As both Kubernetes and AI usage grows, how do we keep operations consistent and simple?
This project simplifies MLOps in Kubernetes by providing Kubeflow in Helm and Terraform package formats. This allows scaling Kubeflow usage with the rest of your production systems.
Kubeflow provides a cloud-native AI platform which can be used to deploy applications in scientific computing, traditional machine learning, and generative AI.
This module is primarily focussed on the Jupyter notebook environment initially such that
- Developers can deploy and access notebook instances
- Notebook instances can use GPUs necessary for deep learning
- This can be done across different cloud providers (ranging from individual VMs to managed services like Amazon's EKS)
This system is built on top of the official Kubeflow Manifests repo which contains Kustomizations for the various components of Kubeflow.
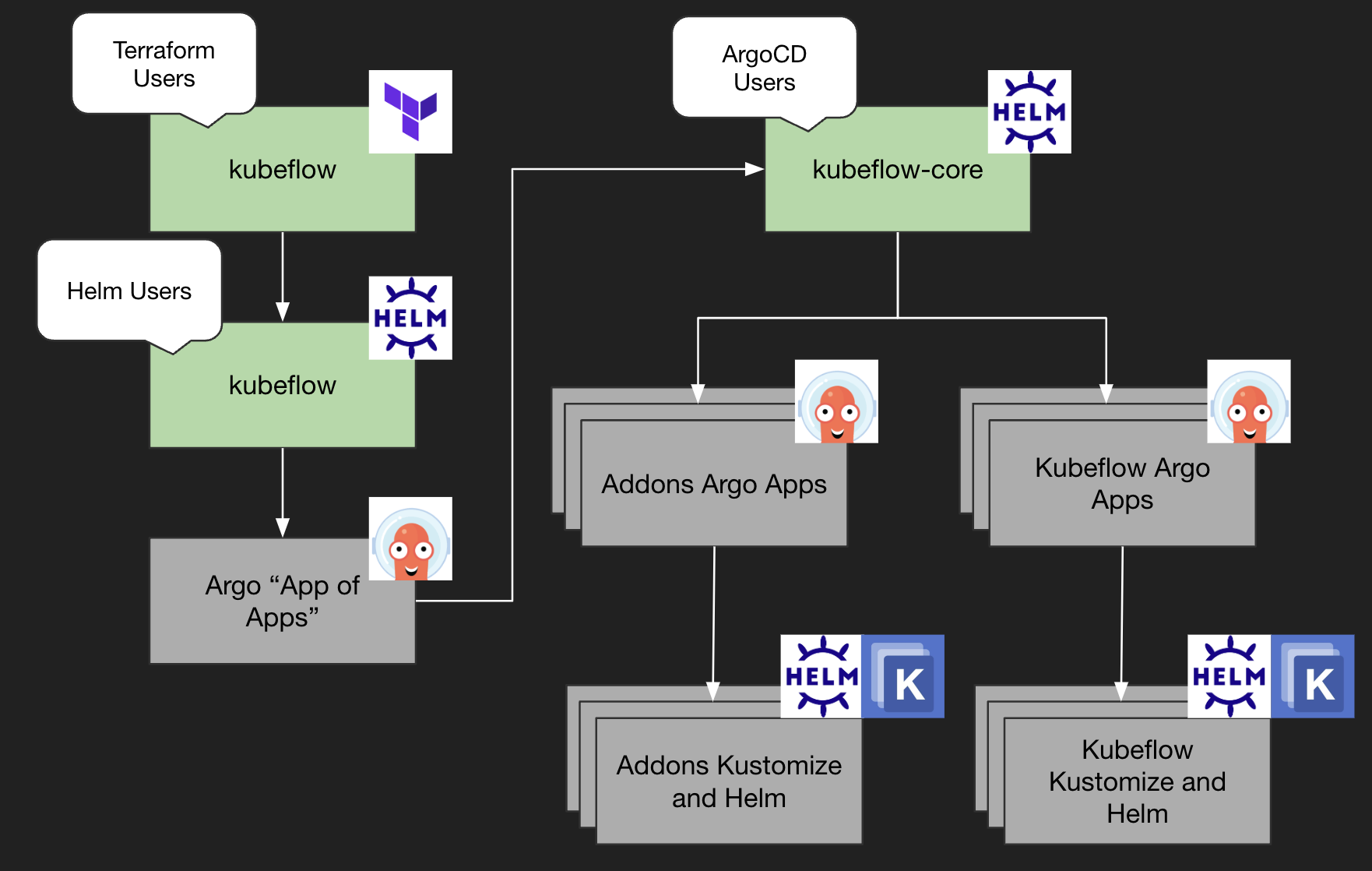
We provide a terraform and helm-based interface for managing Kubeflow via GitOps. Because Kubeflow is a collection of modular components, this project relies on ArgoCD for combining them.
- Integrate with production systems that already use Terraform and Helm
- Embrace GitOps for Kubernetes resources on the popular ArgoCD project
- Enable adoption of cloud-native/AI tools beyond the scope of Kubeflow (e.g. Ray, MLFlow)
- Terraform module: A simple entrypoint for those new to Argo and looking for a 1-click experience
- kubeflow chart: A high-level helm entrypoint for setting up Kubeflow Argo Apps
- kubeflow-core chart: A lower-level argo apps chart which can be invoked in the "argo app-of-apps" pattern.
The default configuration of Kubeflow provided is designed to run on a cluster with 2cpus and 8G memory.
Note that as all of our examples are implemented in Terraform, we recommend using the Terraform module to start off. The helm charts are likely to be a more viable interface as you move into production.
We recommend trying out this module in a development environment first.
To do so, follow the k3s tutorial.
# install argo (necessary for orchestration)
helm repo add argo-cd https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
helm install -n argocd --create-namespace argo-cd argo-cd/argo-cd
# install kubeflow
helm install kubeflow -n argocd oci://ghcr.io/treebeardtech/helm/kubeflow --version x.y.zIn order to integrate Kubeflow with your production systems there are some changes you may want to make:
(see Terraform Modules page)
# resource or data for your k8s cluster
...
# Initialize provider
provider "helm" {
...
}
# Call Kubeflow module
module "treebeardkf" {
source = "../.."
}You can incrementally add Kubeflow to your K8s cluster by installing the terraform module.
Some considerations:
- If you are calling this Terraform module from your own module, ensure you pass in resources to the
depends_onfield so that Kubeflow installs after they finish setup. - If you already have Istio and Cert Manager installed, you will need to ensure Kubeflow works with them. See examples/k3s-existing-istio for a configuration that we have tested like this.
It's critical to not use the default password for internet-facing deployments.
See the See examples/eks-https-loadbalancer for deployment with a non-default dex password (passed in via terraform CLI)
Note that dex will only pick up new config at start -- you may have to restart the dex pod manually for a password change to take effect.
Follow the eks-https-loadbalancer example to see how you can setup an https loadbalancer for you Kubeflow deployment
This is best done by using the external DNS operator.
If you are new to external DNS, follow the docs for setting up a deployment, then use this guide to connect external DNS to the istio gateway service for your Kubeflow deployment.
The eks-https-loadbalancer example also shows this.
Profiles are a Kubeflow abstraction that lets you securely isolate users from each other. See the Kubeflow docs on profiles
Lots of the config used to define your Kubeflow instance has has no dependency on Terraform resource outputs such as role ARNs.
These may best be stored in a git repo and referenced using Argo's multiple sources feature
Using this approach you can invoke this terraform module (or the underlying bootstrap helm chart) with config like the following that combines injected values with values from a git repo.
See the gitops example for details.
- Manually remove any manually created Kubeflow resources, e.g. Notebook Servers and Volumes
- Remove the terraform module, e.g. with
terraform destroyif you have installed directly from CLI - Clean up remaining resources, e.g. Istio leaves behind some secrets that can prevent successful re-installation. You may also want to clear out CRDs, persistent volumes and namespaces
Moving the deployment between different states of configuration can be challenging due to the dependencies between components in the cluster.
If you have made a change to a dependency such as istio, or an auth component such as dex, it can be a good idea to re-create pods such that they re-initialise. This can be done by scaling to 0 then back up again, or simply deleting a pod managed by a deployment.