Windows command-line tool for interacting with Bluetooth LE devices
Windows 10, BT 4.0 adapter
-
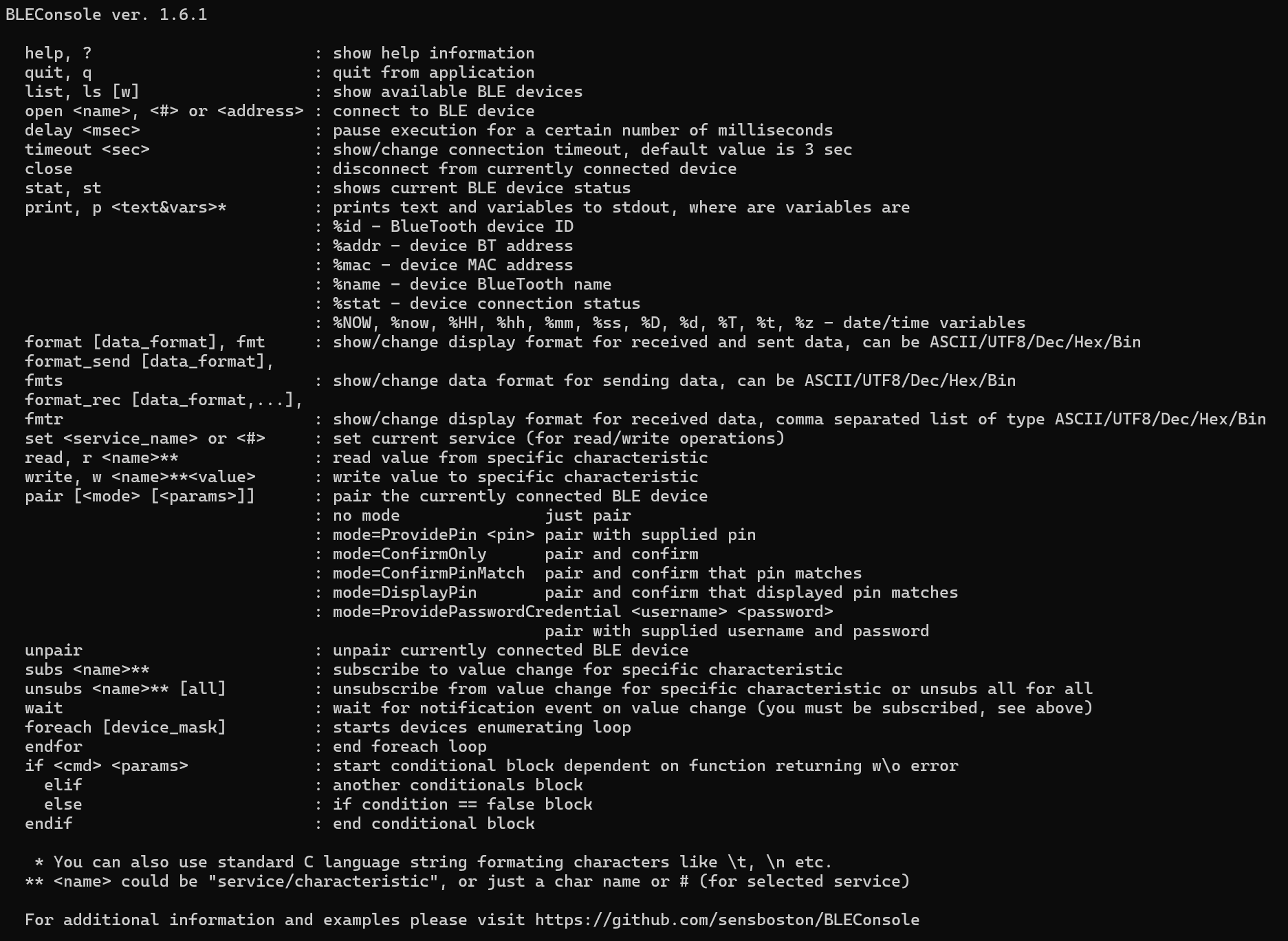
help, ? : show help information
-
quit, q : quit from application
-
list, ls [w] : show available BLE devices
-
open or <#> : connect to BLE device
-
timeout : show/change connection timeout, default value is 3 sec
-
delay : pause execution for a certain number of milliseconds
-
close : disconnect from currently connected device
-
stat, st : shows current BLE device status
-
print, p <text&vars>* : prints text and variables to stdout, where are variables are:
- %id : BlueTooth device ID
- %addr : device BT address
- %mac : device MAC address
- %name : device BlueTooth name
- %stat : device connection status
- %NOW, %now, %HH, %hh, %mm, %ss, %D, %d, %T, %t, %z : date/time variables
-
format [data_format], fmt : show/change display format, can be ASCII/UTF8/Dec/Hex/Bin
-
set <service_name> or <#> : set current service (for read/write operations)
-
read, r ** : read value from specific characteristic
-
write, w ** : write value to specific characteristic
-
subs ** : subscribe to value change for specific characteristic
-
unsubs ** [all] : unsubscribe from value change for specific characteristic or unsubs all for all
-
wait : wait seconds for notification event on value change (you must be subscribed, see above)
-
foreach [device_mask] : starts devices enumerating loop
-
endfor : end foreach loop
-
if : start conditional block dependent on function returning w/o error
- elif : another conditionals block
- else : if condition == false block
-
endif : end conditional block
* you can also use standard C language string formating characters like \t, \n etc.
** could be "service/characteristic", or just a char name or # (for selected service)
BLEConsole.exe < cmd.txt, where is cmd.txt is a simple text file with content:
// Loop for each device
foreach
// Connect and if successfull
if open $
//Read first characteristic of first service
read #0/#0
// Close connection to device
close
endif
endfor
- Blank/empty lines are ignored.
- Comments can be added by preceding them with
//
You can use BT name or # or address provided by list command. For example, run BLEConsole, type ls and it should list available BT devices, like
BLE: ls
# Address Name
#00: 85:41:35:3f:d6:8a TOZO-S2
#01: 65:b3:6e:8d:ba:f4 F2
#02: e4:98:bb:5f:80:53 LEDnetWF02004100000
Note: The list consists of devices that Windows has seen in the past time. Not all devices may be available at this moment.
Than use command open #1 or open TOZO-S2 or open 85:41:35:3f:d6:8a to connect to the device. (you can also use partial name, like TOZ if no more BLE devices with that name exist)
BLE: open #1
Connecting to TOZO-S2.
Found 3 services:
#00: GenericAccess
#01: GenericAttribute
#02: 2800
The open command will automatically list the available services on the device. Now you can set active service and list it's characteristics, by issuing command set #0
BLE: set #0
Selected service GenericAccess.
#00: DeviceName RW
#01: Appearance R
#02: PeripheralPreferredConnectionParameters R
#03: 10918 R
Now you can read or write characteristics of the active service.
Read a characteristic by # or name, like read #0
BLE: read #0
TOZO-S2
Write a characteristic by # or name, like write #0 value
BLE: write #0 123
If you already knew your service name/#, you can avoid previous step and read characteristic after successful connection to BLE device, like read #1/#0
Data will be interpreted in the selected format Here we select hexadecimal as the format for both sending and receiving.
BLE: format hex
Current send data format: Hex
Current received data format: Hex
You can also directly write a value to a known service/characteristic. For example here we write an (hexadecimal) array of data to service (0xFFFF) / characteristic (0xFF01)
BLE: write 0xFFFF/0xFF01 00 04 80 00 00 0d 0e 0b 3b 23 00 00 00 00