-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 21
Points
Input data is available here.
Graphite has functions to pre-process pointsets obtained from 3D scanners, and reconstruct surfaces from them.

Raw scanned pointsets often have spurious points that one needs to remove. For instance, the raw armadillo from Stanford scanning archives is surrounded by a cloud of outliers.
Invoke the command Points/preprocessing/detect outliers. It finds
the outliers by detecting points that have one of their nb nearest neighbors
further away than radius. Detected outliers are displayed as red dots.
Depending on the dataset, you may need to play a bit with the parameters.
For the Armadillo, default parameters miss a couple of points, so use
nb=30 and radius=0.005.
Once you are happy with the result, invoke Points/delete selected points.

If tuning the parameters is hard, you may also manually pick some
points, using the select vertex tool. Use the left button to select
a point, and the right button to unselect.

Scanned pointsets are often a bit noisy (left image), due to small
registration errors or simply to noise in the acquisition process. To
smooth-out this noise, use Points/Preprocessing/smooth point set. It
iteratively projects each point onto a plane fit to its nb_neighbors
nearest neighbors. In the present example, we used nb_neighbors=45.

Graphite has two surface reconstruction methods:
-
SSSR/Co3Ne (Simple and Scalable Surface Reconstruction), that uses the existing points to create a triangulated mesh. Note: by default, SSSR does one iteration of pointset smoothing before reconstruction (can be deactivated in the advanced parameters).
-
Poisson Surface Reconstruction (by Misha Kahzdan), that uses an octree.
In addition, it also has 2D Delaunay, for reconstructing surfaces from digital elevation models or airborne LIDAR data.


It all depends on the data, this is the reason why we keep both methods in Graphite/Geogram. For the Armadillo pointset (top image), there are some registration errors and remaining outliers. Poisson reconstruction does a good job for smoothing the problematic points without losing geometric details, whereas Co3Ne reconstruction, that has no choice than using the existing points, exhibits some artifacts. For the Horse pointset (bottom image), the pointset is clean, but has a huge variation of density. This causes bulges in Poisson reconstruction, whereas SSSR/Co3Ne reconstruction nicely interpolates the pointset.

Graphite has commands to generate a regular point sampling on a
surface (Points/Sampling/sample surface) and in a volume
(Points/Sampling/sample volume). For volume sampling, the mesh needs
to be tetrahedralize (use Volume/tet meshing).
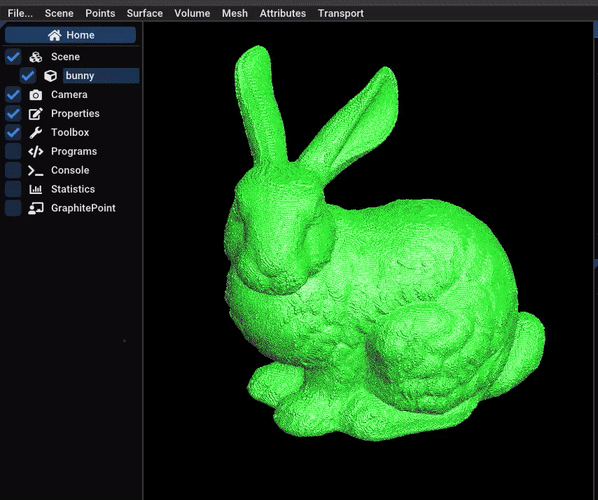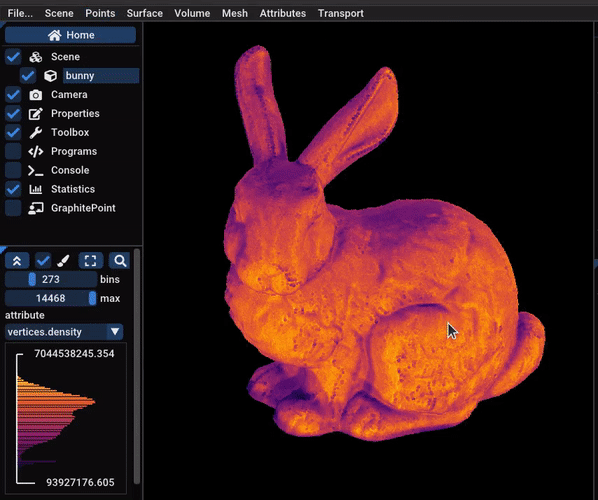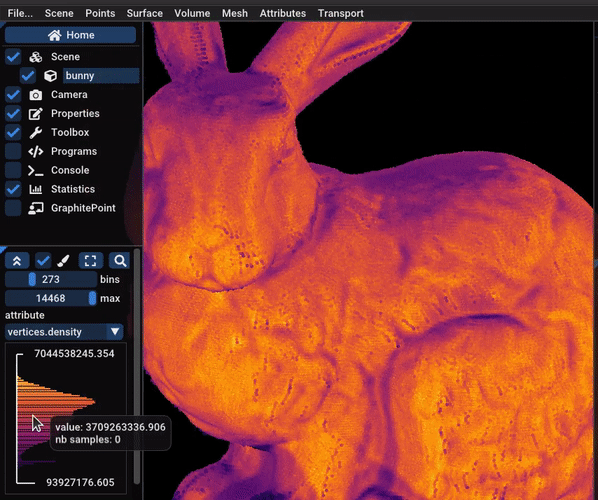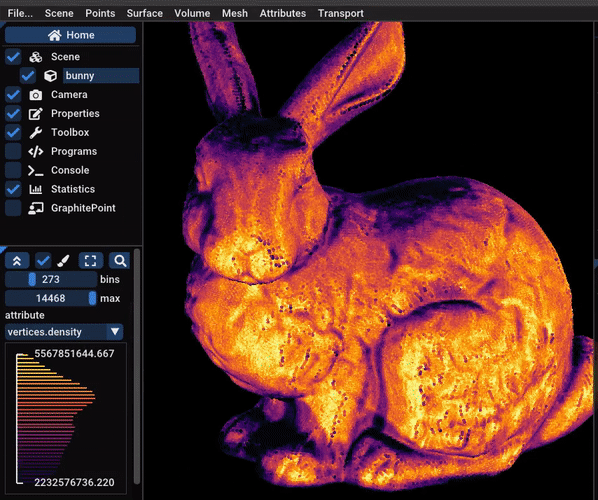
One can estimate the density of a pointset by counting the number of
points in spheres of a given radius centered on each point. It is
useful to show the zones of the pointset that are undersampled (often
the top and the bottom, like in the video).
- Graphite pointset commands reference
- Geogram programmer's tutorial on pointsets (see also references herein)