding a context.
The following chapters describe the process in terms of code execution. The architecture and working principles of LSTM are quite complicated concepts and I recommend reading following article, if you're not familiar with it: https://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/
The network will be learning by words. Not letters, not characters, not sentences - but words. It has some disadvantages ('do', 'does', 'did', 'done' are completely other, independent words), but it works quite good in general.
Since the algorithms like numbers, all words must be changed to numbers. The numbers are not randomly distributed - they are integers and mean a ranking of words' frequencies. The most common words will have a number zero, the second will have one, etc. After such operation all sentences become sequences of numbers.
Different sites, different contexts, but - fortunately - the same language! Since English is a widely used language, lots of English NLP neural networks have been already trained. :) This is a good information, because as a result we can load into our network a set of pre-trained word vectors called embeddings. Such vectors describe a position of a word in a space of words, where words with similair meansing are placed next to each other.
It means that before we train our network with IMDB reviews, we will pass all words through the filter of their meaning in English.
Word embeddings for this project have been produced with word2vec method, which is described e.g. here: https://pathmind.com/wiki/word2vec
The net is constructed from three layers:
- Embeddings layer - non-trainable layers of pre-trained word sequences.
- LSTM layer - the only hidden layer.
- Number of hidden units: 10 as a default, but can be changed. As the hidden units are the learning capacity of the network, I suggest overriding the default with some bigger value (128 is often selected arbitrarily or empirically).
- Number of epochs: 10 as a default, but can be changed (preferably for some smaller value at the beginning, e.g. 3 or 5). One epoch is a pass of entire dataset (forward and backward) through the neural network. It's done only once within one epoch.
- Batch size: 32 as a default, so 32 training samples will be fed in one iteration.
- Dropout: 0.5 as a fixed value. Dropout prevents overfitting, by randomly dropping some samples. It improves model performance.
- Activation function:
tanhfunction as a fixed value.
- Dense layer - the output layer to collect all results in desired format with
softmaxactivation function.
Layers are combined in a form of stack, which is a behaviour of Keras Sequential model.
The script can be run using command line (it's been implemented with argparse library). It accepts following parameters:
-d,--data_path- path to the file with input data (required),-e,--embedding_path- path to the file with pre-trained embeddings (required),-r,--rnn_dim- number of hidden units in LSTM layer (default: 10, optional),-s,--save_dir- path to a saving of trained model (required),-E,--epochs- number of training epochs (default: 10, optional),-b,--batch_size- size of a single batch (default: 32, optional),-v,--verbose_level- verbosity mode (0 = silent (default), 1 = progress bar, 2 = one line; optional).
Since it's only a script, you should also have all required libraries installed (see: requirements.txt in this repo).
There is an optimized version of Keras' LSTM provided called CuDNNLSTM. As it's presumably 5-10x faster than LSTM, without any loss of quality, I suggest trying it as a form of upgrading the project.
Neural networks tend to perform better with normalized data, so the values should be normalized using e.g. sci-kit MinMaxScaler. It would probably better perform with softmax or tanh functions (depending of type of normalization).
The code is squeezed into one file. Some parts could be easily extracted (most of methods could be static).