English | 中文
Seata is a very mature distributed transaction framework, and is the de facto standard platform for distributed transaction technology in the Java field. Seata-PHP is the implementation version of PHP language in Seata multilingual ecosystem, which realizes the interoperability between Java and PHP, so that PHP developers can also use Seata-PHP to realize distributed transactions.
Before learning about the
Seata-PHP, let's first understand what's theSeata
A distributed transaction solution with high performance and ease of use for microservices architecture.
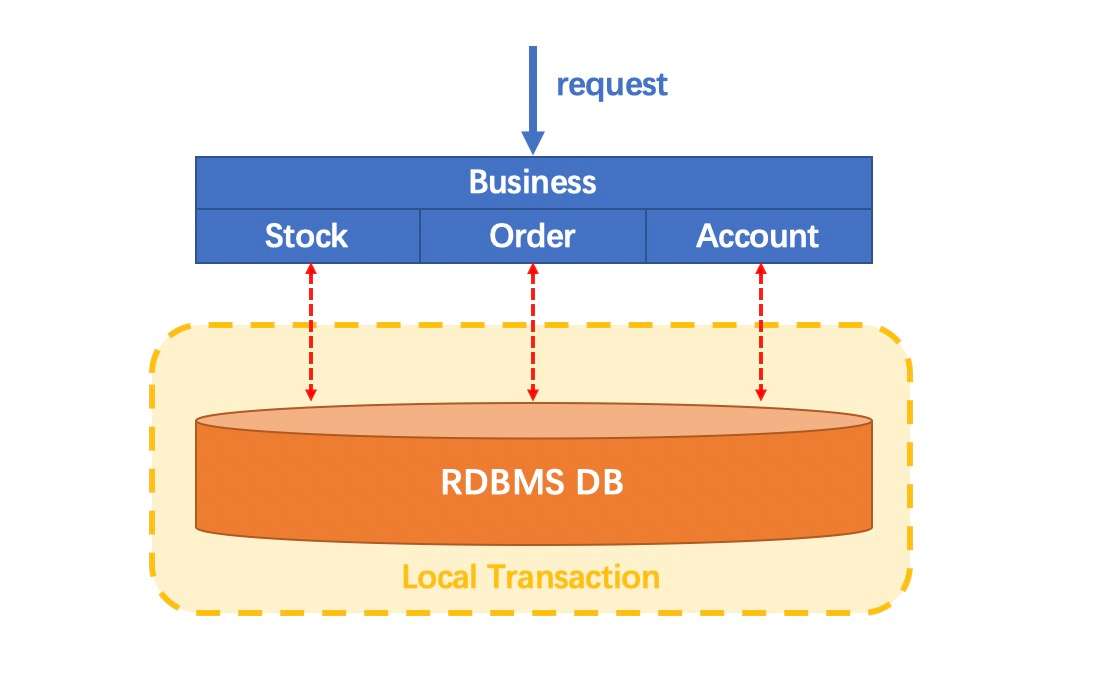
Let's imagine a traditional monolithic application. Its business is built up with 3 modules. They use a single local data source.
Naturally, data consistency will be guaranteed by the local transaction.
Things have changed in a microservices architecture. The 3 modules mentioned above are designed to be 3 services on top of 3 different data sources (Pattern: Database per service). Data consistency within every single service is naturally guaranteed by the local transaction.
But how about the whole business logic scope?
Seata is just a solution to the problem mentioned above.
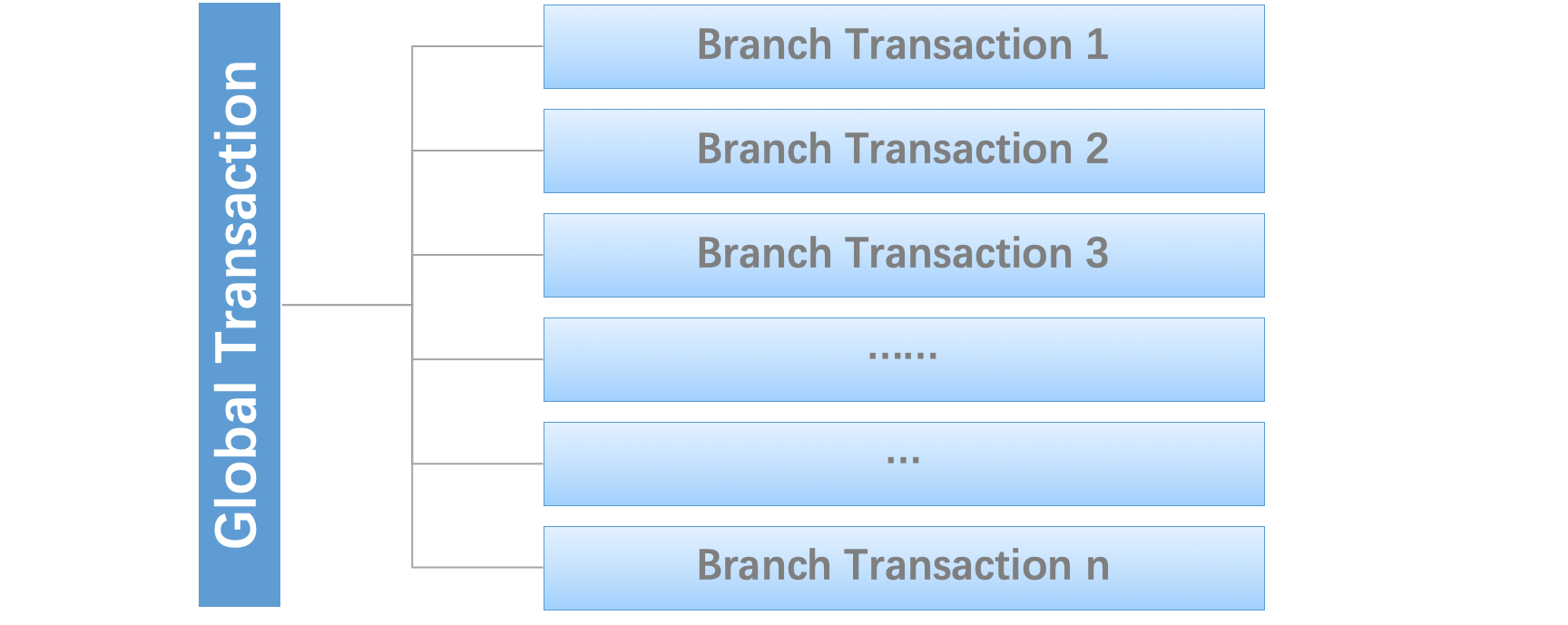
Firstly, how to define a Distributed Transaction?
We say, a Distributed Transaction is a Global Transaction which is made up with a batch of Branch Transaction, and normally Branch Transaction is just Local Transaction.
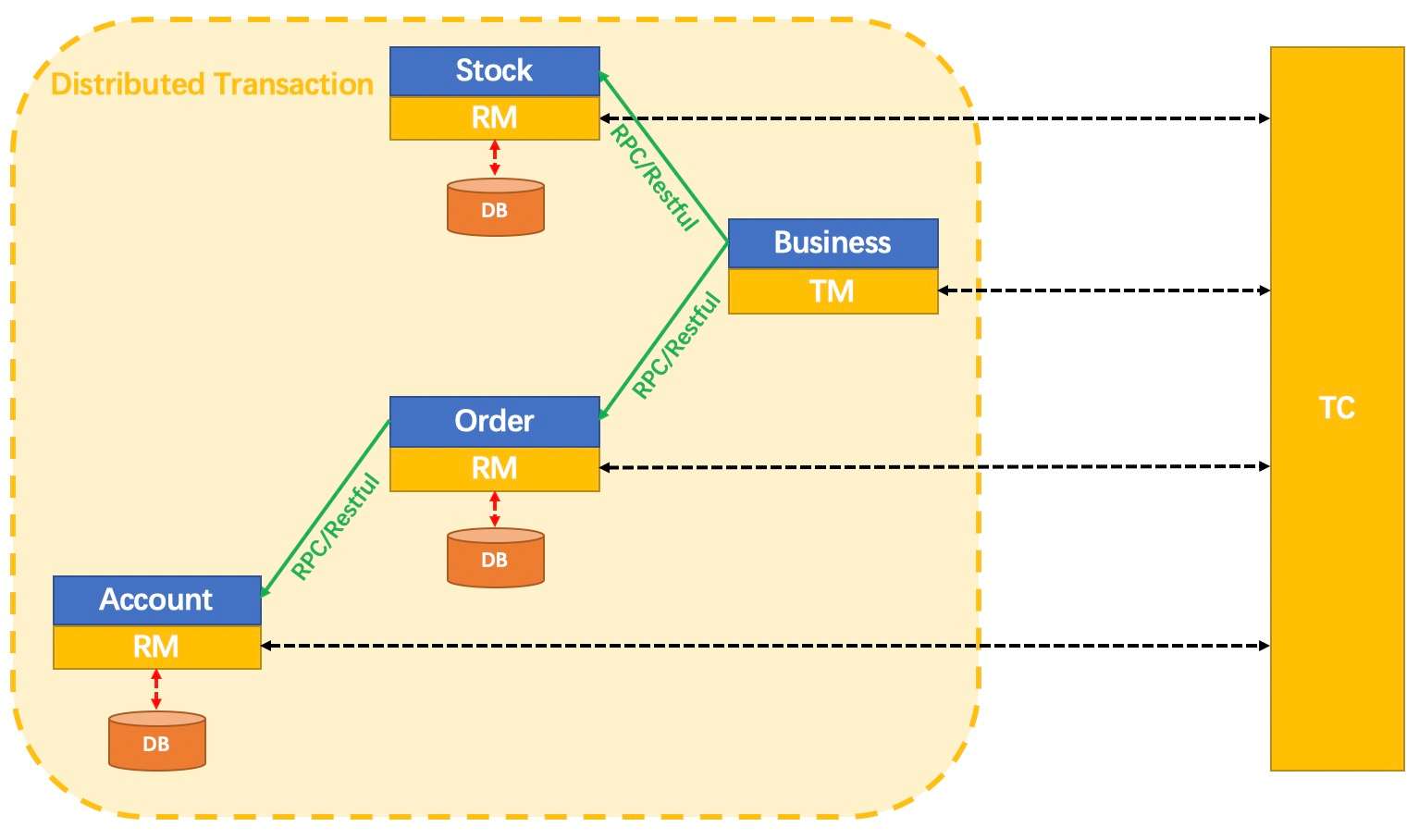
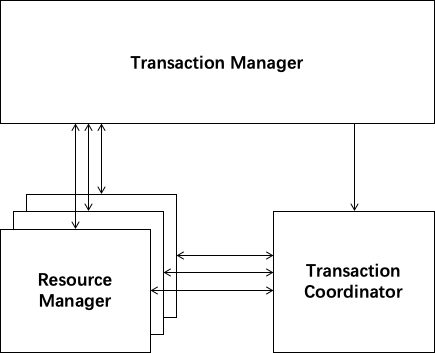
There are three roles in Seata Framework:
-
Transaction Coordinator(TC): Maintain status of global and branch transactions, drive the global commit or rollback.
-
Transaction Manager(TM): Define the scope of global transaction: begin a global transaction, commit or rollback a global transaction.
-
Resource Manager(RM): Manage resources that branch transactions working on, talk to TC for registering branch transactions and reporting status of branch transactions, and drive the branch transaction commit or rollback.
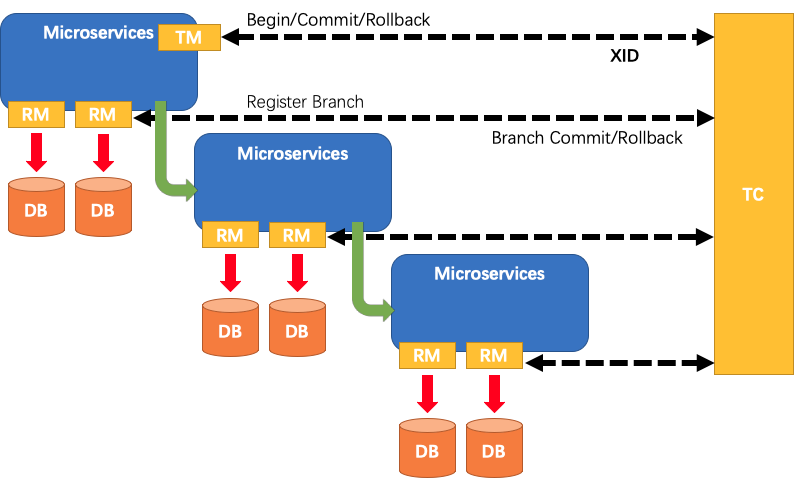
A typical lifecycle of Seata managed distributed transaction:
-
TM asks TC to begin a new global transaction. TC generates an XID representing the global transaction.
-
XID is propagated through microservices' invoke chain.
-
RM registers local transaction as a branch of the corresponding global transaction of XID to TC.
-
TM asks TC for committing or rollbacking the corresponding global transaction of XID.
-
TC drives all branch transactions under the corresponding global transaction of XID to finish branch committing or rollbacking.
For more details about principle and design, please go to Seata wiki page.
- TCC
- XA
- AT
- SAGA
- TM
- RPC communication
- Transaction anti suspension
- Null compensation
- Registration Center
- Metric monitoring
- Examples
-
First download seata java and Start the TC service. For the specific process, refer to seata deployment guide Documentation
-
Run seata-php whith seata-skeleton
Seata-PHP is currently in the construction stage. Welcome colleagues in the industry to join the group and work with us to promote the construction of Seata-PHP! If you want to contribute code to Seata-PHP, you can refer to the code contribution Specification document to understand the specifications of the community, or you can join our community DingTalk group: 44788115 and communicate together!
Seata-PHP uses Apache license version 2.0. Please refer to the license file for more information.